Catabolism of Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleotide and MCQs for GPAT, NEET UPSC, Pharmacist, CSIR NET and Nursing Exam
Catabolism of purine nucleotide
The end product of catabolism of purine is uric acid. Mammals oxidize the uric acid to allantoin, which further get converted into urea and then ammonia.
Reactions of catabolism of purine nucleotide
- Firstly the phosphate group is removed to form nucleoside adenosine or guanosine by action of nucleotidase enzyme
- Adenosine is then deaminated to inosine by adenosine deaminase
- Inosine is then hydrolyzed to a purine base hypoxanthine and ribose-1-phosphate
- Hypoxanthine is oxidized to xanthine which is further converted into uric acid.
- Breakdown of guanosine yields guanine and ribose-1-phosphate
- Guanine undergoes guanine undergoes hydrolytic removal of its amino acid and yields xanthine which in turn is converted to uric acid.

This picture is taken only for educational purpose from www.researchgate.net
Catabolism of pyrimidine nucleotides
The end products of catabolism of pyrimidine nucleotide are water soluble compounds like:
- CO2
- NH3
- Beta-alanine
- Beta-amino-iso-butyrate
In human beings, beta-amino-iso-butyrate is trans-aminated to methylmalonate semialdehyde which is further converted to succinyl-CoA .
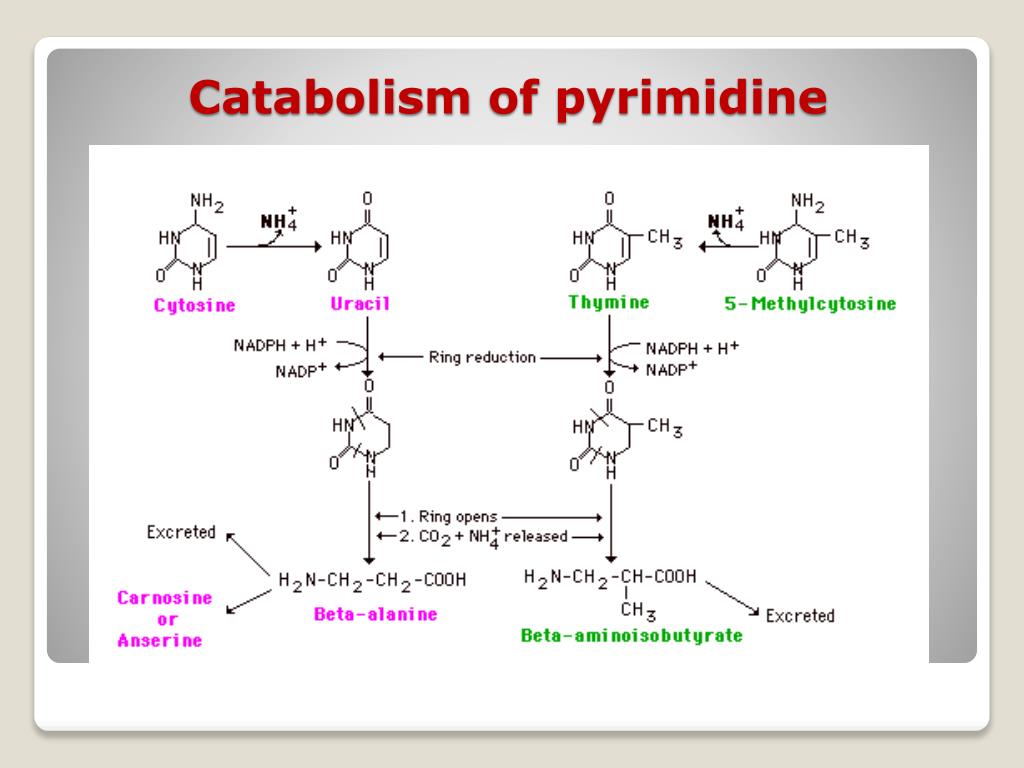 This picture is taken only for educational purpose from image1.slideserve.com
This picture is taken only for educational purpose from image1.slideserve.com
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What is the catabolic end product of purine nucleotide?
A. Uric acid
B. NH3
C. CO2
D. Both B and C
2. What is the catabolic end product of pyrimidine nucleotide?
A. Uric acid
B. NH3
C. CO2
D. Both B and C
3. In which animal, uric acid is further converted into allantoin?
A. Whales
B. Lions
C. Giraffe
D. Zebra
4. Which enzyme catalyzes the deamination of adenosine to inosine?
A. Adenosine synthase
B. Adenosine deaminase
C. Inosine synthase
D. Inosine synthetase
5. Which of the following is the not the end product of pyrimidine nucleotide?
A. Urea
B. CO
C. Alpha-aminoisobutyrate
D. All of the above
6. Which of the following serve as precursor of acetyl-CoA?
A. NH3
B. Urea
C. Uric acid
B. Beta alanine
7. Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of xanthine oxidase?
A. Deaminase
B. Transaminase
C. Guanase
D. Xanthine synthase
8. Match the following-
A. Adenosine 1. Hypoxanthine
B. Methylmalonate semialdehyde 2. Xanthine
C. Guanine 3. Succinyl-CoA
D. Inosine 4. Inosine
9. Which out of uric acid and ammonia is more soluble in water?
A. Uric acid
B. Ammonia
C. Both
D. None
10. What is the product of the breakdown of guanosine by phosphorylase enzyme along with guanine?
A. Ribose-5-phosphate
B. Xylulose-5-phosphate
C. Ribose-1- phosphate
D. Both B and C
11. Which enzyme removes the phosphate group of nucleotide?
A. Nucleotide transferase
B. Nucleoside synthetase
C. Lyase
D. none of the above
12. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. Uric acid works as potent anti-oxidant
B. Human enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of pseudouridine
C. Transamination of beta-isobutyrate form methylmalonate semialdehyde
D. End product of pyrimidine catabolism are highly water soluble
13. In the 4th reaction of Catabolism of purine nucleotide, the molecular oxygen is converted to which compound?
A. water
B. CO2
C. H2O2
D. All of the above
ANSWERS-
1. Uric acid
2. Both B and C
3. Whales
4. Adenosine deaminase
5. All of the above
6. Beta alanine
7. Guanase
8. A – 4 B – 3 C – 2 D – 1
9. Ammonia
10. Ribose-1-phosphate
11. None of the above
12. Human enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of pseudouridine
13. H2O2
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- 1. Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 331-333
2. U Satyanarayana, U Chakrapani- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no