FLUBIPROFEN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
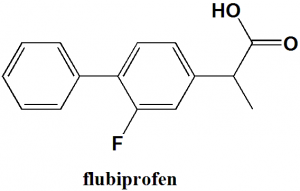
Flubiprofen
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-2-(2-fluorobiphenyl-4-yl)propanoic acid
Classification
- NSAID
- Propionic acid class
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 244.26 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 110.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 8 mg/ml |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.8 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Biphenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Flubiprofen reversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme. Due to this, the prostaglandin synthesis pathway is obstructed and the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin is reduced.
- The decrease in level of prostaglandin also decreases the transmission of impulses for inflammation, pain, swelling and fever.
- It inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of propionic acid derivatives can be summarized as follows:
- Anti-inflammatory activity of the drug can be increased by substitution of an α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
- Related side effects of the drug can be decreased by substitution of an α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
- (+)-enantiomer possess greater activity than (-)-enantiomer.[1]
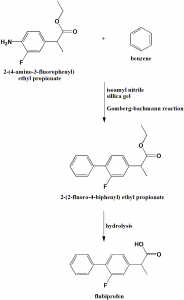
Method of synthesis
i. Coupling reaction between 2-(4-amino-3-fluorophneyl) ethyl propionate and benzene through Gomberg-bachmann reaction and taking isoamyl nitrile as diazotization reagent and silica gel as dehydrating agent to obtain 2-(2-fluoro-4-biphenyl) ethyl propionate.
ii. On hydrolysis of the last gives flubiprofen with 50% yield. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Flubiprofen is used for:
- Reducing pain and joint stiffness due to arthritis
- Used before eye surgery as it prevents pupil of eye from narrowing
Side Effects
Side effects of Flubiprofen are:
- Skin rash
- Changes in vision
- Shortness of breath
- Weight gain
- Swelling
- Stomach bleeding
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- Difficulty in urination
- Anemia
- Skin reactions
- Indigestion
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Tremors
- Stomach pain
- Confusion
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Sweating
- Ringing in ears
MCQs
Q.1 Mechanism of action of Flubiprofen is due to?
a) Reversibly inhibition of COX enzyme
b) Irreversibly inhibition of COX enzyme
c) Reversibly inhibition of Anticholinestrase
d) Irreversibly inhibition of Anticholinestrase
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug Flubiprofen is/are?
a) Reducing pain due to Rheumatoid arthritis
b) Treatment of vascular degeneration
c) As an anesthesia prior to dental surgery
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of Propionic acid NSAIDs?
I. Anti-inflammatory activity of the drug can be increased by substitution of an α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
II. Related side effects of the drug can be decreased by substitution of an α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
III. (+)-enantiomer possess greater activity than (-)-enantiomer
a) I, II, III
b) II
c) I, III
d) II, III
Q.4 Number of chiral centers present in the structure of Flubiprofen is?
a) 3
b) 5
c) 1
d) 4
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug Flubiprofen?
- Molecular weight: 150.3 gm/mol
- Physical appearance: Solid
- Melting point: 78-820C
- Octanol/water partition coefficient: 3.8
a) TFFT
b) FTTF
c) TTFF
d) FFFF
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drugs are?
I. Flubiprofen: (RS)-2-(2-fluorobiphenyl-4-yl)propanoic acid
II. Haloperidol: 4-[4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl]-1-(4-fluorophenyl)butan-1-one
III. 6-Mercaptopurine: 3,7-dihydropurine-6-thione
IV. Mechlorethamine: 2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
a) I, II
b) II, III, IV
c) I, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Flubiprofen | A. Barbiturate anticonvulsant |
| ii. Phenobarbital | B. NSAIDs |
| iii. Pyridostigmine | C. Benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic |
| iv. Lorazepam | D. Cholinestrase inhibitor |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
d) i-A, ii-B, iii-C, iv-D
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-a
4-c
5-b
6-d
7-b