Atrophy: Definition, Causes, Pathogenesis, Symptoms and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
“Shrinkage in the size of the cell by loss of cell substance is known as atrophy.”
1.] It represents a form of adaptive response.
2.] When a sufficient number of cells are involved, the entire tissue or organ get diminished in size or become atrophic.

This image is taken for education purpose form medicalnewstoday.com
CAUSES OF ATROPHY: –
Following are some of the major causes of atrophy: –
- Decreased workload
- Loss of innervation
- Diminished blood supply
- Inadequate nutrition
- Loss of endocrine stimulation
- Aging
PATHOGENEIS OF ATROPHY: –
When a limb is immobilized in a plaster cast, or when muscles become paralyzed from loss of innervation as in poliomyelitis, atrophy of muscles ensues. In adult, the brain undergoes progressive atrophy, presumably as atherosclerosis narrows its blood supply, and the sex gland shrinks with depletion of endocrine stimulation. Some of these stimuli are physiologic like; the loss of endocrine stimulation following the menopause, whereas others are clearly pathologic like; loss of nerves.
Atrophic cells may have diminished function, they are not dead. Atrophy represents a reduction in the structural components of the cell. The cell contains fewer mitochondria and myofilaments and are lesser amount of endoplasmic reticulum. The biochemical mechanisms responsible for atrophy are incompletely understood, but there is a finely regulated balance between protein synthesis and degradation in normal cell and, either decreased synthesis or increased catabolism, or both may cause atrophy.
In many situations atrophy is also accompanied by marked increase in the number of autophagic vacuoles. The formation of autophagic vacuoles can be surprisingly rapid. For example, in experimental occlusion of portal venous blood supply to the liver lobe, large number of autophagic vacuole are formed within 5 to 10 minutes after the blood supply is occluded.
SYMPTOMS OF ATROPHY: –
Following are the symptoms of atrophy:
- Balance problem like difficulty in walking
- Difficulty in speech and swallowing of food
- Improper balance and coordination
- Memory loss
- Facial weakness
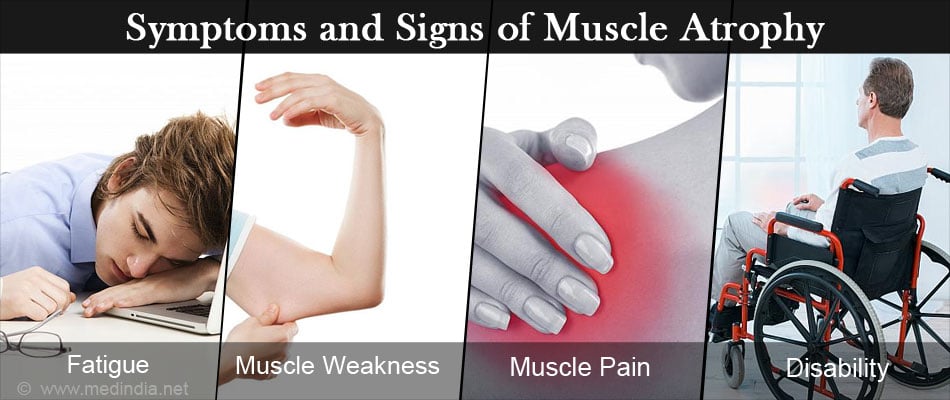
This image is taken for educational purpose from medindia.net
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: –
1.] Shrinkage in size of cell is called?
a. Atrophy
b. Apoptosis
c. Hypertrophy
d. All of the above
2.] Loss of substances from the cell is known as?
a. Apoptosis
b. Atrophy
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
3.] Atrophy is which type of response?
a. Adaptive response
b. Non adaptive response
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
4.] Which of the following are the causes of atrophy?
a. Ageing
b. Decreased workload
c. Loss of innervation
d. All of the above
5.] Loss of endocrine stimulation is an example of?
a. Atrophy
b. Apoptosis
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
6.] Diminished blood supply and inadequate nutrition are the causes of?
a. Apoptosis
b. Atrophy
c. Hypertrophy
d. All of the above
7.] In atrophy increase in the number of autophagic vacuoles occur. True or False
a. True
b. False
8.] Which of the following are the symptoms of atrophy?
a. Difficulty in speech
b. Difficulty in swallowing
c. Memory loss
d. All of the above
9.] Facial weakness is the feature of?
a. Atrophy
b. Hypertrophy
c. Metaplasia
d. None of the above
10.] Atrophy represents a reduction in the structural components of the cell. True or False?
a. True
b. False
SOLUTIONS: –
1.] (a) Atrophy
2.] (b) Atrophy
3.] (a) Adoptive response
4.] (d)
5.] (a) Atrophy
6.] (b) Atrophy
7.] (a)
8.] (d)
9.] (a) Atrophy
10.] (a)
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCES: –
1.] Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no.37 – 38.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no.47 – 48.