OXYBUTYNIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Oxybutynin
IUPAC nomenclature
4-Diethylaminobut-2-ynyl 2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethanoate
Classification
Oxybutynin is an acetylcholine antagonist. It is a muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 357.5 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 129-130°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 50 mg/ml |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 4.3 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Cyclohexyl |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
Oxybutynin converts in it’s active metabolite N-desethyloxybutynin which competitively inhibits the postganglionic type 1,2 and 3 muscarinic receptors. This results in relaxing the bladder and hence, helps in increasing the urine capacity in the bladder. It decreases the frequent urge for urination and delays the desires for frequent voids.[1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
Method of synthesis
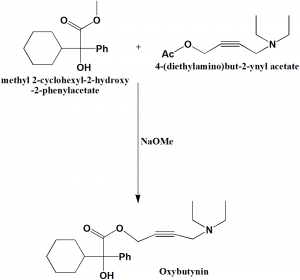
Methyl 2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate and 4-(diethylamino)but-2-ynyl acetate reacts together in the presence of sodium methoxide to yield oxybutynin.
Therapeutic Uses
Oxybutynin is used for:
- Treatment of overactive bladder
- Reducing the frequent trips to bathroom
- Reducing the urge for frequent voids
Side Effects
Side effects of Oxybutynin are:
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Stomach pain
- Upset stomach
- Unusual taste in mouth
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Decreased sweating
- Dry mouth
MCQ
Q.1 “4-Diethylaminobut-2-ynyl 2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethanoate” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Trihexyphenidyl
b) Propantheline
c) Oxybutynin
d) Oxazepam
Q.2 Melting point of Oxybutynin is?
a) 152-162°C
b) 129-130°C
c) 205.5°C
d) 258.5°C
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Propantheline | A. Benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic |
| ii. Oxazepam | B. Barbiturate |
| iii. Clozapine | C. Muscarinic antagonist |
| iv. Thiamylal | D. Benzpines |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-A, ii-B, iii-D, iv-C
d) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
Q.4 Mechanism of action of Propantheline is based on?
a) Blocking the Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
b) Blocking the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
c) Agonizing the adrenergic receptors
d) Both a) and c)
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug trihexyphenidyl
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide..
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
a) TFTF
b) FTFT
c) TTTT
d)FFTF
Q.6 Steps involved in the synthesis of Oxybutynin from Methyl 2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate in the correct sequence is?
I. Reaction with 2-diisopropylaminoethanol
II. Reaction with 4-(diethylamino)but-2-ynyl acetate
III. Alkylation using methylbromide
a) I – II – III
b) I – III
c) II
d) II – I – III
Q.7 The drug Oxybutynin is mainly used for?
a) Overactive bladder
b) Muscle spasm
c) Depression
d) Constipation
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-b
3-b
4-a
5-c
6-c
7-a