METOPROLOL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
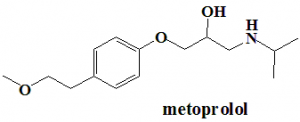
Metoprolol
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-1-[4-(2-Methoxyethyl)phenoxy]-3-[(propan-2-yl)amino]propan-2-ol.
Classification
Metoprolol is a selective ß1-adrenergic antagonist
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 237.36 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 120°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Water solubility is 0.06M |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.15 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Metoprolol acts as ß1-adrenergic antagonist for the cardiac cells.
- By producing negative inotropic effects, there is decrease in the cardiac output. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Increasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
- Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
- Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
- Aryloxypropanolamines are more potent than aryloxyethanolamines. [2]
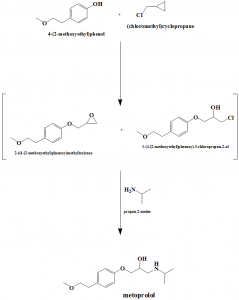
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of 4-(2-methoxyethyl)phenol and epichlorohydrin in aqueous alkaline condition produces epoxide.
ii. It is distilled under high vacuum for purification.
iii. Epoxide is then treated with isopropylamine in isopropyl alcohol at reflux to yield metoprolol. [3]
Therapeutic Uses
Metoprolol is used for treatment of:
- Angina
- Hypertension
- Heart failure
Side Effects
Side effects of metoprolol are:
- Itching or rashes in skin
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia
- Depression
- Confusion
- Memory problems
- Dizziness
- Tiredness
- Very slow heartbeats
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Coldness in palm and feet
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug metoprolol-
| i. Increasing side chain length | A. Prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side. |
| ii. Aryloxypropanolamines are | B. Stimulates appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side |
| C. Less potent than aryloxyethanolamines | |
| D. More potent than aryoxyethanolamines |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Metipranolol: (RS)-4-{[-2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propyl]oxy}-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl acetate.
- Esmolol: 3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol
- Bisoprolol: (RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxybenzamide
- Metoprolol: (RS)-1-[4-(2-Methoxyethyl)phenoxy]-3-[(propan-2-yl)amino]propan-2-ol
a) TFFT
b) TFTF
c) TTFF
d) TTFT
Q.3 Number of chiral centers present in the structure of metoprolol?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 Mechanism of action of metoprolol is based on?
a) Blocking of α1-adrenergic receptors
b) α1-adrenergic agonism
c) ß1-adrenergic antagonism
d) None of these
Q.5 Which amongst the following is not a therapeutic use of drug metoprolol?
a) Angina
b) Hypertension
c) Heart failure
d) Ocular hypertension
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Metipranolol: nonselective ß-adrenergic antagonist
II. Metoprolol: selective ß1-adrenergic antagonist
III. Amphetamine: nonselective α-adrenergic agonist
IV. Clonidine: Mixed acting sympathomimetics
a) I, III
b) I, II
c) II, III, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 What chemical compound can be reacted with isopropylamine in isopropyl alcohol to produce metoprolol?
a) Epoxide
b) Benzene
c) Hydroquinone
d) Epichlorohydrine
ANSWERS
1-b
2-a
3-b
4-c
5-d
6-b
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Benfield P, Clissold SP, Brogden RN. Metoprolol. Drugs. 1986 May 1;31(5):376-429 [2] [2] Lemke TL, Williams DA, Foye WO. Principles of medicinal chemistry. Williams & Wilkins; 2017, 356. [3] Aguilar CA, Llado JB, inventors; Medichem SA, assignee. Synthesis and preparations of metoprolol and its salts. United States patent application US 12/158,950. 2009 Oct 1.