ETODOLAC Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
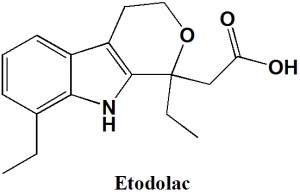
Etodolac
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-2-(1,8-Diethyl-4,9-dihydro-3H-pyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetic acid
Classification
- NSAID
- Pyranocarboxylic acid
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 287.35 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 146.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 16 mg/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.5 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Indole, pyran |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Etodolac inhibits COX enzyme by binding with the upper portion of the COX enzyme active site and prevents arachidonic acid by binding with the active site.
- Etodolac is 5-50 times more selective for COX-2 than COX-1.
- It also produces central action on the hypothalamus and produces antipyresis effects, which results in peripheral dilation, increased cutaneous blood flow and subsequent heat loss.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of class Pyranocarboxylic acid can be summarized as follows:
- Substitution on the pyran ring with R1 as an alkyl group and R2 as an acetic acid function increases the anti-inflammatory activity.
- On increasing the length of the acid chain, or ester or amide derivatives inactivates the drug.
- Α-methylacetic acid derivatives are also found to be inactive compounds.
- Substitution of R1 as ethyl or n-propyl gives the compounds 20 times more active than methyl. Substitution on the 8th position of the aromatic ring is most beneficial.
- Most active compounds of this class were found to be 8-ethyl, 8-n-propyl, and 7-fluoro-8-methyl derivatives. [1]
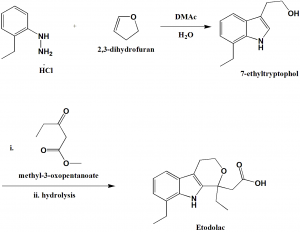
Method of synthesis
i. To the solution of 2-ethyl phenyl hydrazine hydrochloride in DMAc-H2O; 2,3-dihydrofuran is added drop-wise and heated to get 7-ethyl tryptophol.
ii. 7-ethyltryptophol is reacted with methyl-3-oxopentanoate followed by hydrolysis to give etodolac.[2]
Therapeutic Uses
Etodolac is used for:
- Management of mild to moderate pain
- Treatment of osteoarthritis
- Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Side Effects
Side effects of Etodolac are:
- Allergic reactions
- Skin reactions
- Signs of heart attack or stroke
- Chest pain
- Numbness
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling of legs
- Slurred speech
- Vision changes
- Rapid weight gain
- Stomach bleeding
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- No urination
- Anemia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Indigestion
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Ringing sounds in ears
MCQs
Q.1 Which statements are correct with respect to the physicochemical properties of drug etodolac?
I. Molecular weight:287.35 gm/mol
II. Appearance: It is solid
III. Melting point: 146.5oC
a) I, II
b) II, III
c) I, II, III
d) I, III
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Etodolac | A. ethyl 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate |
| ii. Pentazocine | B. (5α,6α)-7,8-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-ol |
| iii. Diphenoxylate | C. (RS)-2-(1,8-Diethyl-4,9-dihydro-3H-pyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)acetic acid |
| iv. Codeine | D. 2-dimethylallyl-5,9-dimethyl-2′-hydroxybenzomorphan |
a) i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
c) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
Q.3 Mechanism of action of etodolac includes?
I. Antipyresis effects due to action on hypothalamus
II. Inhibition of COX-1 enzyme
III. Inhibition of COX-2 enzyme
IV. Reducing the level of Ach synaptic junction
a) II, IV
b) I, II, III
c) I, IV
d) II, III, IV
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Etodolac: NSAID
- Prednisolone: Antibiotics
- Anastrozole: 5-α reductase inhibitor
- DTIC: Triazine alkylating agent
a) TFFT
b) FTFT
c) FFTF
d) TTTT
Q.5 Most active compound of class Pyranocarboxylic acid derivative NSAIDs was found to be?
a) 7-fluoro-8-methyl derivatives
b) 8-butyl derivatives
c) 2-methyl derivatives
d) All of the above have same activitiesolac can synthesized from 7-ethyltryptophol through the steps-
I. ydrolysis
II. Reaction with methyl-3-oxopentanoate
III. Reduction
IV. Decarboxylation
a) II – III – I
b) II – IV – I
c) IV – I – II
d) II – I
Q.7 Side effect of drug Etodolac?
a) Allergic reactions
b) Shortness of breath
c) Stomach bleeding
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-a
3-b
4-a
5-a
6-d
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, Roche VF, Zito SW. FOYE. S Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Seventh Edition Copyright. 2013. [2] Patel VR and Desai HT. A optimized process for the synthesis of a key starting materialfor etodolac, a non steroidal anti- inflammatory drug. IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry. Vol. 4 (5), 2013, pp. 3-5