Lipogenesis: De novo synthesis of fatty acids and MCQs For GPAT, CSIR NET, NEET, GATE
The process of new synthesis of fatty acids from the acetyl-CoA is called lipogenesis.
Location:- It mainly occurs in liver and mammary glands; but are also formed in minute amounts in apidose tissue, kidney and brain cells.
Steps of lipogenesis
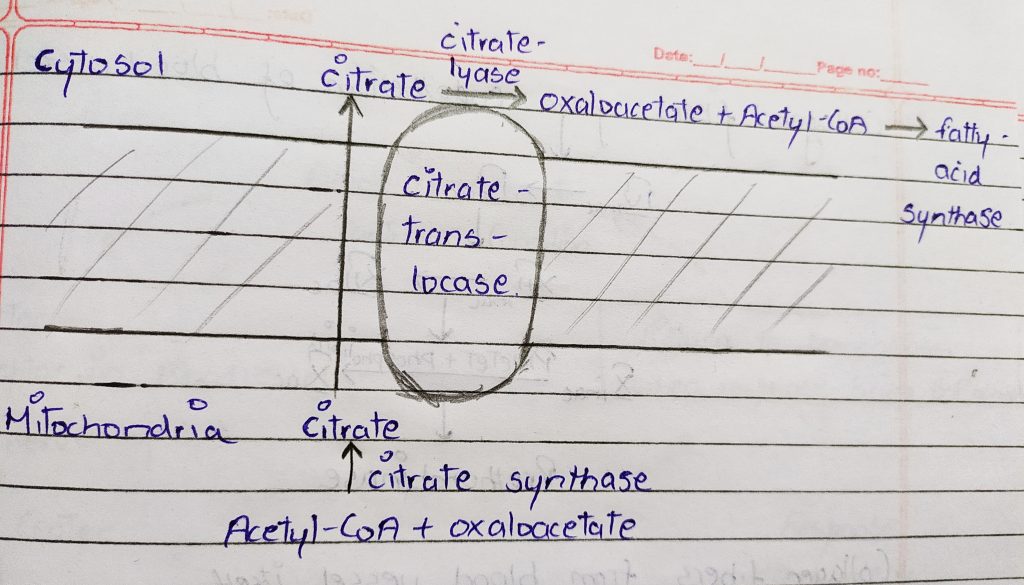
1. transport of acetyl-CoA from mitochondria to cytosol
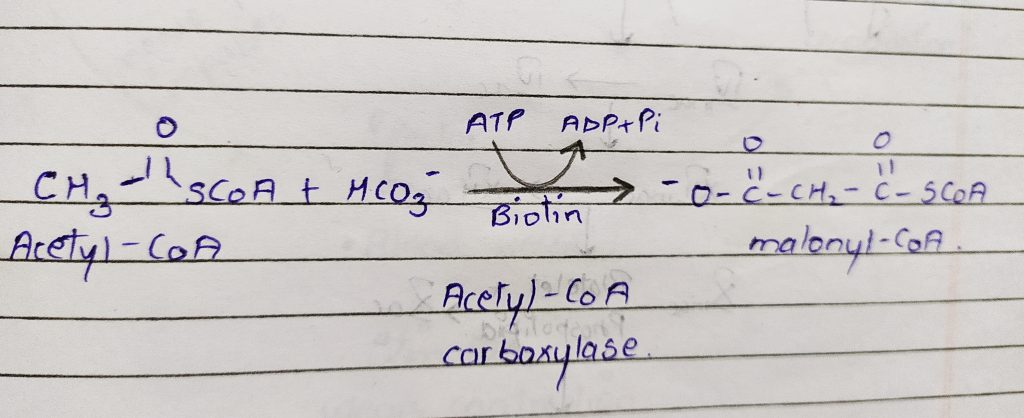
2. carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl- CoA.
The carboxylation of acetyl-CoA is the rate limiting step of fatty acid synthesis
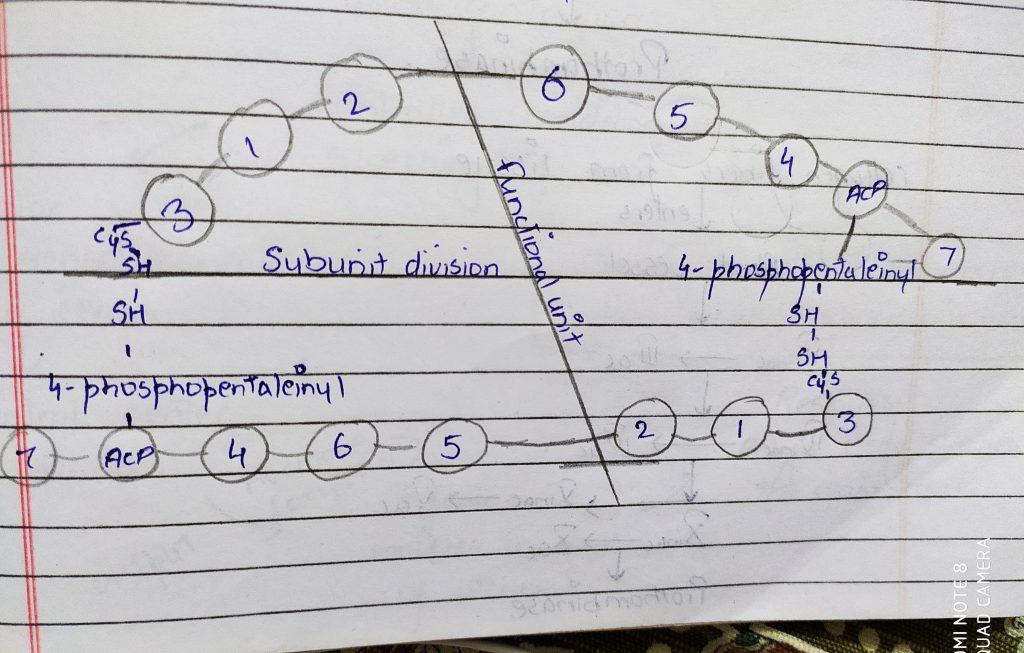
3. Reactions of fatty acid synthase complex
Fatty acid synthase complex is a multi-enzyme complex which have different catalytic reaction site on it. The active one is the dimeric and is arranged in head to tail form. This synthase complex have 7 enzymatic site on it and one ACP (acylcamer protein) site.
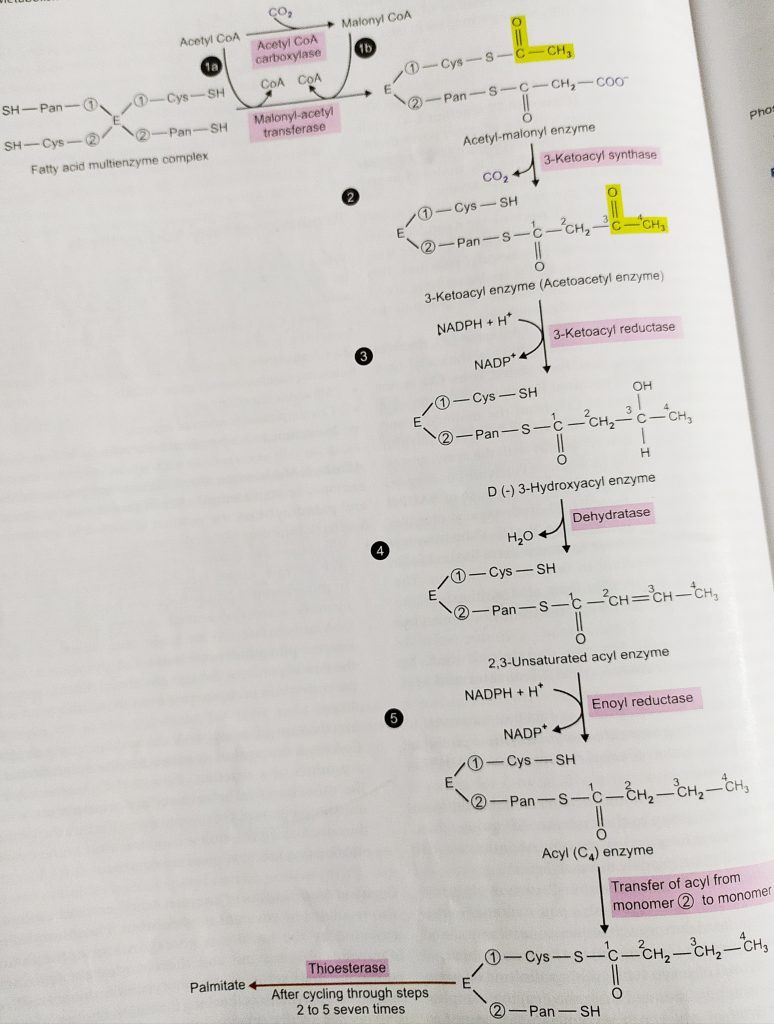
Pathway for De novo synthesis
Regulation of lipogenesis
These are divided in three types
- Enzymatic regulation:- acetyl-CoA carboxylase is a rate limiting enzyme for this pathway. This enzyme is activated by citrate and is inhibited by palmitoyl-CoA.
- Hormonal regulation:-
1. Insulin activates the acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
2. Glucagon inhibits the acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme
- Nutritional regulation:-
1. if the diet is rich in carbohydrate and contains low fat than it stimulates the rate limiting enzyme
2. In case of starvation, diabetes mellitus and rich fat diet; the rate limiting enzyme is inhibited and thus inhibits the fatty acid synthesis.
Multiple choice questions (MCQs)
- What is lipogenesis?
A. synthesis of lipid B. catabolism of phospholipid
C. synthesis of fatty acids D. catabolism of fatty acids - which fatty acid contains 16 carbon skeleton?
A. palmitic acid B. glutamic acid
C. Lauric acid D. Myristic acid - Where does lipogenesis takes place?
A. cytosol B. mitochondria
C. ribosomes D. nucleus - In which organ, lipogenesis occur mostly?
A. liver B. lungs
C. mammary glands D. both A and C - Which of the following is the 2nd step of lipogenesis?
A. transport of acetyl-CoA from mitochondria to cytosol
B. carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA
C. Reactions of synthesis using fatty acid synthase complex
D. none of the above - Match the following –
a. acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1. stimulates acetyl-CoA carboxylase
b. thioesterase 2. inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase
c. insulin 3. malonyl-CoA
d. glucagon 4. palmitic acid - In which situation, fatty acid synthesis is stimulated?
A. carbohydrate rich diet D. citrate
C. insulin D. all of the above - Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. lipogenesis is same as lypolysis
B. fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA
C. Insulin activates the acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
D. Glucagon inhibits the acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme - Which type of diet inhibits lipogenesis?
A. carbohydrate rich B. fat rich diet
C. protein rich diet D. all of the above - Which enzyme is known as the rate limiting enzyme?
A. thioesterase B. enolreductase
C. ketoacyl synthase D. acetyl-CoA carboxylase - How many enzymatic sites does fatty acid synthase complex have?
A. 8 B. 6
C. 7 D. 5 - Which form of energy is required for the conversion of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA?
A. NADH B. GTP
C. AMP D. None of the above - In which tissue, lipogenesis occur in minute amounts?
A. adipose tissue B. areolar tissue
C. epithelium D. elastic tissue - In which type of cell lipogenesis occur in minute amounts?
A. nerve cell B. kidney cell
C. brain cell D. both B and C - Synthesis of fatty acids begins from which compound?
A. acyl-CoA b. acetyl-CoA
C. phospholipid D. lipoproteins
ANSWERS:-
1. synthesis of fatty acids
2. palmitic acid
3. cytosol
4. both A and c
5. carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA
6. a – 3 b – 4 c – 1 d – 2
7. all of the above
8. lipogenesis is same as lypolysis
9. fat rich diet
10. acetyl-CoA carboxylase
11. 7
12. none of the above
13. adipose tissue
14. both B and C
15. acetyl-CoA
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 224-230 .