PHENYTOIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
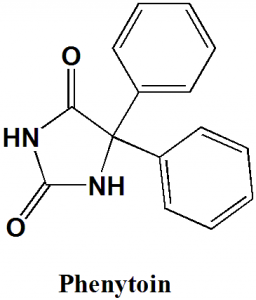
Phenytoin
IUPAC nomenclature
5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione.
Classification
Phenytoin is a hydantoin derivative anticonvulsant drug.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 252.27 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 296.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Insoluble in cold water; soluble in acetic acid |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.47 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Imidazolidine, phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
Phenytoin targets voltage-gated sodium channel and inhibits the positive feedback loop that results in neuronal propagation of high frequency action potential. In this way, seizures are prevented.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of hydantoins can be described as follows:
- For the activity of the drug, a phenyl or other aromatic substituent is necessary.
- Substitution with an alkyl group at position 5 will result in the sedative properties of drug.
- Some hydantoins may also exhibit properties against chemically induced convulsions.
- Many hydantoins are ineffective against electroshock induced convulsions.
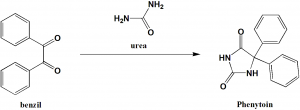
Method of synthesis
Phenytoin can be synthesized by rearrangement on the reaction of urea and benzil.[1]
Therapeutic Uses
Phenytoin is used for:
- Prevention and control of seizures
Side Effects
Side effects of phenytoin are:
Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Insomnia
- Drowsiness
- Slow heartbeat
- Unusual eye movements
- Confusion
- Slurred speech
- Loss of coordination
- Blurred vision
- Increased hair growth
- Increased thirst
- Increased urination
- Bone pain
- Joint pain
- Weak bones
MCQs
Q.1 What are the correct statements related with the physicochemical properties of Phenytoin drug?
I. Molecular weight = 252.27 gm/mol
II. It appears as pale yellow crystals
III. It is very soluble in cold water
IV. Piperidine ring is present in the structure
a) I
b) I, II, IV
c) II, III
d) I. II. III. IV
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Phenytoin | A. 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione |
| ii. Butabarbital | B. (RS)-N’-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)-N,N-diethyl-pentane-1,4-diamine |
| iii. Favipiravir | C. 5-butan-2-yl-5-ethyl-1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione |
| iv. Chloraquine | D. 6-fluoro-3-hydroxypyrazine-2-carboxamide |
a) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
Q.3 Steps for mechanism of action for drug phenytoin?
I. Neuronal propagation is inhibited
II. Inhibition of positive feedback loop of voltage-gated sodium channel
III. Seizures are prevented
IV. Meningitis is prevented
a) I – II – IV
b) I – II – III
c) II – I – III
d) II – I – IV
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Phenytoin: Antiviral drug
- Ritonavir: HIV protease inhibitor
- Ritonavir: Guanosine nucleoside antiviral drug
- Triazolam: Benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
a) TFTT
b) TTFF
c) FFTT
d) FTFT
Q.5 Type of ring present in the structure of Phenytoin is?
a) Imidazolidine
b) Piperazine
c) Piperidine
d) Pyridine
Q.6 Starting chemicals required for the synthesis of phenytoin are?
I. Urea
II. Phenol
III. Benzil
IV. Sodium amide
a) I , III
b) III , II
c) II , IV
d) III , II
Q.7 Side effect of drug Phenytoin are?
a) Slow heartbeats
b) Loss of coordination
c) Increased growth of hairs
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-c
4-d
5-a
6-a
7-d