THIORIDAZINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
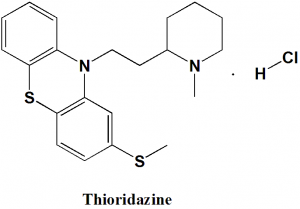
Thioridazine hydrochloride
IUPAC nomenclature
10-[2-(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)ethyl]-2-methylsulfanylphenothiazine;hydrochloride
Classification
Thioridazine hydrochloride is phenothiazine antipsychotic drug.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 407 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Pale yellow solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 158-160°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | N/a |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenothiazine, piperidine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Thioridazine blocks postsynaptic dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors in brain.
- Thioridazine also blocks α-adrenergic effects
- Depresses the release of hypothalamic and hypophyseal hormones
- Depresses the reticular activating system
- Due to these, basal metabolism, temperature, wakefulness, vasomotor tone and emesis of the body is affected.
Structure Activity Relationship
Structure activity relationship of phenothiazine can be described as follows:
- Tilting of side chain towards ring A grants favorable Vander Waal’s interaction of the side chain. This interaction decides the potency of the drug towards the dopamine receptors.
- Optimal neuroleptic activity occurs when the ring A substituent is in the 2nd-position.
- A trifluoromethyl substituent provides a greater number of favorable Van der Waal’s contacts with the side chain than the chlorine substituent. Thus, phenothiazne with trifluoromethyl substituents are more potent than those with chlorine substituent.
- A piperazine side chain provides more Van der Waal’s contacts with 2-substituent than the alkylamino side chain. Thus, piperizine phenothiazine are more potent in antischizophrenic effects than alkylamino phenothiazines.
- Hydroxyethylpiperazine side chain phenothiazines displays more favorable Van der Waal’s interactions with ring A than simple piperazines.
- In the thioxanthene and xanthenes containing ring systems, the cis forms are more potent neuroleptics than the trans isomers.
- Phenothiazine analogues having the presence of exolytic double bond are more potent than the corresponding compounds lacking the exolytic double bonds. [1]
Method of synthesis
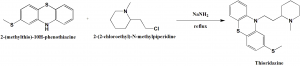
Thioridazine can be synthesized through reaction of 2-(methylthio)-10H-phenothiazine with 2-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylpiperidine in refluxing xylene in the presence of refluxing sodium amide.
Therapeutic Uses
Thioridazine hydrochloride is used for:
- Treatment of schizophrenia
- Reducing nervousness
- Reducing aggression
- Reducing negative thoughts
- Reducing hallucinations
Side Effects
Side effects of Thioridazine hydrochloride are:
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Blurred vision
- Headache
- Restlessness
- Drowsiness
- Difficulty in urinating
- Constipation
- Tremors
- Infections
- Jerking movements
MCQs
Q.1 What are the correct statements related with the physicochemical properties of thioridazine hydrochloride drug?
I. Molecular weight = 407 gm/mol
II. It appears as pale yellow solid
III. It is soluble in water
IV. Phenothiazine ring is present in the structure
a) I, II, III
b) I, II, IV
c)III, IV
d) I. II. III. IV
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Thioridazine | A. 10-[2-(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)ethyl]-2-methylsulfanylphenothiazine |
| ii. Mephobarbital | B. 5-ethyl-5-pentan-2-yl-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-diazinane-4,6-dione |
| iii. Triflupromazine | C. Phenyl-5-ethyl-1-methylbarbituric acid |
| iv. Thiopental | D. N,N-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazin-10-yl]propan-1-amine |
a) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
Q.3 Types of receptors blocked by the Thioridazine hydrochloride drug?
I. Dopaminergic D1
II. Dopaminergic D2
III. ß-adrenoceptors
IV. α-adrenoceptors
a) I, III, IV
b) I, II
c) III, IV
d) I, II, IV
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Thioridazine hydrochloride: Phenothiazine antipsychotic drug
- Oxazepam: benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
- Triazolam: Guanosine nucleoside antiviral drug
- Ribavirin: Benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
a) TFTF
b) TTFF
c) FFTT
d) FFFT
Q.5 Greater potency of phenothiazines with trifluoromethyl substitution is due to?
a) Greater number of favourable Van der Waal’s contacts
b) Bleaching action of chlorine
c) Affinity of fluorine with potassium is higher
d) High molecular weight of fluorine
Q.6 Starting chemicals requires for the synthesis of thioridazine drug are?
I. 2-(methylthio)-10H-phenothiazine
II. 2-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylpiperidine
III. Sodium amide
IV. 4-chloro-3-cyclopentene
a) I, III, IV
b) I, II, III
c) II, III, IV
d) I, II, IV
Q.7 Side effect of drug Thioridazine hydrochloride are?
a) Tremors
b) Infections
c) Difficulty in urination
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-d
2-c
3-d
4-b
5-a
6-b
7-d