Digestion and Absorption of Lipids and Proteins and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, SSC, Pharmacist exam
Proteins
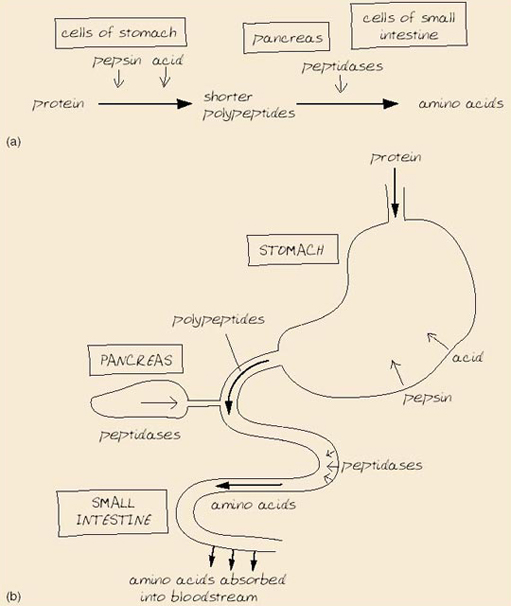
- Digestion of proteins:- digestion of proteins starts in the stomach where proteins undergo breakdown and forms peptides by the action of an enzyme called as pepsin. Digestion continues in small intestine where the enzymes of pancreatic juice like- trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase and elastase also converts the proteins into peptides but these enzymes differ in their function like trypsin, chymotrypsin and elastase breaks the peptide bond between amino acid and its neighbor amino acid while the carboxypeptidase splits the amino acid at the carboxyl end of peptide. Digestion of proteins is completed by two peptidases of brush border which are aminopeptidases and dipeptidases, where aminopeptidase splits the amino acid at the amino end of peptide and dipeptidase splits the dipeptide in each amino acid.
- Absorption of proteins:- most of the proteins are absorbed as amino acid through the active transport method that occurs in duodenum and jejunum. About 95-98% of amino acid in small intestine is digested and absorbed.
Different types of transporters carry different types of amino acid like some amino acids are transported by Na dependent secondary transport process and enters absorptive cells in the villi. Dipeptides and tripeptides are transported via secondary active transport with hydrogen ion. After this the amino acid move out of the absorptive cells and enter the blood capillary of the villus by diffusion. Amino acid is then transported in the blood to the liver through the hepatic portal system.
Lipids
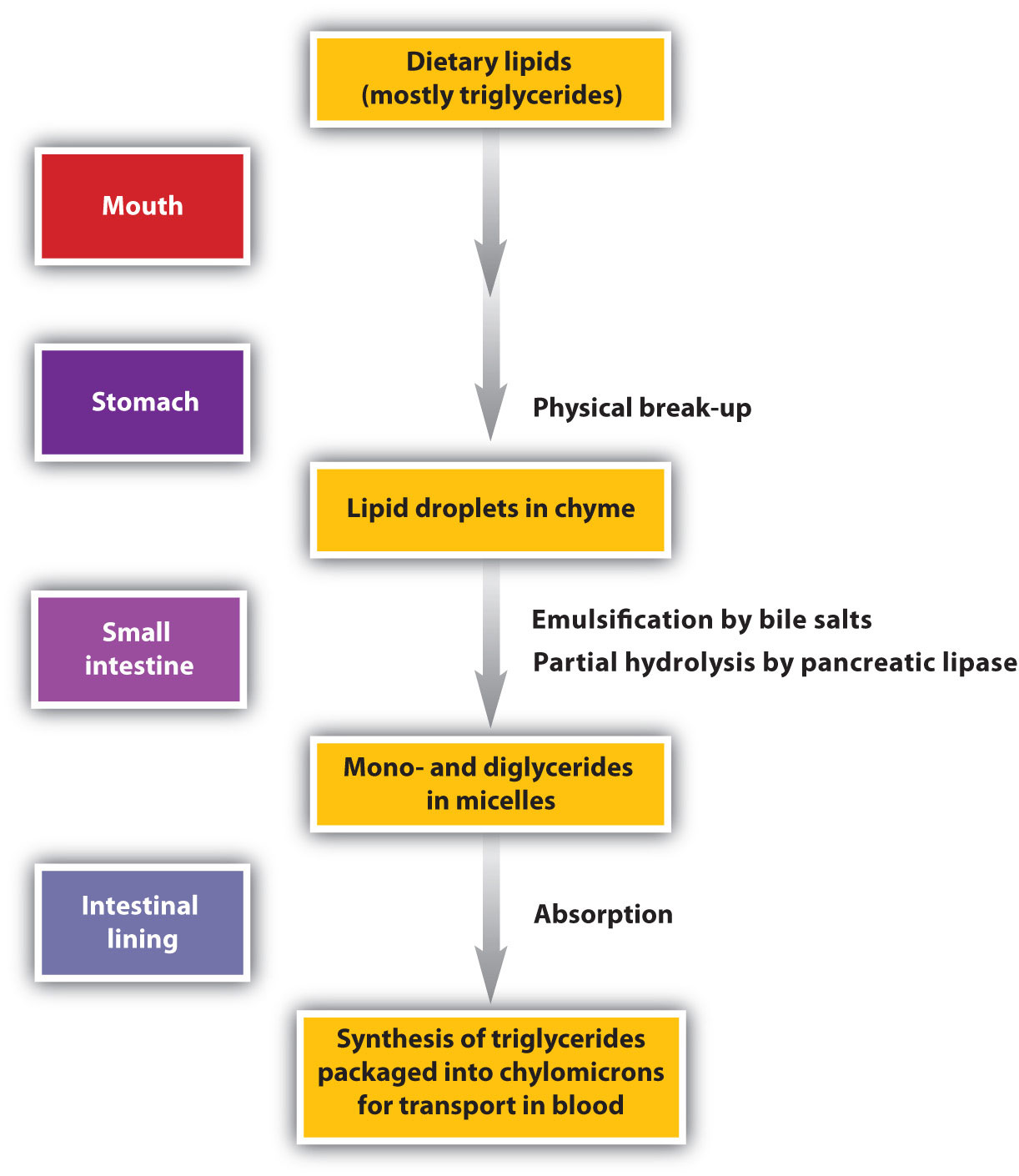
- Digestion of lipids:- the most found lipid in the food are the triglycerides, which consist of one glycerol molecule bonded with 3 fatty acid molecules. Enzymes that splits triglycerides and phospholipids are known as lipases. The lipases used in digestion process of lipids are lingual lipase, gastric lipase and pancreatic lipase. Some of the lipid is digested in stomach by the action of lingual and gastric lipase but the major portion of lipids are digested by pancreatic lipase in small intestine. The triglycerides undergo breakdown into monoglycerides and fatty acids, where fatty acids can either be short chain fatty acids or long chain fatty acids.
Before the large lipid molecule containing triglycerides are digested, the undergo emulsification- a process by which large lipid molecules splits into several small lipid molecules. Bile contains bile salts which are amphipathic in nature that is it has a hydrophobic nature as well as hydrophilic nature. The hydrophobic region binds with large lipid molecule while the hydrophilic region binds with the chyme. This results in breakdown of large lipid molecules in smaller one which makes digestion more effective.
- Absorption of lipids:- all the lipids produced from food are absorbed by simple diffusion. As the result of emulsification and digestion, the triglycerides splits into mono-glycerides and fatty acids in which fatty acids can either be short chain or long chain fatty acids. Short chain fatty acids are small in size because of which they easily enter the absorptive cells via simple diffusion n like amino acids then enter the blood capillary of the villus. But the long chain fatty acids and mono glycerides are large molecules and cannot be suspended and dissolved in chyme. The bile salts help these large molecule to increase their solubility in watery chyme and also help forming micelles which acts as a carrier. The micelles move out of the small intestine and reaches the absorptive cells and in this way mono glycerides and long chain fatty acids enters the absorptive cells. These molecules cannot directly enter the blood capillary because of their large size so they enter lymphatic vessels, reaches the thoracic duct and then through right subclavian vein enters into the blood.
Multiple choice question (MCQs)
1. Where do digestion of proteins takes place?
A. mouth B. stomach
C. small intestine D. stomach and small intestine
2. What is the function of aminopeptidase?
A. splits amino acids at amino end of peptide
B. splits in 2 amino acids
C. splits amino acid at the carboxyl end of peptide
D. break peptide bond between amino acid and its neighbor
3. Where do the digestion of lipids takes place?
A. small intestine B. stomach
C. small intestine mouth and stomach D. small intestine and stomach
4. which of the following enzymes participate in digestion of proteins?
A. trypsin B. chymotrypsin
C. elastase D. all of the above
5. Which of the following statement is true?
A. trypsin breaks peptide bond at carboxyl end
B. lipases include only pancreatic and lingual lipase
C. Bile salts are necessary of absorption of lipids
D. elastase enzyme is used for digestion of lipid
6. what helps the large molecules of lipids to increase their solubility in watery chyme?
A. bile salts B. fatty acids
C. micelles D. hydrophilic region
7. through which vein, the long chain fatty acids enters into the blood?
A. subclavian vein B. jugular vein
C. external carotid vein D. internal carotid vein
8. Match the following-
A. carboxypeptidase 1. breaks the peptide bond between amino acid and its neighbor
B. elastase 2. Break peptide bond at carboxyl end
C. dipeptidase 3. Breaks dipeptide in each amino acid
D. lipases 4. Used for digestion of lipid
9. what is emulsification?
A. small molecules of lipid combine to form large molecule
B. large molecule split into smaller molecules
C. it is a process which enhances solubility of lipid
D. none of the above
10. which method is used for the transport of amino acids?
A. simple diffusion B. facilitated diffusion
C. passive transport D. none of the above
ANSWERS:-
- stomach and small intestine
- splits amino acids at amino end of peptide
- small intestine, mouth and stomach
- all of the above
- Bile salts are necessary of absorption of lipids
- bile salts
- subclavian vein
- A – 1 B – 2 C – 3 D – 4
- large molecule split into smaller molecules
- none of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 954-958.