Preservatives, Types of Preservatives, Properties of Preservatives and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam
Preservatives: If these materials prevent the initiation and growth of microorganisms in products, they are known as bactericidal preservatives. Some preservatives, either by concentration or activity, may only maintain the bacteria level in the product at the time of manufacture and are referred to as bacteriostatic preservatives.
Examples – Alcohol, Benzalkonium chloride, Boric acid, Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA), Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT), Butylparaben, Methylparaen, Phenol, Phenethyl Alcohol, Potassium Sorbate, Propylene Glycol, Propylparaben, Sorbic Acid.
1.Alcohol: INN: Alcohol; Ethanol; Ethanolum
Synonyms: Ethanol; Ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol
Chemical Name CAS Number: Ethanol
Molecular Formula: C2H6O
Description: A clear, volatile liquid with a characteristic odor and burning taste.
Properties: Miscible with water and glycerin; boiling point 78°C.
Incompatibilities: Acacia solutions (precipitation of the acacia gum), oxidizing materials while in acidic conditions.
Use: As a preservative in concentration greater than 10%; as a disinfectant in concentrations of 60–90%; as a co-solvent for certain active pharmaceutical ingredients or in film coating and tablet printing unit operations; and as a vehicle for both oral and topical finished products.
2.Benzalkonium chloride:
INN: Benzalkonium chloride; Benzalkonii chloridum
Synonyms: Alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride; BKC; BAC
Chemical Name & CAS Number: alkyldimethyl(phenylmethyl) ammonium chloride (8001-545 ammonium chloride (8001-54-5)
Molecular Formula: [C6H5CH2N(CH3)2R]Cl, where R can be–C8H17, C12H25, C14H29 and C16H23
Structure:
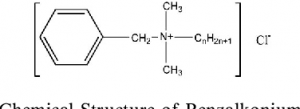
Description: A white to yellow-white powder, flake, or gel.
Properties: 10% solution pH 5–8; hygroscopic; soapy to touch; density 0.98g/cc; very soluble in water and alcohol.
Incompatibilities: Aluminum salts, anionic surfactants, citrates, iodides, hypromellose, hydrogen peroxide, lanolin, nitrates, and nonionic surfactants in high concentrations, proteins, permanganates, salicylates, and tartrates.
Use: Preservative.
3.Boric Acid:
INN: Boric acid; Acidum boricum
Synonyms: Boracic Acid; Orthoboric Acid; Boracic acid; boron trihydroxide
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Boric acid (10043-35-3)
Molecular Formula: H3BO3
Description: Hygroscopic white crystalline powder
Properties: Soluble 1 g in 18 mL water, 18 mL alcohol; 5% solution pH 3.5-4.1; density 1.435 g/cc.
Incompatibilities: Strong bases, alkali, reacts violently with potassium and acid anhydrides and complexes with glycerin.
Uses: As a buffer and preservative for eye drops.
4.Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA), Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT): Discussed in antioxidant article already. Please refer that article.
5.Butylparaben:
INN: Butyl Parahydroxybenzoate; butylparaben
Synonyms: Butoben, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid butyl ester
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Butyl-4-hydroxybenzoate(94-26-8)
Molecular Formula: C11H14O3
Structure:

Description: White to off-white crystalline powder that is odorless and tasteless.
Properties: Very slightly soluble in water or glycerin, freely soluble in propylene glycol, melting range 68–72°C.
Incompatibilities: Avoid nonionic surfactants, as these reduce antimicrobial effectiveness, due to micellization. Possible absorption of butylparaben by plastic bottles is under investigation.
Use: Antimicrobial preservative for liquid and semi-solid preparations.
6.Methylparaben:
INN: Methyl hydroxybenzoate; methyl parahydroxybenzoate; Methylis parahydroxybenzoas
Synonyms: 4-hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester; methyl-p-hydroxybenzoate
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate(99-76-3)
Molecular Formula: C8H8O3
Structure:
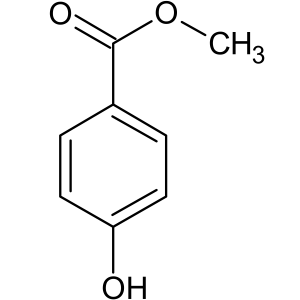
Description: White to off-white crystalline powder that has a slight burning taste.
Properties: Antimicrobial activity against most organisms, most effective in ph range of 4–8; density of 1.352 g/cc; pKa 8.4 at 22°C; solubility in water 1 in 400, in propylene glycol 1 in 5, in glycerin 1 in 60, in ethanol 1 in 2.
Incompatibilities: Nonionic surfactants (e.g., polysorbate), talc, bentonite, tragacanth gum, sodium alginate, sorbitol, and methylcellulose.
Uses: As an antimicrobial preservative in all known delivery systems.
7.Phenol:
INN: Phenol; Phenolum
Synonyms: Carbolic Acid; hydroxybenzene; oxybenezene; phenic acid; phenyl hydrate; phenyl hydroxide; phenylic acid; phenylic alcohol
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Phenol (108-95-2)
Molecular Formula: C6H6O
Structure:
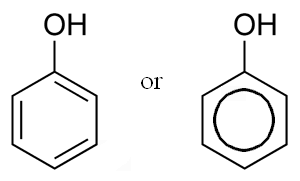
Description: Colorless to light pink, interlaced, or separate, needle-shaped crystals, or a white or light pink, crystalline mass; characteristic odor; when undiluted, it whitens and cauterizes the skin and mucous membranes; when gently heated, phenol melts, forming a highly refractive liquid; liquefied by the addition of 10% of water.
Properties: Solubility 1 g in 15 mL water; very soluble in alcohol, glycerin, chloroform, ether, or fixed and volatile oils; sparingly soluble in mineral oil; vapor is flammable; gradually darkens on exposure to light and air; specific gravity 1.07; boils at 182°C; congeals at not less than 39°C.
Incompatibilities: Produces a liquid or soft mass when triturated with camphor, menthol, acetanilide, acetophenetidin, aminopyrine, antipyrine, ethyl aminobenzoate, methenamine, phenyl salicylate, resorcinol, terpin hydrate, thymol, and several other substances, including some alkaloids. It also softens cocoa butter in suppository mixtures. Traces of iron in various chemicals (such as alum, borax, etc. may produce a pink to violet color.
Uses: As a caustic, disinfectant, topical anesthetic; a preservative for some injections; used in several proprietary antiseptic mouthwashes, hemorrhoidal preparations, and burn remedies.
8.Phenylethyl Alcohol:
INN: Phenylethyl alcohol
Synonyms: Benzeneethanol; phenethanol; benzyl carbinol; benzylmethanol; β-hydroxyethyl benzene; 2-phenylethyl alcohol; pheneylethanol; PEA
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Phenethyl alcohol [60-12-8]
Molecular Formula: C8H10O
Structure:
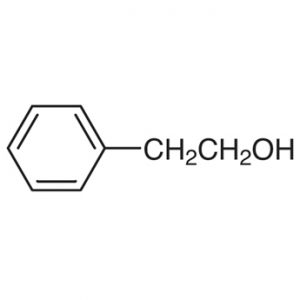
Description: Colorless liquid with a rose-like odor and a sharp, burning taste.
Properties: Solubility is 1 g in 60 mL water or 1 mL alcohol, chloroform, or ether; very soluble in fixed oils, glycerin, or propylene glycol; slightly soluble in mineral oil; solidifies at 27°C; specific gravity 1.017-1.020.
Uses: As an antimicrobial preservative.
9.Potassium sorbate:
INN: Potassium sorbate; Kalii sorbas
Synonyms: 2,4-hexadienoic acid (E,E)-potassium salt; potassium (E,E) sorbate
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Potassium (E,E)-hexa-2,4- dienoate (24634-61-5)
Molecular Formula: C6H7KO2
Structure:
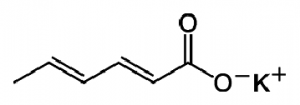
Description: White crystals or powder with a characteristic odor.
Properties: Solubility 1 g in 1.7 mL water, 1.8 mL of propylene glycol or 35 mL alcohol; density 1.36 g/cc; melting point ca. 270°C with decomposition.
Uses: As a preservative.
10.Propylene glycol:
INN: Propylene glycol; Propyleneglycolum
Synonyms: 1,2-Dihydroxypropane; 2-hydroxypropanol; methyl ethylene glycol; methyl glycol; propane-1,2-diol
Chemical Name & CAS Number: 1,2-Propanediol (57-55-6)
Molecular Formula: CH3CH(OH)CH2OH
Structure:
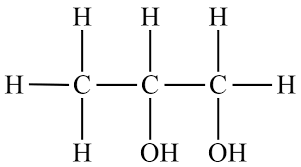
Description: Clear, colorless, viscous, and practically odorless hygroscopic liquid; with a slightly acrid taste.
Properties: Miscible with water, alcohol, acetone, or chloroform; soluble in ether; dissolves many volatile oils; immiscible with fixed oils; specific gravity 1.035-1.037; viscosity approximately 58 mPa s.
Uses: As a solvent; preservative; humectants.
11.Propylparaben:
INN: Propyl hydroxybenzoate; Propyl parahydroxybenzoate; Propylis parahydroxybenzoas; Propylparaben
Synonyms: 4-hydroxybenzoic acid propyl ester; propagin; propyl ρ-hydroxybenzoate
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Propyl 4-hydroxybenzoate(94-13-3)
Molecular Formula: C10H12O3
Structure:
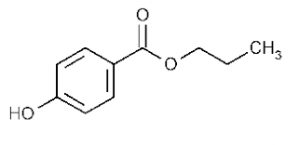
Description: White crystalline odorless and tasteless powder
Properties: Very poorly soluble in water, 1 in 250 of glycerin, 1 in 4 of propylene glycol; density 1.288 g/cc.
Incompatibilities: Nonionic surfactants (incorporation into micelles); may be absorbed by some plastics and discolors in the presence of iron.
Use: As an antimicrobial agent.
12.Sorbic Acid:
INN: Sorbic acid; Acidum sorbicum
Synonyms: 2,4-hexadienoic acid; 2-propenylacrylic acid
Chemical Name & CAS Number: (E,E)-Hexa-2,4-dienoic acid(22500-92-1)
Molecular Formula: C6H8O2
Structure:
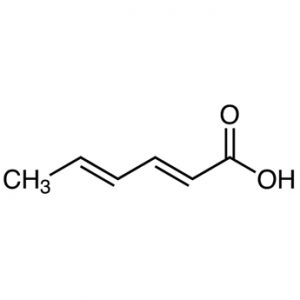
Description: Free-flowing, white, crystalline powder, with a characteristic odor.
Properties: Solubility 1 g in 400 mL water, 10 mL alcohol or 19mL propylene glycol; melting point 135°C; density 1.2 g/cc.
Incompatibilities: Bases, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents. Some functionality is lost in the presence of nonionic surfactants.
Uses: As a preservative.
Multiple choice questions:
1.Materials that prevent the initiation and growth of microorganisms in products are known as
a)antioxidants
b)preservatives
c)chelating agents
d)buffers
2.Which of the following are examples of preservatives?
a)Phenethyl Alcohol
b)Potassium Sorbate
c)Propylene Glycol
d)All of these
3.What are the synonyms of Alcohol?
a)Ethanol
b)Ethyl alcohol
c)Grain alcohol
d)All of these
4.Which of the following are physical properties of Benzalkonium chloride?
a)White to yellow-white powder
b)White crystalline odorless and tasteless powder
c)Colorless liquid with a rose-like odor
d)Colorless to light pink
5.H3BO3 is molecular formula of
a)Alcohol
b)Benzalkonium chloride
c)Boric acid
d)Sorbic acid
6.Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA) is used as
a)antioxidant
b)preservative
c)buffer
d)a and b
7.Butylparaben is used as
a)Antimicrobial preservative for liquid
b)Antimicrobial preservative for semi-solid preparations
c)Both of these
d)None of these
8.C8H8O3 is molecular formula of
a)Methylparaen
b)Phenol
c)Phenethyl Alcohol
d)Potassium Sorbate
9.Phenol shows incompatibility with
a)camphor
b)menthol
c)acetanilide
d)all of these
10.Phenylethyl Alcohol is used as
a)antioxidant
b)antimicrobial preservative
c)buffer
d)chelating agent
11.Potassium sorbate has molecular formula
a)C6H8O2
b)C10H12O3
c)C6H6O
d)C6H7KO2
12.1,2-Propanediol is chemical name of
a)Sorbic acid
b)Propylparaben
c)Propylene glycol
d)Potassium sorbate
13.Propylparaben is
a)Very poorly soluble in water
b)Highly soluble in water
c)soluble in both water as well as organic solvents
d)partially soluble in organic solvent
14.Synonym of Sorbic Acid is/are
a)2,4-hexadienoic acid
b)2-propenylacrylic acid
c)both of these
d)none of these
15.Which of the following are physical properties of Sorbic acid?
a)Free-flowing powder
b)White, crystalline powder
c)A characteristic odor
d)All of these
Solutions:
- b)preservatives
- d)All of these
- d)All of these
- a)White to yellow-white powder
- c)Boric acid
- d)a and b
- c)Both of these
- a)Methylparaen
- d)all of these
- b)antimicrobial preservative
- d)C6H7KO2
- c)Propylene glycol
- a)Very poorly soluble in water
- c)both of these
- d)All of these
References:
- Remington Essential of Pharmaceutics, 1st edition 2013, page no. 686, 687,698,696,697,698,699 ,700.
- Raymond C Rowe Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 10th edition 2009, page no. 17-19, 56-58, 68-70, 78-81, 441-445, 485-487, 490-491, 579-581, 592-594, 596-598, 672-675.
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE