AZATADINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
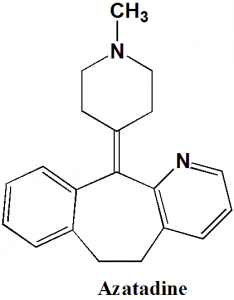
Azatadine
IUPAC nomenclature
11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine
Classification
- H1-receptor antihistamine
- Piperidine derivative antihistamine drug
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 290.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 152-154oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Very Soluble |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.59 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Piperidine ring |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Azatadine antagonizes the effect of histamine HA-receptors by competing with free histamine for binding at HA-receptor sites. This helps in reducing the negative symptoms occurring due to HA-receptor binding and tissue injury response involving histamine release.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of first generation H1-receptors antagonist can be summarized as:
- Ethylene chain gives maximum activity.
- Increasing or decreasing the chain length decreases the activity of drug, but promethazine is an exception.
- Chain may be present in saturated or unsaturated form, or sometimes a part of a ring system.
- Diaryl substitution is essential for significant H1 receptor affinity.
- Terminal nitrogen atom should be tertiary in nature.
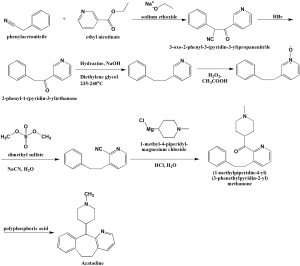
Method of synthesis
i. Phenylacetonitrile reacts with ethyl nicotinate in presence of sodium ethoxide to give 3-oxo-2-phenyl-3-(pyridin-3-yl)propanenitrile.
ii. The reaction of the last with hydrogen bromide produces 2-phenyl-1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethanone.
iii. The above formed compound is reacted with hydrazine in presence of sodium hydroxide in diethylene glycol to get 2-phenethylpyridine.
iv. On treatment of last with hydrogen peroxide in acetic acid produces an intermediate which on reaction with dimethyl sulfate followed by sodium cyanide in water gives 3-phenethylpyridine-2-carbonitrile.
v. The above formed compound is reacted with 1-methyl-4-piperidyl-magnesium chloride in aqueous hydrochloric solution to give (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) (3-phenethylpyridin-2-yl) methanone.
vi. Azatadine is produced by reacting last with phosphoric acid. [1]
Medicinal Uses
Azatadine is used for treatment of:
- Itching
- Hives
- Runny nose
- Rashes
- Watery eyes
- Relief of upper respiratory mucosal congestion
- Relief of nasal congestion
- Relief of Eustachian t.b. congestion
Side Effects
Side effects of Azatadine are:
- Dizziness
- Sleepiness
- Fatigue
- Dry mouth
- Difficulty in urination
- Enlarged prostate
MCQs
Q.1 Correct statements from the following related with the physicochemical properties of drug Azatadine are?
I. Molecular weight: 350.2 gm/mol
II. Appearance: Solid
III. Melting Point: 105.5oC
IV. Solubility: Very soluble
a) I, II, IV
b) I, III, IV
c) II, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Azatadine | A. (RS)-6-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzo[d]imidazole |
| ii. Dimethindene | B. N,N-Dimethyl-2-[3-(1-pyridin-2-ylethyl)-1H-inden-2-yl]ethan-1-amine |
| iii. Famotidine | C. 3-[({2-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}methyl)sulfanyl]-N-sulfamoylpropanimidamide |
| iv. Pentoprazole | D. 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine |
a) i-D, ii-B, iii-C, iv-A
b) i-A, ii-B, iii-D, iv-C
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
d) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
Q.3 Mechanism of action of drug azatadine involves?
I. Competes for histamine at HA-receptor
II. Blocks α-adrenoceptors
III. Alkylation of DNA
a) I, III
b) I, IV
c) I, II, III
d) I
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Azatadine: H1-receptor antihistamine drug
- Enflurane: Inhalational anesthetics
- Tripelenamine: Narcotic analgesic
- Dexamethasone: Sedative-hypnotics
a) TFTF
b) TTFF
c) FFTF
d) TFFT
Q.5 Terminal nitrogen in the structure of first generation H1-receptor antagonist should be in which form?
a) Primary
b) Secondary
c) Tertiary
d) Quaternary
Q.6 Type of rings present in the structure of Azatadine?
I. Pyridine
II. Piperazine
III. Piperidine
IV. Benzodiazepine
a) I, IV
b) I
c) II, III
d) II
Q.7 Side effect of drug Azatadine is/are?
a) Difficulty urination
b) Sleepiness
c) Enlarged prostate
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-c
2-a
3-d
4-b
5-c
6-d
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] US 3 301 863 (Schering Corp.; 31.1.1967; prior. 24.4.1963, 13.12.1963, 21.12.1964,18.3.1965).