RABEPRAZOLE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Rabeprazole
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-2-([4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole.
Classification
- Proton pump inhibitors
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 359.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to yellowish white solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 99-100oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in water and methanol; insoluble in ether |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.6 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Pyridine, benzimidazole |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Rabeprazole is a prodrug which requires protonation via an acidic environment to get activated form Sulphenamide.
- Sulphenamide covalently binds with cystien residues via disulfide bridges on the α subunit of H/K ATPaseenzyme system.
- Thereby it inhibits the H+/K+ ATPase pump which in turn inhibits the gastric acid secretion or formation of hydrochloric acid in parietal cells
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of Heteroaryl- and heterocyclyl-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]Pyridine derivatives acting as acid pump antagonists can be summarized as:
- The inhibitory property of drugs depends on hydrophobic group substituted at the left side ortho-position of the phenyl ring.
- Increase in hydrophobic value increases the activity.
- Increasing the GTCI value decreases the activity.
- Small molecule substitutions may participate in hydrophobic interaction as well as steric interactions. [1]
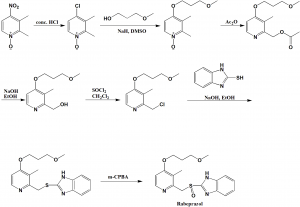
Method of synthesis
i. 4-nitro-2,3-dimethylpyridine-N-oxide is heated with conc. HCl to get 4-chloro-2,3-dimethylpyridine-N-oxide.
ii. Last is reacted with sodium 3-methoxypropan-1-olate in DMSO to get 4-alkoxy intermediate.
iii. On reaction of intermediate with acetic anhydride, produces O-acetyl intermediate.
iv. On alkaline hydrolysis of the above formed intermediate produces pyridine-2-ylmethanol.
v. The last is chlorinated using thionyl chloride to get a chloro intermediate.
vi. The above formed intermediate is condensed with help of 2-mercaptobenzimidazole in the presence of a base to get 2-((pyridine-2-ylmethyl)thio)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole derivative.
vii. Oxidation of last with meta-chloroperbenzoic acid yields rabeprazole.[2]
Medicinal Uses
Rabeprazole is used for treatment of:
- Stomach ulcers
- Active duodenal ulcers
- Active benign gastric ulcer
- GERD
- Erosive esophagitis
- Zollinger-Errison syndrome
- pylori eradication
Side Effects
Side effects of Rabeprazole are:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Headache
- Low magnesium blood level
- Irregular heartbeat
- Muscle spasms
- Seizures
- Lupus
- Diarrhea
- Blood in stool
MCQs
Q.1 “(RS)-2-([4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Rabeprazole
b) Nimodipine
c) Promethazine
d) Clemastine
Q.2 Melting point of Rabeprazole is?
a) 100oC
b) 193oC
c) 160 oC
d) 652oC
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Rabeprazol | A. Proton pump inhibitor |
| ii. Ranitidine | B. Calcium channel blocker |
| iii. Metformin | C. Antidiabetic agent |
| iv. Nimodipine | D. H2-antihistamine |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Q.4 Mechanism of action of Rabeprazole includes?
I. Inhibition of H+/K+ ATPase pump
II. Antagonistic effects on H2-receptor.
III. Effects on Muscarinic receptors
IV. Reduction in acidity of stomach
a) I, II
b) I, IV
c) I, II, III
d)I, III
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for general structure activity of Heteroaryl- and heterocyclyl-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]Pyridine derivatives acting as acid pump antagonists drugs can be?
- The inhibitory property of drugs depends on hydrophobic group substituted at the left side ortho-position of the phenyl ring.
- Increase in hydrophobic value increases the activity.
- Increasing the GTCI value decreases the activity.
- Small molecule substitutions may participate in hydrophobic interaction as well as steric interactions
a) TTFT
b) TFTF
c) TTTT
d) FFTT
Q.6 Type of ring structure present in the structure of rabeprazole is?
a) Benzimidazole
b) Pyrimidine
c) Pyran
d) Phenyl
Q.7 The drug Rabeprazole is mainly used for treatment of?
a) Stomach ulcers
b) GERD
c) Zollinger-Errison syndrome
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-a
4-b
5-c
6-a
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Agarwal N, Bajpai A, Gupta SP. A quantitative structure-activity relationship and molecular modeling study on a series of heteroaryl-and heterocyclyl-substituted imidazo [1, 2-a] pyridine derivatives acting as acid pump antagonists. Biochemistry Research International. 2013 Jan 1;2013.[2] [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of best-seller drugs. Academic press; 2016 Jan 7.