MEFENAMIC ACID Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Mefenamic acid
IUPAC nomenclature
2-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)aminobenzoic acid
Classification
- NSAID
- Anthranylic acid derivatives
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 241.28 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 230.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in solution of alkali hydroxides; sparingly soluble in ether; slightly soluble in ethanol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 4.2. |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Mefenamic acid binds with COX-1 and COX-2 and inhibits the action of prostaglandin synthetase.
- Due to this, the level of prostaglandins decreases and the symptoms of pain are temporarily reduced.
Structure Activity Relationship
General SAR for anthranylic acid derivatives can be summarized as follows:
- Activity decreases when substitution on anthranilic acid ring.
- Activities due to substitution on the N-aryl ring follows the general order m > o > p.
- For disubstitution products, activity was found to be maximum when o and m positions are substituted near to each other on the N-aryl ring.
- Substitutions on the N-aryl ring with such groups which leads the ring to be noncoplanar with the anthranilic acid ring increases the binding of the drug and hence, increases the activity (meclofenamic acid being more active than flufenamic acid).
- NH-moiety of the anthranilic ring is important for the activity of the drug, and replacement of NH- moiety with O, CH3, S, SO2, N-CH3 or N-COCH3 groups decreases the activity of drug.
- Position of the acidic function is important for the activity and not the nature of acidic function. [1]
- Replacement of carboxylic acid function with isosteric tetrazole function has no significant effect on the activity of compound.[1]
Method of synthesis
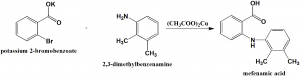
Potassium salt of 2-bromobenzoic acid is reacted with ,3-dimethylaniline in the presence of copper(II) acetate to give mefenamic acid. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Mefenamic acid is used for:
- Short-term treatment for mild to moderate pain
- Decreasing menstrual pain
Side Effects
Side effects of mefenamic acid are:
- Skin rash
- Changes in vision
- Shortness of breath
- Weight gain
- Swelling
- Stomach bleeding
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- Difficulty in urination
- Anemia
- Skin reactions
- Indigestion
- Nausea
- Tremors
- Stomach pain
- Confusion
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Headache
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Mefenamic acid?
a) 2-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)aminobenzamide
b) 2-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)aminobenzoic acid
c) 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-ylthieno[2,3-e]thiazine-3-carboxamide
d) 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-ylthieno[2,3-e]thiazine-3-Carboxylic acid
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of Anthranylic acid derivatives?
I. Activity decreases when substitution on anthranilic acid ring.
II. Activities due to substitution on the N-aryl ring follows the general order m > o > p.
III. For disubstitution products, activity was found to be minimum when o and m positions are substituted near to each other on the N-aryl ring.
IV. Substitutions on the N-aryl ring with such groups which leads the ring to be noncoplanar with the anthranilic acid ring increases the binding of the drug and hence, increases the activity
a) I
b) III
c) I, II
d) IV
Q.3 Mefenemic acid can be synthesized by the reaction of 2,3-dimethylbenzamine in presence of copper(II)acetate with?
a) Potassium 2-bromo-benzoate
b) Saccharine
c) Mulch’s reagent
d) All of the above
Q.4 Side effects of drug mefenamic acid is/are?
a) Skin rash
b) Abdominal pain
c) Easy bleeding
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with the correct number of the chiral carbons they have in their structure:
| i. Mefenamic acid | A. 3 |
| ii. Etodolac | B. 1 |
| iii. Naloxone | C. 2 |
| iv. Dextropropoxyphene | D. 0 |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Q.6 An example of drug from class NSAIDs?
a) Methotrexate
b) Glycopyrrolate
c) Mefenamic acid
d) Salbutamol
Q.7 The type of ring system found in Mefenamic acid?
I. Phenyl
II. Pyridine
III. Anthracene
IV. Thiophene
a) I, III
b)II, III, IV
c) I
d) II, IV
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-b
2-b
3-a
4-d
5-c
6-c
7-c