OMEPRAZOLE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
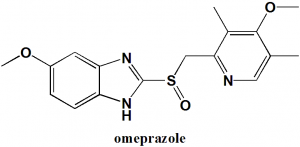
Omeprazole
IUPAC nomenclature
5-Methoxy-2-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methanesulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole
Classification
- Proton pump inhibitors
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 345.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 155 oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in ethanol; slightly soluble in acetone |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.23 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Imidazole, pyridine |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Omeprazole covalently binds with cystien residues via disulfide bridges on the α subunit of H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system.
- Thereby it inhibits the H+/K+ ATPase pump which in turn inhibits the gastric acidsecretion or formation of hydrochloric acid in parietal cells
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of Heteroaryl- and heterocyclyl-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]Pyridine derivatives acting as acid pump antagonists can be summarized as:
- The inhibitory property of drugs depends on hydrophobic group substituted at the left side ortho-position of the phenyl ring.
- Increase in hydrophobic value increases the activity.
- Increasing the GTCI value decreases the activity.
- Small molecule substitutions may participate in hydrophobic interaction as well as steric interactions. [1]
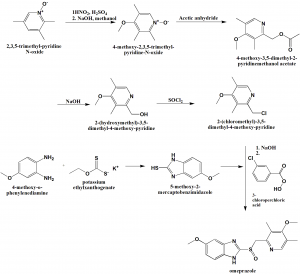
Method of synthesis
i. 2,3,5-trimethyl-pyridineN-oxide is reacted with HNO2/sulfuric acid followed by NaOH in ethanol to get 4-methoxy-2,3,5-trimethylpyridine N-oxide.
ii. The last is reacted with acetic anhydride to get 4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinemethanol acetate
iii. The above formed compound is reacted with sodium hydroxide to get 2-(hydroxymethyl)-3,5-dimethyl-4-methoxy-pyridine.
iv. On reaction of the last with thionyl chloride produces 2-(chloromethyl)-3,5-dimethyl-4-methoxy-pyridine.
v. The last is reacted with 5-methoxy2-mercaptobenzimidazole which is synthesized by reaction of 4-methoxy-o-henylenedimine and potassium ethylxanthogenate, in presence of NaOH, followed by reaction with 3-chloroperbenoic acid to get omeprazole. [2]
Medicinal Uses
Omeprazole is used for treatment of:
- Active duodenal ulcers
- To reduce the risk of duodenal ulcers by eradicating Helicobacter
- Active benign gastric ulcer
- GERD
- Erosive esophagitis
- Pathologic hypersecretory conditions
- Heart burn
Side Effects
Side effects of Omeprazole are:
- Abodominal pain
- Headache
- Low magnesium blood level
- Irregular heartbeat
- Muscle spasms
- Seizures
- Lupus
- Diarrhea
- Blood in stool
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Omeprazole?
a) 5-Methoxy-2-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methanesulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole
b) (R)-(+)-2-([3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole
c) (RS)-1-[(4-chlorophenyl)- phenyl-methyl]-4- [(4-tert-butylphenyl) methyl] piperazine
d) (R)-(+)-2-([3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl)-imidazole
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the General structure activity of Heteroaryl- and heterocyclyl-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]Pyridine derivatives acting as acid pump antagonists?
I. The inhibitory property of drugs depends on hydrophobic group substituted at the left side ortho-position of the phenyl ring.
II. Increase in hydrophobic value decreases the activity.
III. Increasing the GTCI value increases the activity.
a) I
b) II, III
c) I, III
d) I, II, III
Q.3 Types of rings present in the structure of omeprazole?
I. Imidazole
II. Pyridine
III. Pyrolle
IV. Phenyl
a) I, II
b) I, IV
c) II, IV
d) II, III
Q.4 Side effects of drug Omeprazole is/are?
a) Low magnesium blood level
b) Seizures
c) Lupus
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct molecular weight-
| i. Omeprazole | A. 426.6 gm/mol |
| ii. Carbinoxamine | B. 266.4gm/mol |
| iii. Oxatomide | C. 345.4 gm/mol |
| iv. Cyclizine | D. 290.79 gm/mol |
a) i-A, ii-B, iii-C, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
c) i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
Q.6 An example of drug from class proton pump inhibitor?
a) Omeprazol
b) Sotalol
c) Glycopyrrolate
d) All of the above
Q.7 Octanol/water partition coefficient of Omeprazole is?
a) 2.23
b) 3.2
c) 4.8
d) 7.1
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-a
4-d
5-c
6-a
7-a