PROPRANOLOL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
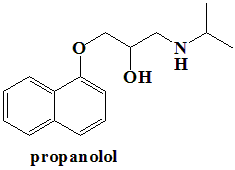
Propranolol
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-1-(1-methylethylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol.
Classification
Propranolol is a nonselective ß-adrenergic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 259.34 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in solid form. |
| 3 | Melting point | 96°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 61.7 mg/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.48 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Naphthalene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Propranolol blocks ß-adrenergic receptors.
ii. This leads to vasoconstriction, inhibition of angiogenic factors and basic growth factors of fibroblast, induction of apoptosis of endothelial cells and regulation of RAAS system. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Increasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
- Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
- Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
- Aryloxypropanolamines are more potent than aryloxyethanolamines. [2]
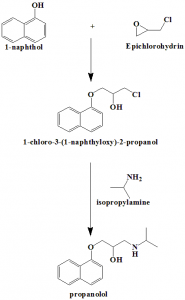
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of 1-naphthol with epichlorohydrin gives 1-chloro-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-propanol.
ii. Latter compound is reacted with iso-propylamine to give propranolol. [3]
Therapeutic Uses
Propranolol is used for treatment of:
- Tremors
- Angina
- Hypertension
- Heart rhythm disorders
- Treatment and prevention of heart attacks
- Reducing migraine headaches
Side Effects
Side effects of propranolol are:
- Uneven or slow heartbeats
- Lightheadedness
- Wheezing
- Trouble in breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
- Vision problems
- Coldness of hands and feet
- Depression
- Confusion
- Hallucinations
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Itching
- Tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Dark urine
- Jaundice
- Low blood sugar
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Swelling of face and tongue
- Eyes burning
- Skin pain
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Stomach cramp
- Impotency
- Decreased sex drive
- Insomia
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Propranolol?
a) (RS)-1-(1-methylethylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol.
b) methyl (RS)-3-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl}propanoate
c) (RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol
d) (RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxybenzamide
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of Propranolol?
I. Increasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
II. Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
III. Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
a) I, III
b) II, III
c) I, II, III
d) I, II
Q.3 The correct order for the synthesis of drug propranolol from 1-naphthol can be?
I. Reaction with epichlorohydrin
II. Reaction with isopropylamine
III. Reduction
a) III – II – I
b) I – III – II
c) I – II
d) III – I
Q.4 Side effects of drug propranolol is/are?
a) Uneven heartbeats
b) Trouble breathing
c) Vision problems
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct molecular weights-
| i. Propranolol | A. 295.37 gm/mol |
| ii. Esmolol | B. 309.4 gm/mol |
| iii. Bisoprolol | C. 325.4 gm/mol |
| iv. Metipranolol | D. 259.34 gm/mol |
a) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
b) i-B, ii-A, iii-C, iv-D
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
d) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
Q.6 An example of drug from class Nonselective ß-adrenergic antagonist?
a) Dopamine
b) Dobutamine
c) Propranolol
d) Metaraminol
Q.7 The type of ring system found in Propranolol?
a) Naphthalene
b) Carbazoline
c) Imidazoline
d) No ring is present
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-c
4-d
5-d
6-c
7-a