PYRIDOSTIGMINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
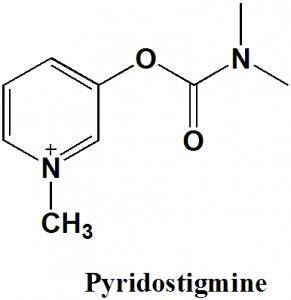
Pyridostigmine
IUPAC nomenclature
(1-methylpyridin-1-ium-3-yl) N,N-dimethylcarbamate
Classification
- Reversible anticholinestrase
- Carbamates
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 181.21 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 153oC |
| 4 | Solubility | 1.04e+00 g/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.554 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyridine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Drug competes with acetylcholine for the attachment to anticholinestrase, thus, inhibits anticholinestrase for the acetylcholine.
- This increases the concentration of the acetylcholine at the synaptic cleft and hence, increases the efficiency of the cholinergic transmission.
Structure Activity Relationship
General SAR for carbamates anticholinestrases can be summarized as follows:
- Variation of the chain length influence AchE inhibition.
- Most potent AChE inhibitor for the series was found to be having 7 methyl groups attached in the chain.
- Replacement of the xanthone nucleus with other aryl groups decreases the AChE inhibitory activity.
- Presence of polar group on the aromatic moiety is essential for the activity of drug.
- If the flexible chain is replaced by the rigid linear ethyne group, activity of the drug is lost, which shows that, a flexible chain is necessary for the activity.
- Introduction of the tertiary amino group into saturated ring decreases the activity, but activity is not fully lost.
- Changing the length of the carbamic N-substituent has a significant effect on the selectivity of the drug. [1]
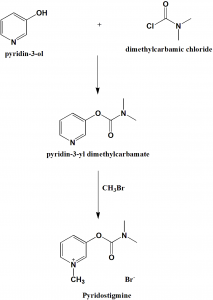
Method of synthesis
i. 3-hydroxypiridine is reacted with dimethylaminocarbamoyl chloride to give 3-(dimethylaminocarbamoyl)pyridine.
ii. The above formed compound is reacted with methylbromide to produce pyridostigmine. [2]
Medicinal Uses
Pyridostigmine is used for:
- Treatment of myasthenia gravis
Side Effects
Side effects of Pyridostigmine are:
- Salivation
- Fasciculation
- Bowel cramps
- Diarrhea
- Allergic reactions
- Dizziness
- Vision changes
- Convulsions
- Drowsiness
- Loss of consciousness
- Headache
- Dysarthria
- Arrhythmia
- Decreases pupil size
- Cardiac arrest
- Hypotension
- Respiratory depression
- Bronchospasm
- Respiratory arrest
- Rash
- Urticaria
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Muscle cramps
- Flushing
- Weakness
MCQs
Q.1 Mechanism of action of Pyridostigmine is due to?
a) Reversibly inhibition of COX enzyme
b) Irreversibly inhibition of COX enzyme
c) Stimulation of Anticholinestrase for acetylcholine
d) Inhibition of Anticholinestrase for acetylcholine
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug Pyridostigmine is/are?
a) Treatment of myasthenia gravis
b) Treatment of Sores
c) Treatment of peptic ulceration
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of Carbamates anticholinestrase?
I. Variation of the chain length influence AchE inhibition.
II. Most potent AChE inhibitor for the series was found to be having 7 methyl groups attached in the chain.
III. Replacement of the xanthone nucleus with other aryl groups increases the AChE inhibitory activity.
a) I, II, III
b) I, II
c) I, III
d) II, III
Q.4 Number of chiral centers present in the structure of Pyridostigmine is?
a) 0
b) 5
c) 1
d) 4
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug Pyridostigmine?
I. Molecular weight: 181.21 gm/mol
II. Physical appearance: Solid
III. Melting point: 3510C
IV. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 5.8
a) TFFT
b) FTTF
c) TTFF
d) FFFF
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drugs are?
I. Pyridostigmine: (RS)-2-(2-fluorobiphenyl-4-yl)propanoic acid
II. Flavoxate: 2-(1-piperidyl)ethyl 3-methyl-4-oxo-2-phenylchromene-8-carboxylate
III. Chlorazepate: 7-Chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid
IV. Amphetamine: 2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
a) I, II
b) II, III, IV
c) I, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Pyridostigmine | A. Barbiturate anticonvulsant |
| ii. Methabarbital | B. Anticholinestrase |
| iii. Codeine | C. Benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic |
| iv. Clorazepate | D. Morphine analogue |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
d) i-A, ii-B, iii-C, iv-D
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-d
2-a
3-b
4-a
5-c
6-a
7-b
REFERENCES
[1] Rampa A, Piazzi L, Belluti F, Gobbi S, Bisi A, Bartolini M, Andrisano V, Cavrini V, Cavalli A, Recanatini M, Valenti P. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: SAR and kinetic studies on ω-[N-methyl-N-(3-alkylcarbamoyloxyphenyl) methyl] aminoalkoxyaryl derivatives. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2001 Nov 8;44(23):3810-20. [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.