Introduction to Protein Metabolism: Digestion and Absorption and MCQs for GPAT, NEET, CSIR NET, SSC
Proteins are the structural and functional constituent of the body. Regular supply of dietary proteins is essential for the cell integrity and its functions. dietary proteins produce nitrogen which metabolized by the body
Digestion of proteins
Proteolytic enzymes which are produced by the stomach, small intestine and pancreas perform the breakdown of proteins into its amino acids. Digestion in mouth of proteins does not occur, protein digestion starts from stomach
1. Digestion in stomach
In stomach, the protein diet stimulate the secretion of gastrin. The gastrin in turn stimulates the secretion of HCL, pepsin and renin. These three works for the digestion of proteins.
- Hydrochloric Acid:– the parietal cell secrete HCL. The hydrochloric acid denature the protein and also function in the breakdown of the amide bond with the help of proteases. It also provides acidic medium for the work of pepsin.
- Pepsin:- It is secreted by pepsinogens in form of proenzyme (inactive form). It is further activated by pepsin itself or because of high concentration of HCL. It works in two ways
- It functions for the breakdown of peptide bond of aromatic amino acid like phenylalanine, tryptophan. and also breaks the peptide bond of acidic amino acid like aspartic acid and glutamic acid.
- So the pepsin cleave the long polypeptide chain into a mixture of smaller oligopeptide and some amino acids.
- Rennin:– It is secreted in infants only and is also known as chymosin.
- It functions to clot the milk by the hydrolysis of milk protein.
- Renin also stimulates the conversion of casein into paracasein. Paracasein then in the presence of calcium form calcium paracaseinate complex (insoluble curd). the further reaction is carried out by pepsin.
2. Digestion in small intestine
Digestion in small intestine occur in two ways:
- By the action of pancreatic enzyme
- Endopeptidase:- It cleaves the inter peptide bond and produces smaller amino acids. It is secreted by the pancreas in the inactive form.
- Trypsin:- Hydrolysis the peptide bond whose carboxy group is contributed by lysin and arginine.
- chymotrypsin:- It hydrolysis the peptide bond of aromatic amino acid and of leucine, histidine, aspargine
- elastase:- Cleave the peptide bond formed by the smaller non-polar amino acid like glycine, alanine and serine.
- Endopeptidase:- It cleaves the inter peptide bond and produces smaller amino acids. It is secreted by the pancreas in the inactive form.
| Proenzyme (inactive form) | Enzyme (active form) |
| Trypsinogen | Trypsin |
| Chymo-trypsinogen | Chymotrypsin |
| Pro-elastase | Elastase |
- Exopeptidase:– It cleaves the terminal peptide bond. Is is of two types
- Carboxypeptidase: Secreted by pancreas and it act on the C-terminal of peptide bond of amino acid.
- Aminopeptidase: Secreted by mucosal cell and act on the N-terminal of peptide bond of amino acid.
- By the action of intestinal protease
- Aminopeptidase:- It is the type of exopeptidase. and act on the N-terminal of peptide bond.
- dipeptidase:- It breaks the dipeptide into each amino acid. It finally converts all the ingested protein into amino acid.
Absorption of Proteins
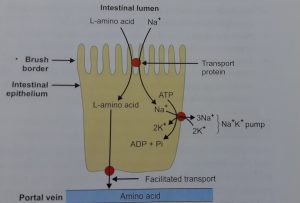
- The absorption of amino acid requires a transport mechanism, especially requiring ATP and specific transporter proteins
- Many transporters have sodium-dependent mechanism
- Several sodium-independent transport proteins are found in brush border membrane. these proteins are not specific for each amino acid but they are specific for structurally similar amino acids
- D-amino acids are transported by passive transport
- After digestion of amino acids, they pass from the gut through the hepatic portal vein to the liver
The below diagram explains the transport of L-amino acids across the intestinal membrane.
Multiple choice questions (MCQs)
1. Where do digestion of protein takes place?
A. Mouth
B. Small intestine
C. Stomach
D. Both b and C
E. All of the above
2. What stimulate the secretion of gastrin?
A. Pepsin
B. Protein diet
C. Lipid diet
D. Both A and B
3. What is the daily protein requirement of an adult man?
A. 50-70g
B. 180-200g
C. 70-100g
D. 20-30g
4. Pepsin breaks the peptide bond of which type of protein?
A. Aromatic amino acid
B. Basic amino acid
C. Acidic amino acid
D. Both A and C
5. Match the following-
A. Dipeptidase 1. Results in each amino acid
B. Trypsin 2. Hydrolyze the peptide bond
C. Carboxy peptidase 3. Breaks the C-terminal of peptide bond
D. Hydrochloric acid 4. Denature of protein
6. Is renin and rennin same? If no, why?
A. Both are same
B. No, renin regulates water balance and rennin function is to clot milk
C. No, rennin regulates water balance and renin function is to clot milk
D. No, Rennin regulates BP and renin regulates electrolyte balance
7. Which of the following is pancreatic enzyme?
A. Aminopeptidase
B. Elastase
C. Tyrpsin
D. All of the above
8. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. Exopeptidase consist of elastase, trypsin etc
B. Amino acids are more stable than imino acid
C. Carboxypeptidase is calcium dependent enzyme
D. Dipeptidase is cobalt and magnesium dependent enzyme
9. What is the inactive form of elastase?
A. Pro elastase
B. Elastinogen
C. Elastin
D. none of the above
10. Through which vein, amino acids after digestion reaches the liver?
A. Renal vein
B. Hepatic portal vein
C. Carotid vein
D. none of the above
11. What is the inactive form of chymotrypsin?
A. Pro chymotrypsin
B. Chymotrypsinogen
C. Chymotrysinase
D. None of the above
12. What is the function of chymotrypsin?
A. Break peptide bond of aromatic amino acid
B. Break peptide bond of aliphatic amino acid
C. Break peptide bond of acidic amino acid
D. Break peptide bond of basic amino acid
13. Aminopeptidase breaks which terminal of peptide bond?
A. C-terminal
B. N-terminal
C. D-terminal
D. All of the above
14. Which of the following breaks the C-terminal of peptide bond?
A. Aminopeptidase
B. Dipeptidase
C. Trypsin
D. None of the above
15. Which of the following is a zinc containing enzyme?
A. Pepsin
B. Trypsin
C. Carboxypeptidase
D. Elastase
ANSWERS:-
1. Both B and C
2. Protein diet
3. 70-100g
4. Both A and C
5. a – 1 b – 2 c – 3 d – 4
6.No, renin regulates water balance and rennin function is to clot milk
7. All of the above
8. Exopeptidase consist of elastase, trypsin etc
9. Pro elastase
10. Hepatic portal vein
11. Chymotrypsinogen
12. Break peptide bond of aromatic amino acid
13. N-terminal
14. None of the above
15. Carboxypeptidase
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 263-265.