PIROXICAM Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
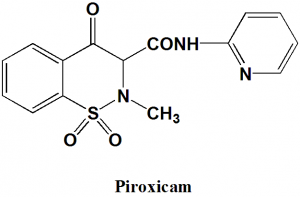
Piroxicam
IUPAC nomenclature
4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-yl-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide
Classification
- NSAID
- Oxicames
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 331.3g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 199°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 23 mg/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.06 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyridine, thiazine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Piroxicam reversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase enzyme which causes peripheral inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis.
- Piroxicam also prevents the aggregation due to platelets through inhibiting the migration of the leukocytes into the site of inflammation which prevents the formation of thromboxane A2.
Structure Activity Relationship
General SAR for Oxicams can be summarized as follows:
- Substitution on the nitrogen atom of the thiazine ring gives optimum activity.
- Substitution on the caboxamide with aryl group gives compounds with greater activity than when substituents are alkyl groups.
- N-heterocyclic compounds are more acidic than N-aryl carboxamides.
- Primary carboxamides are more potent than secondary carboxamides.
- m-substituted derivatives are more potent than p-substituted derivatives.
- Maximum activity is found with m-Cl substituent in the aryl series.
- Substitution on the carboxamide Nitrogen with heteroaryl group gives compound with seven fold greater anti-inflammatory activity than the aryl group substitution. [1]
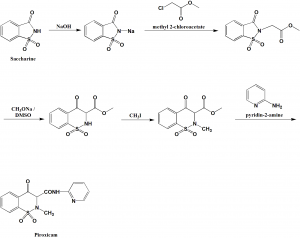
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of saccharine with sodium hydroxide to give a sodium salt.
ii. Sodium salt so produced is reacted with methyl chloroacetate to give saccharine-substituted acetic acid ethyl ester.
iii. The above formed product undergoes rearrangement on reaction with dimethylsulfoxide to produce 1,1-dioxide-3-methoxycarbonyl-3,4-dihydro-2-H-1,2-benzothiazin-4-one.
iv. Last undergoes methylation at the nitrogen atom using methyl iodide followed by reaction with 2-aminopyridine to give piroxicam. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Piroxicam is used for:
- Treatment of pain and swelling due to rheumatoid arthritis
Side Effects
Side effects of piroxicam are:
- Nausea
- Upset stomach
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Hypertension
- Easy bleeding
- Painful swallowing
- Ringing in ears
- Mood changes
- Change in amount of urine
- Stiff neck
- Vision problem
- Swelling ankles
- Tiredness
- Weight gain
- Dark urine
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Pale skin
- Allergic reactions
MCQs
Q.1 “4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-yl-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Piroxicam
b) Epinephrine
c) 6-fluorouracil
d) Oxymetazoline
Q.2 Melting point of piroxicam is?
a) 199oC
b) 981K
c) 273K
d) None of the above
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Piroxicam | A. Non-selective adrenergic agonist |
| ii. Epinephrine | B.ß1-adrenergic agonist |
| iii. Dopamine | C. α1-adrenergic agonist |
| iv. Methyldopa | D. NSAID |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
Q.4 Correct statements from below which are related with the mechanism of action of piroxicam can be??
I. It irreversibly inhibits COX
II. It prevents aggregation of platelets
III. There is increase in the amount of prostaglandins due to the drug.
IV. Piroxicam also inhibits the migration of leukocytes at the site of inflammation.
a) II ,IV
b) III, II
c) IV , I
d) II , III
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of oxicams can be?
- Substitution on the nitrogen atom of the thiazine ring gives optimum activity.
- Substitution on the caboxamide with aryl group gives compounds with greater activity than when substituents are alkyl groups.
- N-heterocyclic compounds are more acidic than N-aryl carboxamides.
- Primary carboxamides are more potent than secondary carboxamides.
a) TFFT
b) FFTT
c) FTFT
d) TTTT
Q.6 Type of ring present in the structure of piroxicam?
a) Pyridine
b) Thiazine
c) Anthracene
d) Both a) and b)
Q.7 The drug piroxicam is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of seizures
b) As an anesthetic
c) Reducing pain due to arthritis
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-b
4-a
5-d
6-d
7-c