PROPYLHEXEDRINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
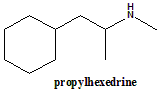
Propylhexedrine
IUPAC nomenclature
(±)-1-cyclohexyl-N-methylpropan-2-amine.
Classification
Propylhexedrine is an α-adrenergic agonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 155.28 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in solid form |
| 3 | Melting point | 122-124°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Cyclohexyl ring |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
I. Propylhexedrine causes serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine transporters to reverse their direction of flow.
II. This leads to release of these transmitters from vesicles to the cytoplasm and then to the synapse.
III. Propylhederine also antagonizes the action of VMAT2 which results in more release of neurotransmitters.
Structure Activity Relationship
The SAR of Adrenergic agonist can be discussed as follows:
- Primary or secondary aliphatic amine separated by two carbons from a substituted benzene ring is essential for the high agonist activity.
- The hydroxyl substituted carbon must be in the R configuration for the maximal direct activity.
R1 substitution:
- When R1 is increased in size, activity of alpha receptors decreases and activity of the beta receptors increases
- Activity of both alpha and beta receptors is maximum when R1 is methyl group.
- Alpha agonist activity decreases when R1 is larger than methyl, and went negligible when R1 is isopropyl.
- Large lipophillic groups can afford compounds with alpha blocking activity.
- N-substituent provides selectivity for different receptors.
- Arylalkyl group can provide beta selectivity, increased cell penetration and increased lipophillicity for the longer duration of action.
R2 substitution:
- Ethyl group can eliminate the alpha activity of the drug.
- Erythrostero isomers have maximal activity.
- The additional methyl group makes the drug more selective for the alpha2
R3 substitution on the aromatic ring:
- 3’,4’-dihydroxy substituted benzene ring has poor oral activity.
- 3’, 5’-dihydroxy compounds are orally active.
- At least one of the groups is required which can form hydrogen bonds. And if only one group is present then it is preferred at 4’ position to retain the beta2
If phenyl group has no phenolic substituent then it may act directly or indirectly. [1]
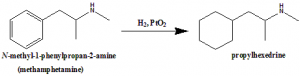
Method of synthesis
Propylhedrine can be synthesized from methamphetamine through reduction of the aromatic ring by Adam;s catalyst to form a cyclohexyl moiety.
Therapeutic Uses
Propylhexedrine is used:
- As a nasal decongestant
Side Effects
Side effects of propylhexedrine are:
- Restlessness
- Anxiousness
- Tremors
- Sweating
- Nasal rebound Congestion
- Nose dryness
- Burning nasal passage
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug Propylhexedrine.
| i. Large lipophillic groups at R1 | A. Elimination of α-activity |
| ii. N-substituent at R1 | B. Afford compounds with α-blocking activity. |
| iii. Ethyl group at R2 | C. Provides selectivity for different receptors |
| iv. 3’, 5’-dihydroxy compounds | D. Orally active drug |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
d) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Propylhexedrine: (±)-1-cyclohexyl-N-methylpropan-2-amine
- Metaraminol: (S,S)-2-methylamino-1-phenylpropan-1-ol.
- Pseudoephedrine: 4-(2-aminopropyl)phenol
- Hydroxyamphetamine: (RS)-[4-(1-Hydroxy-2-tert-butylamino-ethyl)-2-(4-methylbenzoyl)oxy-phenyl] 4-methylbenzoate
a) TFFF
b) FTTF
c) TFFT
d) FFFF
Q.3 Type of ring present in the structure of propylhexedrine?
a) Benzene
b) Imidazol
c) Cyclohexyle
d) Purine
Q.4 Propylhexedrine shows its effect through?
a) Agonism of α-receptors
b) Agonism of ß-receptors
c) Antagonism of α-receptors
d) Antagonism of ß-receptors
Q.5 Propylhexedrine is used for?
a) Treatment of AIDS.
b) Temporary relief of nasal congestion
c) As an antineoplastic drug
d) None of the above
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Pseudoephedrine is an α-adrenergic agonist.
II. Mechlorethamine is an alkylating agent.
a) I
b) II
c) I, II
d) None
Q.7 Propylhexedrine can be synthesized by reduction of?
a) Methamphetamine
b) Levorphanol
c) Clonazepam
d) Phenytoin
ANSWERS
1-b
2-a
3-c
4-a
5-b
6-c
7-a