Surface and interfacial phenomenon: Solubilization and detergency and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam
SOLUBILIZATION: It can be defined as the preparation of a thermodynamically stable isotropic solution of a substance normally insoluble or very slightly soluble in a given solvent by the addition of component or by any suitable methods.
SOLUBILITY: The maximum amount of solute that can be dissolve in a given amount of solvent.
FACTORS THAT EFFECT SOLUBILIZATION:
NATURE OF SOLUTE AND SOLVENT: ◦ The amount of solute that dissolves depends on what type of solute it is. While only 1 gram of lead (II) chloride can be dissolved in 100 grams of water at room temperature, 200 grams of zinc chloride can be dissolved. This means that a greater amount of zinc chloride can be dissolved in the same amount of water than lead II chloride.
TEMPERATURE: Generally in many cases solubility increases with the rise in temperature and decreases with the fall of temperature but it is not necessary in all cases. However we must follow two behaviors:
In endothermic process solubility increases with the increase in temperature and vice versa EXAMPLE: solubility of potassium nitrate increases with the increase in temperature.
In exothermic process solubility decrease with the increase in temperature. EXAMPLE: solubility of calcium oxide decreases with the increase in temperature.
Gases are more soluble in cold solvent than in hot solvent.
PRESSURE: For solid and liquid solutes, changes in pressure have practically no effect on solubility For gaseous solutes, an increase in pressure increases solubility and a decrease in pressure decreases solubility.
PARTICLE SIZE: Solubility will increase with the decrease size of solute particle because of the additional surface energy. This effect is generally small unless particles become very small typically smaller than 1 micro meter.
Detergency: It is most important property of surface active agents. Surface active agents are referred as detergents. The term Detergency is mostly used in the cleaning / removing of grease, oil and dirt from the solid surface. The principle of detergency is based on the formation of micelle.
The process needs many of the actions specific to surfactant molecules.
- The surfactant requires good wetting properties to ensure good contact with the solid surface.
- It also has the ability to remove dirt into the bulk liquid.
- This property is achieved by lowering the surface tension of the medium in which surfactants is dissolved.
- By lowering this interfacial tension between two media or interfaces (e.g. air/water, water/stain, stain/fabric) the surfactant plays a key role in the removal and suspension of dirt.
- The lower surface tension of the water makes it easier to lift dirt and grease off of dirty dishes, clothes and other surfaces, and help to keep them suspended in the dirty water.
- The water-loving or hydrophilic head remains in the water and it pulls the stains towards the water, away from the fabric.
- The surfactant molecules surround the stain particles, break them up and force them away from the surface of the fabric.
- They then suspend the stain particles in the wash water to remove them. If the dirt is oily it may be emulsified or solubilized by the surfactant.
MICELLES: When surfactant are added to water, they self-assemble into little sphere called micelles with the hydrophilic head facing out and hydrophobic tail pointing in.
TYPES OF MICELLES:
SPHERICAL MICELLES: The micelles which are arranged in spherical form are called spherical micelles.
ROD SHAPE MICELLES: The micelles which are arranged in rod form are called rod shaped micelles.
LAMELLAR MICELLES: The micelles which are arranged in plates (lamellae) form are called lamellar micelles.
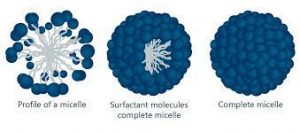
Fig 1 – Micelle (taken from Micelle Kruss scientific)
FORMATION OF MICELLE:
Micelles form when the polar head and the non polar tails arrange in a special way. They are usually driven to arrange either with the polar heads out (oil in water) or with the polar head in (water in oil). Micelles only form when the concentration of surfactant is greater than the critical micelle concentration (CMC). The surfactant is any surface active material that can part the surface upon entering. The CMC is the concentration above surfactant when micelles will form spontaneously. The higher the concentration, the more micelles there are. Micelle formation also depend on the Krafft temperature. This temperature is when surfactants will form micelles. If the temperature is below the Krafft temperature, then there is no spontaneous formation of micelles. As the temperature increases, the surfactant will turn into a soluble form and be able to form micelles from a crystalline state. The hydrophobic effect is also a driving force that needs to be taken into account. This effect is characterized by the fact that like to form intermolecular aggregates in aqueous substances and in intramolecular molecules. Micelle formation can be summed up by thermodynamics, driven by entropy and enthalpy.
Multiple choice questions (MCQs)
1.Which of the following process does not occur at the interface of phases?
a)Crystallization
b)Heterogenous catalysis
c)Homogeneous catalysis
d)Corrosion
2.The preparation of a thermodynamically stable isotropic solution of a substance normally insoluble or very slightly soluble in a given solvent by the addition of component or by any suitable methods is called
a)Solubilization
b)Solubility
c)Both of these
d)None of these
3.The maximum amount of solute that can be dissolve in a given amount of solvent is known as
a)Solubilization
b)Solubility
c)Both of these
d)None of these
4.Which of the following factors effect solubilization?
a)Temperature
b)Pressure
c)Particle size
d)All of the above
5.Generally in many cases solubility _________ with the rise in temperature
a)Increases
b)Decreases
c)No change
d)There is no relation between temperature and solubilization
6.In endothermic process solubility _____ with the increase in temperature
a)Increases
b)Decreases
c)No change
d)There is no relation between temperature and solubilization
7.In exothermic process solubility _____ with the increase in temperature
a)Increases
b)Decreases
c)No change
d)There is no relation between temperature and solubilization
8.For gaseous solutes, an increase in pressure _____ solubility
a)Decrease
b)Increase
c)No change
d)There is no relation between pressure and solubilization
9.Solubility will ____ with the decrease size of solute particle
a)Decrease
b)Increase
c)No change
d)There is no relation between particle size and solubilization
10.Surface active agents are referred as
a)Hydrocolloids
b)Buffering agents
c)Detergents
d)all of the above
11.At high concentration of soap in water, soap behaves as ____________.
a)Molecular colloid
b)Associated colloid
c)Macromolecular colloid
d)Lyophilic colloid
12.When surfactant are added to water, they self-assemble into little sphere called
a)Hydrocolloids
b)Floccules
c)Micelles
d)All of the above
13.Which of the following are types of micelle?
a)Spherical
b)Rod shaped
c)Lamellar
d)All of the above
14.Micelles only form when the concentration of surfactant is greater than the
a)CMC
b)Oil globules
c)Water molecules
d)Anions
15.Which of the following options are correct?
a)Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution is possible at all temperatures.
b)Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution occurs above a particular concentration.
c)Soap solution behaves as a normal strong electrolyte at all concentrations.
d)None of above
Solutions:
- c) homogeneous catalysis
- a)Solubilization
- b)Solubility
- d)All of the above
- a) increases
- a)increases
- b)decreases
- b)increase
- b)increase
- c)detergents
- b) associated colloid
- c)micelles
- d)All of the above
- a)CMC
- b) Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution occurs above a particular concentration.
References:
- Martins Physical Pharmacy, 6th edition 2011, page no. 670-680.
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test