ORPHENADRINE CITRATE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
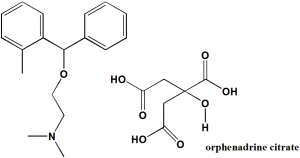
Orphenadrine citrate
IUPAC nomenclature
N,N-dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)-phenylmethoxy]ethanamine;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid.
Classification
Orphinadrine is an acetylcholine antagonist. It is a muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 461.5 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 132-134°C. |
| 4 | Solubility | Sparingly Soluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.77 (of orphinadrine) |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene ring present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- The drug binds with Histamine H1 receptors and NMDA receptors and inhibits them.
- The motor disturbances induced by neuroleptics during hyperkines is also restored by the drug.
- Stimulating effects of cholinergic system is counteracted by the Orphinadrine.
- It also produces relaxation of skeletal muscle spasm and elevates mood. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of N,N-dimethyl phenyl chloride and 2-methane-dimethylethanolamine produces orphenadrine.
ii. Orphenadrine is treated with citric acid to yield orphenadrine citrate.
Therapeutic Uses
Orphenadrine citrate is used for:
- Treatment of muscle spasm
- Treatment of muscle pain
Side Effects
Side effects of Orphenadrine citrate are:
- Dry mouth
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Allergic reactions
- Blurred vision
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
MCQ
Q.1 Orphenadrine citrate?
a) Stimulate nicotinic receptors
b) Stimulates muscarinic receptors
c) Inhibits nicotinic receptors
d) Inhibits muscarinic receptors
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug orphenadrine citrate is/are?
a) Asthma
b) Muscle spasm
c) Emphysema
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of drug Orphenadrine citrate?
I. Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
II. The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
III. Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
a) II
b) I
c) II, I
d) I, II, III
Q.4 The starting chemicals required for the synthesis of drug Orphenadrine citrate?
a) 2-(2’,2’-dimethoxyethyl)propane-1,3-diol.
b) 2-methyl diphenyl methyl chloride
c) N,N-dimethylethanolamine
d) Both b) and c)
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug Orphenadrine citrate is?
I. Imidazole ring is present
II. Freely Soluble in water
III. Present in oil form
a) FFF
b) TTF
c) FFT
d)FTF
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the are?
I. Pilocarpine: (3S,4R)-3-Ethyl-4-((1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one.
II. Orphinadrine: N,N-dimethyl-2-[(2-methylphenyl)-phenylmethoxy]ethanamine;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid.
III. Tiotropium: 7-[(hydroxidi-2-thienylacetyl)oxy]-9,9-dimethyl-3-oxa-9-azoniatricyclo[3.3.1.02,4]nonane bromide
IV. Carbachol: 2-[(Aminocarbonyl)oxy]-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride.
a) I, III
b) II, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) I, II, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Pilocarpine | A. Acetylcholinestrase inhibitor |
| ii. Physostigmine | B. Acetylcholine antagonist-muscarinic antagonist |
| iii. Orphenadrine | C. Acetylcholine mimetic-muscarinic agonist |
| iv. Metocurine | D. Nicotinic antagonist |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
c) i-A, ii-B, iii-D, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
ANSWERS
1-d
2-b
3-d
4-d
5-a
6-c
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Schjelderup L, Harbitz O, Groth P, Aasen AJ. Syntheses of (S)-(+)-trihexyphenidyl hydrochloride and (S)-(+)-procyclidine hydrochloride, two anticholinergics, using (S)-(−)-3-cyclohexyl-3-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoic acid as chiral synthon. Acta Chem. Scand.. 1987 May;41:356.