NITROGLYCERINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
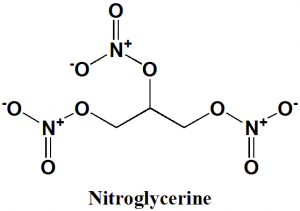
Nitroglycerine
Or
Glyceryl trinitrate
IUPAC nomenclature
1,3-dinitrooxypropan-2-yl nitrate; [3-(nitrooxy)-2-[(nitrooxy)methyl]propyl] nitrate; 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane.
Classification
- Organic nitrate antianginal drug
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 227.09 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Colorless solution |
| 3 | Melting point | 13.5oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Poor solubility in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.62 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Not present |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 2 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Conversion of nitroglycerine into nitric oxide (NO) by mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (mtALDH).
ii. NO activates enzyme guanylate cyclase.
iii. This activates the synthesis of cyclic guanosin 3’,5’-monophosphate (cGMP).
iv. Due to this, there is an activation of the cascade of protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation events in the smooth muscles.
v. Relaxation is caused in the smooth muscles due to dephosphorylation of the myosin light chain of smooth muscles, due to which, there is increased in blood flow in veins, arteries and cardiac tissues.
vi. Heart has to do lesser work and blood pressure and angina tension also reduces. There is increased blood flow in the myocardium.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of organic nitrate antianginal drugs be summarized as:
- The number of nitrate groups determines the potency of organic nitrate for guanylate cyclase activation.
- Increase in nitric group increases the potency.
- Increase in lipophillicity doesn’t have major effect over activation of drug.
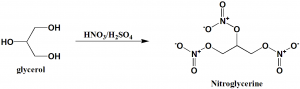
Method of synthesis
Nitration of glycerol with nitric acid produces nitroglycerine. [2]
Medicinal Uses
Nitroglycerine is used for treatment of:
- Angina and chest pain due to cardiovascular disease.
- Peri-operative hypertension
- Inducing intra-operative hypotension
- Acute heart failure
- Pain caused by anal fissure
- Prevention of acute angina attacks
Side Effects
Side effects of Nitroglycerine are:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Flushing
- Allergic reactions
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the organic nitrate antianginal drugs-
| i. Increase in the number of nitric groups | A. Increases the activity of drug |
| ii. Increase in lipophillicity | B. Decreases the activity of drug |
| C. Increases the activation of drug | |
| D. Does not have major effect over activation of drug |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Nitroglycerine: 1,3-dinitrooxypropan-2-yl nitrate; [3-(nitrooxy)-2-[(nitrooxy)methyl]propyl] nitrate; 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane.
- Diclofenac: [2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid
- Levallorphan: (−)-17-allylmorphinan-3-ol
- Sodium salicylate: Sodium;2-hydroxybenzoate
a) FFTF
b) FFFF
c) TTFT
d) TTTT
Q.3 Molecular weight of drug nitroglycerine is?
a) 227.09 gm/mol
b) 652.36 gm/mol
c) 142.45 gm/mol
d) 741 gm/mol
Q.4 Conversion of nitroglycerine into NO is done by?
a) Nitrase enzyme
b) Mitochondrial aldehyde dehyrogenase enzyme
c) Mitochondrial deaminase enzyme
d) None of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug Nitroglycerine?
a) Treatment of angina
b) Treatment of prostate cancer
c) As an antidiabetic drug
d) As an anesthetic
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Nitroglycerine: Organic nitrate antianginal drug
II. Physostigmine: Cholinestrase inhibitor
III. Felbamate: Anticonvulsant
IV. Mechlorethamine: Antineoplastic drug
a) I ,II, III
b) II, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) I, III
Q.7 Nitroglycerine can be prepared by nitration of?
a) Glyceraldehyde
b) Glycerol
c) Trinitroglyceraldehyde
d) Trinitroglycerol
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-b
2-d
3-a
4-b
5-a
6-c
7-b
REFERENCES
[1] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.