CARVEDILOL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Carvedilol
IUPAC nomenclature
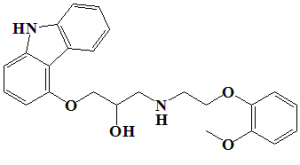
(±)-[3-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-2-hydroxypropyl][2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amine
Classification
Carvedilol is a mixed α/ß blocker.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 406.5 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid; forms colorless crystals from ethyl acetate |
| 3 | Melting point | 114.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Practically insoluble in water; freely soluble in dimethylsulfoxide; soluble in methylene chloride, methanol. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.8 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Carbazol |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Carvedilol inhibits ß-adrenoceptors which results in inhibition of the exercise induce tachycardia.
- Smooth muscles in vasculature relaxes due to the action of carvadilol on α1-adrenergic receptors, which further results in reduced peripheral vascular resistance and an overall reduction in blood pressure.
- Calcium channel blocking and antioxidant activity can also be seen at higher doses of the drug.
- The antioxidant activity of drug prevents oxidation of low density lipoprotein and thus, prevents the uptake of same into coronary circulation. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- The type of N-substitutions such as N-isopropyl and N-t-butyl eliminates α1-activity.
- Arylalkyl groups with α-methyl substituent returns back the α1-affinity but not the intrinsic activity.
- The ß-blocking activity is almost 10-100 that of its α1-blocking activity. [2]
Method of synthesis
i. Condensation of 4-hydroxycarbazole with epichlorohydrin produces 4-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)carbazole.
ii. The latter compound is then reacted with 2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethanamine to produce carvedilol.[3]
Therapeutic Uses
Carvedilol is used for treatment of:
- Hypertension
- Prevention of strokes
- Prevention of heart attacks
- Prevention of kidney problems
Side Effects
Side effects of carvedilol are:
- Dizziness
- Tiredness
- Impotency
- Diarrhea
- Drowsiness
- Lightheadedness
MCQs
Q.1 Carvedilol inhibits exercise induce tachycardia through?
a) Agonism of α1-adrenergic receptors
b) Agonism of α2-adrenergic receptors
c) Antagonism of ß-adrenergic receptors
d) α-adrenergic antagonism
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug Carvedilol is/are?
a) Glaucoma
b) Hypertension
c) Diabetes
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of drug Carvedilol-
I. The type of N-substitutions such as N-isopropyl and N-t-butyl eliminates α1-activity.
II. Arylalkyl groups with α-methyl substituent returns back the α¬1-affinity but not the intrinsic activity.
III. The ß-blocking activity is almost 1.5-folds that of its α1-blocking activity.
a) I, II
b) I, III
c) I, II, III
d) II
Q.4 The starting chemicals required for the synthesis of drug Carvedilol?
a) 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl-ethanol) and benzyl halide
b) Benzyl halide and epoxide
c) 4-hydroxycarbazol and epichlorohydrin
d) None of the above
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug betaxolol-
I. Molecular weight = 307.4 gm/mol.
II. Melting point = 114.5°C
III. Octanol/water partition coefficient = 3.8
a) TFT
b) FFT
c) TTT
d) FTT
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drugs are?
I. Betaxolol: (RS)-1-{4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]-phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol
II. Carvedilol: (RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol
III. Bisoprolol: (±)-[3-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-2-hydroxypropyl][2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amine
IV. Propranolol: (RS)-1-(1-methylethylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol.
a) I, II, IV
b) I, IV
c) III, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Betaxolol | A. ß1-ADRENERGIC AGONIST |
| ii. Carvedilol | B. MIXED ACTING SYMPATHOMIMETICS |
| iii. Epinephrine | C. MIXED α/ß BLOCKER |
| iv. Amphetamine | D. NONSELECTIVE ADRENERGIC AGONISTS |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-B, iii-C, iv-A
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
FREE GPAT online Test: Participate: Click Here
ANSWERS
1-c
2-b
3-a
4-c
5-d
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Ruffolo RR, Gellai M, Hieble JP, Willette RN, Nichols AJ. The pharmacology of carvedilol. European journal of clinical pharmacology. 1990 Mar 1;38(2):S82-8. [2] Lemke TL, Williams DA, Foye WO. Principles of medicinal chemistry. Williams & Wilkins; 2017, 361 [3] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of best-seller drugs. Academic press; 2016 Jan 7.