DIPHENOXYLATE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
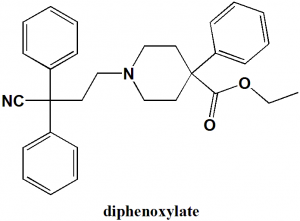
Diphenoxylate
IUPAC nomenclature
Ethyl 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate
Classification
- Diphenoxylate falls under category of anti-diarrheal agents.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 452.6 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 221°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 800 mg/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 6.3 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Piperidine, phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Diphenoxylate acts as opiate receptor agonist which decreases the peristalsis and constrict the sphincture by stimulating the mu receptors in GI.
- Drug also has a direct effect on circular smooth muscle of bowel which results in segmentation and prolongation of the GI transit time.
- Antidirrheal activity of the drug is due to result of enhanced segmentation which allows increased contact of the intraluminal contents with intestinal mucosa.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR for opiates can be summarized as follows:
- Replacement of phenolic hydroxyl into –OCH3/-OC2H5 will make the drug less analgesic and cough suppression will also takes place.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCH3 makes the compound 5 times more active.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with -OC2H5 makes the compound 2.4 times more active than morphine.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCOCH3 will also activates the compound by 4.2 times.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with ketone group inactivates the compound and makes it lesser active.
- By hydrogenation of alicyclic unsaturated linkage, activity increases by 1.2 times.
- On replacement of the methyl group from tertiary nitrogen by hydrogen atom, activity decreases.
- On replacement of N-CH3 by NCH2CH2Ph, activity increases by 14 times.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N-allyl/methallyl/propyl, the compound so formed acts like the Morphine antagonist.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N(CH3)2 Cl– , compound have curare action and it do not possesses any analgesic activity. [1]
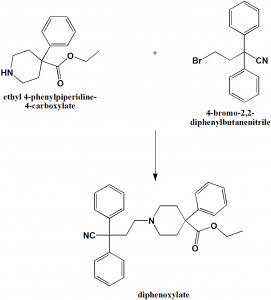
Method of synthesis
i. 2,2-diphenyl-4-carboxylic acid is synthesized from 1-benzyl-4-phenyl-4-cyanopiperidine.
ii. The former compound undergoes ethanolysis in presence of acid followed by benzylation to give diphenoxylate.
Therapeutic Uses
Diphenoxylate is used for:
- Treatment of diarrhea
Side Effects
Side effects diphenoxylate are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Restlessness
- Confusion
- Stomach discomfort
- Changes in mood
- headache
- Loss of appetite
- Tiredness
- Numbness of arms and legs
- Rashes
- Hives
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty in breathing
- Itching
- Swelling of eyes
MCQs
Q.1 Choose the correct option related with the mechanism of action of drug Diphenoxylate?
a) Acts as Opiate receptor antagonist
b) Increases the peristaltic movement of GIT
c) Produces antidiarrheal effects
d) All of the above
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug diphenoxylate is/are?
a) Treatment of diarrhea
b) As an anesthetic
c) Prevention of Diarrhea
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of drug diphenoxylate?
I. Due to presence of asymmetric halogenated carbon in ether, they are lesser anesthetics.
II. Halogenated methyl ethyl ethers are less stable, less potent and have lesser clinical profile than halogenated diethyl ether.
III. Fluorination increases the stability and decreases the flammability.
IV. Compete halogenations of the alkane or ether decreases the anesthetic potency and increases the convulsant potency
a) I, IV
b) II, III
c) III, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.4 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of Diphenoxylate is?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug diphenoxylate is?
I. Molecular weight = 452.6 gm/mol
II. Melting point = 180.2oC
III. Present in creamy liquid form
IV. Ring structure absent
a) FFTF
b) TFFT
c) FTTF
d) TFFF
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drugs are?
I. Diphenoxylate: ethyl 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate
II. Esmolol: methyl (RS)-3-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl}propanoate
III. Loperamide: 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine
IV. Gabapentin: 5-ethyl-5-pentan-2-yl-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-diazinane-4,6-dione
a) I, II
b) II, III, IV
c) II , III
d) III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Mechlorethamine | A. Nitrogen mustard |
| ii. Diphenoxylate | B. Nitrosoureas alkylating agent |
| iii. Carmustine | C. Pyrimidine antagonist |
| iv. 5-FU | D. Antidiarrheal agent |
a) i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
b) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
c) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-a
3-d
4-a
5-d
6-a
7-d