FELBAMATE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
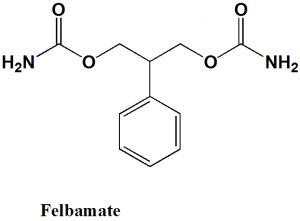
Felbamate
IUPAC nomenclature
(3-carbamoyloxy-2-phenylpropyl) carbamate
Classification
Felbamate is a carbamate derivative anticonvulsant drug.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 238.24 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 152°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water, methanol, ethanol, chloroform. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.3 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl ring |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Felbamate is an antagonist at the strychnine-insensitive glycine-recognition site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-ionophore complex.
- Antagonsim of the NMDA receptor glycine binding site blocks the effects of the excitory amino acids and suppress seizure activity.
- Felbamate may increase the seizure threshold and may decrease the spread of seizure.
- Felbamate also have weak inhibitory effects on GABA-receptor binding, benzodiazepine receptor binding.
Structure Activity Relationship
- If the volume of the substituents is too high, then the interaction with the receptor site will not be effective.
- If the volume of the substituent is too low, then it may not contact with all the regions of the receptors.
- The C-2 – O-4 bond length also affects the docking of the molecule at the particular site.
- Reduction in dipole moment of the drug increases the bioactivity.
- A small negative charge on the nitrogen atom is crucial for positive biological effect. [1]
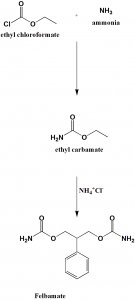
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of ethylchoroformate with ammonia to form ethyl carbamate.
ii. Ethyl carbamate undergoes reaction with quaternary ammonium salt to produce felbamate.
Therapeutic Uses
Felbamate is used for:
- Treatment of seizures
Side Effects
Side effects of Felbamate are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Constipation
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Mood changes
MCQs
Q.1 Choose the correct option related with the mechanism of action of drug Felbamate?
a) Antagonsim of the NMDA receptor glycine binding site blocks the effects of the excitory amino acids and suppresses seizure activity
b) Always decreases the seizure threshold
c) Always increases the spread of seizures
d) All of the above
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug Felbamate is/are?
a) Prevention of seizures
b) Prevention of Diarrhea
c) Prevention of Hypertension
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of drug Felbamate?
I. If the volume of the substituents is too high, then the interaction with the receptor site will be effective.
II. If the volume of the substituent is too low, then it may not contact with all the regions of the receptors.
III. The C-2 – O-4 bond length does not the docking of the molecule at the particular site.
IV. Reduction in dipole moment of the drug increases the bioactivity.
a) I, IV
b) II, III
c) II, IV
d) I, III
Q.4 Ethyl carbamate can be converted into felbamate by reaction with?
a) Quarternary ammonium salt
b) Potassium cyanide
c) Potassium cyanate
d) Ethylchloroformate
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug Felbamate is?
- Molecular weight = 122.24 gm/mol
- Melting point = 140.2oC
- White powder
- Ring structure absent
a) FFTF
b) TFFT
c) FTTF
d) TFFF
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drug are?
I. Felbamate: 5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide.
II. Gabapentin: 1-(Aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid
III. Loxapine: 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine
IV. Secobarbital: 5-ethyl-5-pentan-2-yl-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-diazinane-4,6-dione
a) I, II
b) II, IV
c) II , III
d) III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Felbamate | A. Carbamate derivative anticonvulsant drug |
| ii. Mtx | B. Vinca alkaloids |
| iii. Vinblastin | C. Ethylenimine |
| iv. Thiotepa | D. Folate antagonist |
a) i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
b) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
c) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-c
4-a
5-a
6-c
7-d