DNA Structure and Functions and MCQs for GPAT, NEET, GATE and CSIR NET, Pharmacist, Nursing Exams
DNA serves as a genetic material for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotes, the DNA is present in the nucleus while in prokaryotic cells, it is present with all other cellular contents. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is bound to the protein and forms a complex structure known as chromatin. Small amount of DNA is also present in mitochondria and in chloroplast of plants.
Structure of DNA is of two types:
- The primary structure of DNA:- DNA is a long, thread like macromolecule and is made up of large no. deoxyribonucleotide. Each deoxyribonucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, sugar and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine.
In DNA, the C-1carbon atom of deoxyribose is bonded to N-1 of pyrimidine or N-9 of purine by N-glycosidic bonds. The precise sequence of bases carries the genetic information.
- The secondary structure of DNA:- In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick gave a 3-D model of DNA which has following characteristics:
- It consist of two helical DNA strands wound around the same axis
- The hydrophilic backbones of alternating deoxyribose and phosphate group are on the outside of double helix
- Each nucleotide base of 1 strand is paired with the base of another strand in which adenine bonds to thymine and guanine bonds to cytosine. Adenine is bounded to thymine by 2 hydrogen bonds and guanine is bounded to cytosine by 3 hydrogen bonds.
- The two strands of DNA are anti-parallel and their 3’-5’ phosphodiester bonds runs in opposite direction
- The two anti-parallel polynucleotide chains are not identical in either base sequence or composition; rather they are complementary to each other.
- The DNA double helix is held together by two forces: hydrogen bonds and base stacking interactions
- The Watson-Crick structure is also known as B-form DNA is the most stable structure of DNA
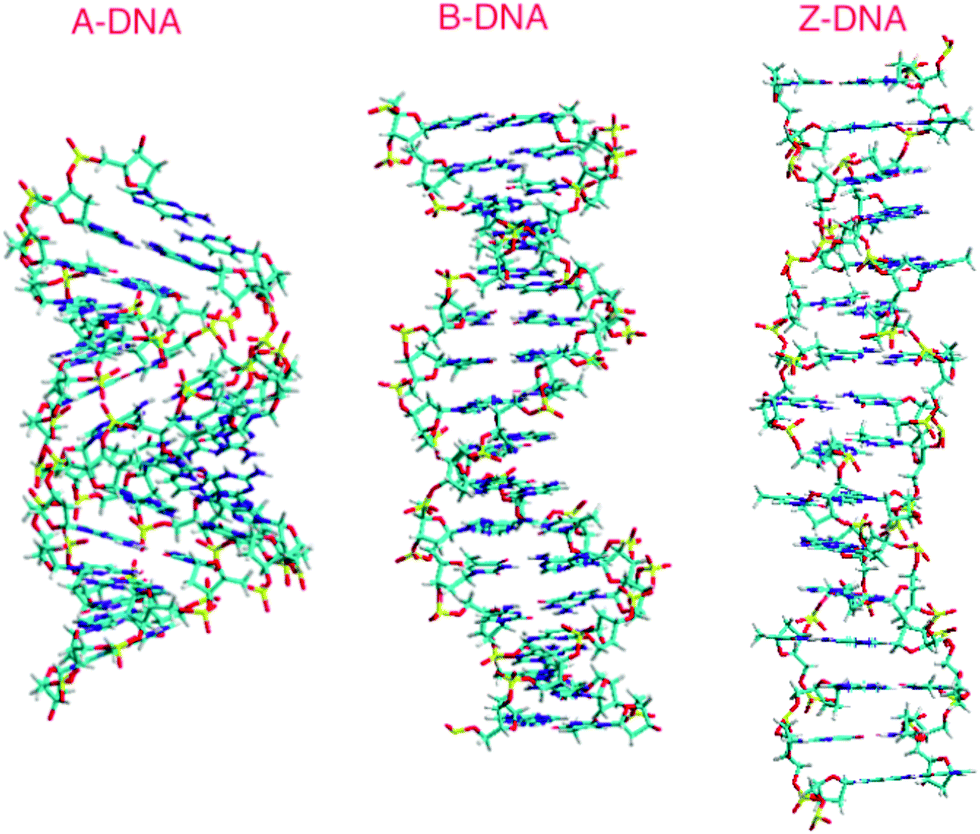
Different structural forms of DNA:
DNA can exist in 3 forms:
- A-DNA
- B-DNA
- Z-DNA
 THIS PICTURE IS TAKEN ONLY FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSE FROM pubs.rsc.org
THIS PICTURE IS TAKEN ONLY FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSE FROM pubs.rsc.org
All the 3 forms have some characteristic features like-
- In all 3 forms, two anti-parallel chains are held together by base pairs
- A-DNA and B-DNA are right handed
- In B-DNA, base pairs are perpendicular to the helix axis
- In A-DNA, base pairs are tilted 20ͦ degree and not perpendicular
- A-DNA is wider and shorter than B-DNA
- Z-DNA is left handed
Functions of DNA
DNA is the store of genetic information. The genetic info stored in the DNA has two functions:
- Source of info for protein synthesis
- It provides info inherited by daughter cells
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. DNA serves as a genetic material for which type of cell?
A. Prokaryotes
B. Eukaryotes
C. Both
D. None
2. Where is DNA present in the eukaryotic cells?
A. Inside the nucleus
B. With other cellular contents
C. Inside the ribosomes
D. Not present
3. In which year, the 3-D structure of DNA was introduced?
A. 1882
B. 1953
C. 1997
D. 2000
4. Which of the following nitrogenous base is not present in DNA?
A. Thymine
B. Adenine
C. Guanine
D. Uracil
5. Which type of bonding is present between the N-1 of pyridine and deoxyribose of DNA?
A. Covalent bond
B. Hydrogen bond
C. N-glycosidic bond
D. Sometimes B and sometimes C
6. How many forms of DNA are present?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 1
7. In which form of DNA, two anti-parallel chains are held together by base pairs?
A. A-DNA
B. B-DNA
C. Z-DNA
D. All of the above
8. Match the following-
A. A-DNA 1. Cytosine
B. Z-DNA 2. Thymine
C. Adenine 3. Left handed
D. Guanine 4. Right handed
9. DNA is bound to which bio-molecule to form complex structure known as chromatin?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Lipids
C. Vitamins
D. None of the above
10. Which carbon atom is bonded to N-9 of purine?
A. C-1
B. C-2
C. C-3
D. Both B and C
11. How many hydrogen bonds are required to form bonding between adenine and thymine?
A. Thousands
B. 1
C. 2
D. Not fixed
12. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. A-DNA is wider and longer than B-DNA
B. Two strands of DNA are anti-parallel
C. DNA double helix is held together by two forces
D. Sequence of bases carries the genetic info
13. How are the two helical strand wounded?
A. Around the opposite axis
B. Around the same axis
C. One above another
D. None of the above
14. Which of the following is the function of DNA?
A. Source of info for lipid metabolism
B. Source of info for carbohydrate metabolism
C. Source of info for protein synthesis
D. All of the above
ANSWERS
1. Both
2. Inside the nucleus
3. 1953
4. Uracil
5. N-Glycosidic bond
6. 3
7. All of the above
8. A – 4 B – 3 C – 2 D – 1
9. None of the above
10. C-1
11. 2
12. A-DNA is wider and longer than B-DNA
13. Around the same axis
14. Source of info for protein synthesis
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- 1. Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 130-133