TAMOXIFEN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
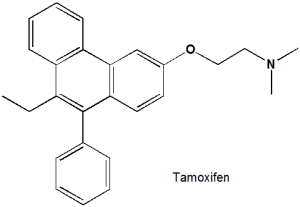
Tamoxifen
IUPAC nomenclature
(Z)-2-[4-(1,2-Diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine.
Classification
Tamoxifen is a selective estrogen receptor modulator. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 371.5 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | Present in solid form |
| 3 | Melting point | 97°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 16.7 mg per liter in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 6.30 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenantherene and a phenyl ring |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | No chiral carbon atom present |
Mechanism of Action
- Tamoxifen competitively inhibits the binding of estrogen to its receptors. This inhibition is main cause for the activity against the breast cancer cells.
- Tumor growth factor α, and insulin like growth factor 1 is decreased by the tamoxifen.
- The level of sex hormone binding globulin is increased by tamoxifen.
- This overall limits the level of freely available estradiol, which further reduced the level of the factors which stimulates the tumor growth.
- Tamoxifen also inhibits the protein kinase C which results in the apoptosis of estrogen receptor positive cells.
Structural Activity Relationship
- Alkylaminoethane side chain is important for the antiestrogenic activity.
- Para hydroxylation of the phenyl ring on carbon 1 of butene can increase the potency of antiestrogen.
- As the hydroxyl group is present in the equivalent position to the 3-phenolic hydroxyl of 17-beta-estradiol, 4-hydroxytamoxifen will have very high binding affinity.
- Substitution for 4-hydroxytamoxifen appears to be optimal to produce a potent antiestrogen.
- The hydroxyl group is critical to locate the alkyl aminoethoxy side chain in the correct position in the steroid-binding site to block estrogen action. [2]
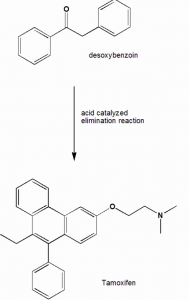
Method of synthesis
An olefinic link is generated by an acid catalyzed elimination reaction on the substituted desoxybenzoin.
Therapeutic Uses
Tamoxifen is used for:
- Adjuvant therapy
- Treatment of metastatic breast cancer
- Treatment of ductal carcinoma
- For the prevention of breast cancer in the women who are at higher risk of it.
- Treatment of ovarian cancer
Side Effects
- Common side effects of tamoxifan include loss of libido, swelling in feet and ankles, vaginal discharge and hot flashes.
- Less common side effects are anxiety, depression, weight loss, vaginal bleeding, menstrual irregularities and nausea.
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct IUPAC nomenclatures
| i. 2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
|
A. Tamoxifen |
| ii. 4-[bis(2-chlorethyl)amino]benzenebutanoic acid
|
B. Cisplatin |
| iii. (SP-4-2)-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)
|
C. Chlorambucil |
| iv. (Z)-2-[4-(1,2-Diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine
|
D. Mechlorethamine |
a) i-A, ii-B, iii-C, iv-D
b) i-D, ii-C, iii-B, iv-A
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-B, iv-A
d) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
Q.2 How many statements below are true with respect to the SAR of the drug Tamoxifen?
- Alkylaminoethane side chain is important for the antiestrogenic activity.
- Para hydroxylation of the phenyl ring on carbon 1 of butene can increase the potency of antiestrogen.
- As the hydroxyl group is present in the equivalent position to the 3-phenolic hydroxyl of 17-beta-estradiol, 4-hydroxytamoxifen will have very high binding affinity.
- Substitution for 4-hydroxytamoxifen appears to be optimal to produce a potent antiestrogen.
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Q.3 The drug tamoxifen has how many chiral carbons in its structure?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 Tamoxifen can be synthesized easily through acid catalyzed elimination reaction of?
a) Guanine
b) Carboplatin
c) Desoxybenzoin
d) None of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is not a therapeutic use of drug Tamoxifen
a) Adjuvent therapy
b) Anxiety
c) Breast cancer
d) Ductal carcinoma
Q.6 The correct classification of the drug Tamoxifen can be?
a) Selective estrogen receptor modulator
b) Selective estrogen receptor down regulator
c) Aromatase inhibitors
d) Progestins
Q.7 How many number of rings are found in the chemical structure of the drug Tamoxifen?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
ANSWERS
1-b
2-d
3-a
4-c
5-b
6-a
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 6thEdn. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. 2008: 820. [2] Murphy CS, Parker CJ, McCague RA, Jordan VC. Structure-activity relationships of nonisomerizable derivatives of tamoxifen: importance of hydroxyl group and side chain positioning for biological activity. Molecular pharmacology. 1991 Mar 1;39(3):421-8.