FOSFESTROL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Fosfestrol
IUPAC nomenclature
[4-[4-(4-phosphonooxyphenyl)hex-3-en-3-yl]phenoxy]phosphonic acid.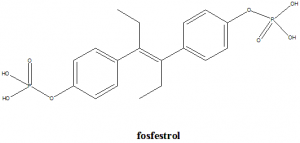
Classification
Fosfestrol falls under the category of estrogens. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 428.3 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | Off white crystalline form. |
| 3 | Melting point | 203-206°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Less than 1 mg/ml in water |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Aromatic ring present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | No chiral center present |
Mechanism of Action
- Fosfestrol is an agonist of estrogen receptors. The drug acts as a prodrug of diethylstilbestrol.
- Fosfestrol is also a strong antigonadotropic drug, and thus, suppresses the levels of testosterone on male. [2]
Structural Activity Relationship
- Phenolic hydroxyl group without the impairement by the substitution of the alkyl groups at ortho position, is important for the higher affinity for the binding with the receptor, and also for the activity of the drug.
- Substitution of the alkyl group at 3’-phenolic hydroxyl results in the lower affinity for binding with estrogen receptors. Although, metabolic activation may occur to produce potent estrogen action.
- Due to higher solubility in the body fat, alkoxytriphenylethenes groups will result in the longer duration of action. Also, there will be metabolic activation to the phenolic derivatives.
- Receptors can be occupied by the bisphenolic compounds to produce estrogen actions.
- Stilbene-like compound is not necessary, only a spacing group is required for the binding site.
- Bisphenolic compound will have higher affinity for the estrogen receptors but also, it results in partial agonist activity in vitro.
- Binding ligand with antiestrogenic properties can be produced by extending the side chain away fro the binding site in a bisphenolic compound.
Therapeutic Uses
- Fosfestrol is used for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer.
- Used for gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist therapy in men having the prostate cancer.
Side Effects
- Common side effects of Fosfestrol include nausea, vomiting, edema and skin reactions.
- Less common side effects are cardiioovascular complications, thrombosis, pain in the genital area, weight gain, feminization and gynecomastia.
MCQs
Q.1 The terms ‘diethylstilbestol diphosphate’ and ‘Honvan’ are associated with which drug?
a) Fosfestrol
b) Carboplatin
c) Toremifene
d) Ethinylestradiol
Q.2 Phenolic hydroxyl group without the impairement by the substitution of the alkyl groups at ……………. position, is important for the higher affinity for the binding with the receptor, and also for the activity of the drug.
a) ortho
b) meta
c) para
d) both ortho and para positions
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct side effects of the drug fosfestrol?
I. Nausea
II. Feminization
III. Edema
IV. Cardiovascular complications
a) I & II
b) I only
c) I, III & IV
d) I, II, III & IV
Q.4 Appearance of fosfestrol drug is?
a) Off white powder form
b) Red crystal form
c) Needle shape crystal form
d) None of the above
Q.5 Which pairs of drug and its classification are true-
| I. | Dactinomycin | Antibiotics |
| II. | Etoposide | Epipodophyllotoxin |
| III. | Fosfetrol | Estrogens |
| IV. | Vinblastin | Glucocorticoids |
a) I, II & IV
b) II & III
c) IV
d)I, II, III
Q.6 Melting point of fosfestrol is?
a) 103°C
b) 203°C
c) 303°C
d) 403°C
Q.7 How many rings are present in structure of fosfestrol?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-d
4-a
5-d
6-b
7-b
REFERENCES
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 6thEdn. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. 2008: 820. [2] DRUCKREY H, BROCK N. On the mechanism of action of stibestrol diphosphate (Honvan) in prostate cancer. Munchener medizinische Wochenschrift (1950). 1961 Apr 7;103:777.