Factors Affecting the Velocity of Enzymatic Reactions and MCQs for UGC NET, NIPER JEE, NEET, GPAT, NORCET
The rate of enzymatic reactions depends on:
- Substrate concentration
- Enzyme concentration
- Effect of Ph
- Effect of temp
- Time
- Activators: it refers to the one that activates the enzymatic reaction. So activators are directly proportional to rate enzymatic reactions
- Inhibitors:– these are the compound that alter the enzyme activity. Hence are inversely proportional to rate of reaction
- Environment:- it includes all the physical factors like light, rays etc.
Substrate concentration
For a given quantity of enzyme, the rate of reaction increases as the concentration of the substrate is increased. At first this relationship is almost linear, but later the reaction curve becomes hyperbolic in shape because of two reasons:
- In the initial phase, for a constant enzymatic concentration, the rate of reaction is directly proportional to the substrate concentration [S]. and follows first order kinetics.
- In the second phase, the activity remains constant because there are no more enzyme molecules , and all the active site are occupied by the substrate molecules. This is called zero order kinetics.
The below curve describes these two points more convincingly.

Enzyme concentration
The rate of reaction is directly proportional to the enzyme reaction as long as [S] is not limiting. The [S] is should be sufficient enough to bound to active site of all the enzyme molecules. The below curve describes more convincingly.

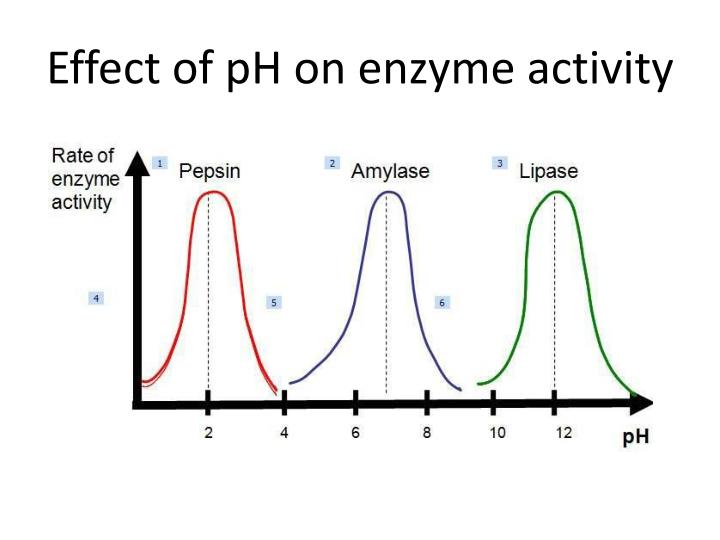
Effect of hydrogen ion concentration (Ph)
Each enzyme has its own Ph at which it works. Below or above this, the enzymatic activity is decreased. for eg: Ph for pepsin is 1.2, for trypsin is 8.0. A bell-shaped curve is obtained on potting enzyme activity against Ph.
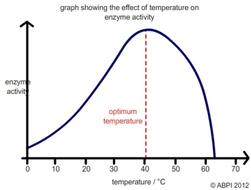
Temperature
Rate of enzymatic reaction increases with an increase in the temperature, only for a narrow small range of temp. Each enzyme performs its best activity at a particular temp known as optimum temp. the enzyme activity decreases both above and below this temp. Increase in the velocity is due to the increase in the kinetic energy to pass over the energy barrier and forms the product. Any further increase in the temp will now decrease the rate of reaction as a result of temp induced denaturation of enzyme protein.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. On which of the following factors, do rate of enzymatic reaction depends?
A. Temperature
B. Ph
C. Time
D. All of the above
2. When we discuss the relation between rate of reaction and [S], what should we do about the enzyme concentration?
A. Remains constant
B. Should increase rapidly
C. Should decrease rapidly
D. No effect
3. What is optimum Ph for pepsin?
A. 1.4
B. 3.2
C. 1.2
D. 4
4. Which of the following factor when plotted against rate of reaction will form a straight line?
A. [S]
B. Enzyme concentration
C. Ph
D. All of the above
5. What is the effect of temperature on rate of reaction?
A. Increases till optimum temp and then decrease
B. Decreases
C. Increases
D. No effect on rate of reaction
6. What is the effect of activators on rate of reaction?
A. Increases rate of reaction
B. Decreases rate of reaction
C. Both
D. None
7. Which of the following factor is always inversely proportional to the rate of enzymatic reaction?
A. [S]
B. Enzyme concentration
C. Ph
D. Inhibitors
8. Match the following-
a. Temp 1. Always directly proportional
b. Ph 2. Always inversely proportional
c. Inhibitors 3. Bell shaped curve
d. Activators 4. Hyperbolic shaped curve
9. What is the optimum Ph for trypsin?
A. 1.2
B. 7
C. 3.4
D. None of the above
10. When all the E form of enzyme Is converted to ES form, which type reaction it is called?
A. First order kinetics
B. Zero order kinetics
C. Second order kinetics
D. Both A and B
11. What is the shape of the curve obtained on plotting rate of enzymatic activity against [S]?
A. Straight line
B. Hyperbolic shape
C. Both
D. None
12. What is the reaction called if the enzymatic activity is directly proportional to [S]?
A. First order kinetics
B. Zero order kinetics
C. Second order kinetics
D. Both A and B
13. The inactivity of which factor is reversible and can be reversed back to normal?
A. High Ph
B. Low Ph
C. Low temp
D. High temp
14. What is the shape of curve on plotting enzymatic activity against Ph?
A. Bell-shaped
B. Hyperbolic
C. Linear
D. None of the above
ANSWERS:-
1. All of the above
2. Remains constant
3. 1.2
4. Enzyme concentration
5. Increases till optimum temp and then decrease
6. Increases rate of reaction
7. Inhibitors
8. a – 4 b – 3 c – 2 d – 1
9. None of the above
10. Zero order kinetics
11. Both
12. First order kinetics
13. Low temp
14. Bell-shaped
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 90,91.