Goiter : Definition, Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Treatment And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
”The term goiter is defined as thyroid enlargement caused by compensatory hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the follicular epithelium in response of thyroid hormone deficiency.”
1.] There are two distinguished morphologic forms of goiter :
- Diffuse goiter (simple non – toxic or colloid goiter).
- Nodular goiter (multinodular goiter or adenomatous goiter).
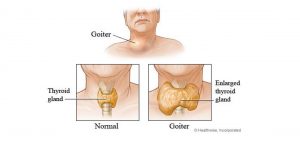
The above image is taken for education purpose only from bcm.edu
PATHOGENESIS :-
In the pathogenesis of both the forms of goiter is generally regarded as the end – stage of long – standing simple goiter. The fundamental defect in the production of thyroid hormone due to many etiologic factor, but most commonly is the dietary lack of iodine. Deficient thyroid hormone production causes excessive TSH stimulation which will lead to hyperplasia. Cyclical hyperplastic stage followed by involution stage completes the picture of simple goiter. Repeated and prolonged changes of hyperplasia result in continued growth of thyroid tissue while the involuted areas undergoes fibrosis, thus completing the picture of nodular goiter.
SYMPTOMS :-
The signs and symptoms of goiter include following :
- Swelling at the base of neck
- Harsh, raspy or strained voice (Hoarseness)
- Breathing difficulty
- Difficulty in swallowing of food due to swelling in the neck
- Coughing
TREATMENT :-
- In case of hyperthyroidism levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Synthroid, Tirosint) can be used to decrease the size of goiter.
- In case if we have inflammation, aspirin or corticosteroids are used to decrease the inflammation caused due to the goiter.
- Radioactive Iodine is also used in case if you have overactive thyroid gland, as it also helps to reduce the goiter or helps to decrease the size of the goiter.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :-
1.] Plunging goiter is ?
a. Solitary nodule
b. Colloid goiter
c. Retro – sternal goiter
d. Medullary Ca
2.] Name a disease cause by the deficiency of iodine ?
a. Thyroid cancer
b. Solitary thyroid nodule
c. Goiter
d. Thyroiditis
3.] Exopthalmic goiter is due to ?
a. Hyposecretion of thyrocalcitonin
b. Hyposecretion of thyroxine
c. Hypersecretion of thyrocalcitonin
d. Hypersecretion of thyroxine
4.] An abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland is called goiter ?
a. True
b. False
5.] Which of the following is the main cause of goiter ?
a. Hypothyroidism
b. Hyperthyroidism
c. Cancer of thyroid gland
d. All of the above
6.] Which of the following statement is incorrect about thyroid hormone ?
a. Regulates BMR
b. Maintain water and electrolyte balance
c. Supports erythropoesis
d. Control blood phosphate level
7.] Which of the following disease is not related to thyroid gland ?
a. Myxoedema
b. Cretinism
c. Acromegaly
d. Goiter
8.] Endemic goiter is a state of ?
a. Increased thyroid function
b. Decreased thyroid function
c. Moderate thyroid function
d. Normal thyroid function
9.] Enlargement of thyroid is called ?
a. Diabetes
b. Goiter
c. Cretinism
d. Myxoedema
10.] A person with the enlarged thyroid gland protruded eyeball, increased BMR and weight loss is suffering from ?
a. Grave’s disease
b. Exopthalmic goiter
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. Addison disease
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (c) Retro – sternal goiter
2.] (c) Goiter
3.] (c) Hypersecretion of thyrocalcitonin
4.] (a)
5.] (d)
6.] (b) Maintain water and electrolyte balance
7.] (c) Acromegaly
8.] (b) Decreased thyroid function
9.] (b) Goiter
10.] (c)
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 797 – 800.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no. 1131 – 1133.