NMR PRINCIPAL AND INSTRUMENTATION, MCQ
NMR PRINCIPAL :-
Nuclei with odd mass or odd number have only property of nuclear spin.
Spin quantum number is more than 0 so compound are NMR active.
Spin quantum number is denoted by “I”
If the external magnetic field is applied the number of possible orientation is calculated by 2I +1.
The theory behind NMR come from the spin of the nuclei and it magnetic field.
When external magnetic field is not applied every nuclei have random spin and it’s magnetic field is random direction.
But when external magnetic field is a applied all nuclei magnetic field are have two possible direction
1. They are parallel to the external magnetic field.
2. They are opposite direction.
If an external magnetic field is a applied energy transfer is possible between ground state to excited state.
When the spin return to its ground state level the absorbed radio frequency energy is emitting at the same frequency level
The emitted radio frequency is directly proportional to the strength of the applied field.
V=ΥBo/2π
Where,
Bo = External magnetic field experience by proton
Υ = magneto gyric ratio (the ratio between the nuclear magnetic moment and angular moment).
NMR has operated by two frequency
1. Constant magnetic radiation
2. Constant EMR frequency
INSTRUMENTATION OF NMR
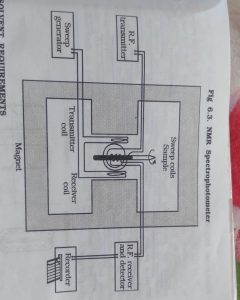
1. Sample Holder:-
5 mm glass tube is used which can hold 0.4 ml liquid sample microtube are used. And 25 cm in length.
2. Magnet :-
Accuracy and quality of the instrument is dependent on the strength resolution increase with increase in the magnetic field strength.
Three types of magnet are used
- 1. Conventional magnet ( 30-60 MHz)
- 2. Permanent magnet electro magnet ( 60,90,100 MHz)
- 3. Super conducting magnet ( 470MHz)
- 3. Sweep generator :- A set of helmboltz coil is located parallel to the magnetic field. They sweep magnetic field.
- 4. RF transmitter :- which is used to applied a radio frequency radiation.
- 5. RF receiver :- To measure the intensity of the unabsorbed radio frequency energy.
- 6. Recorder :- To record the NMR signal obtained from detector.
MCQ.
1. Which mass number of nuclei are NMR active ?
A. Odd
B. Even
C. A&B
D. None
Ans A
2. If the external magnetic field is a applied , the number of possible orientation is calculated by
A. 2I +2
B. 2I + 3
C. 2I +1
D. 2I +4
Ans. C
3. The ratio between the nuclear magnetic moment and angular moment is called
A. Magneto gyric ratio
B. Precessional movement
C. Gyromateric ratio
D. All of the above
Ans A
4. How many ml sample is required in NMR SPECTROSCOPY ?
A. 0.3 ml
B. 0.4 ml
C. 0.5 ml
D. 0.6 ml
Ans . B.
5. Conventional magnetic have frequency of the
A. 90-100MHz
B. 30-60MHz
C. 470 MHz
D. 500 MHZ
Ans. B
6. Super conducting magnet have frequency is
A. 480 MHz
B. 470 MHz
C. 380 MHZ
D. 490 MHz
Ans. B
7. How many cm length of sample holder in NMR ?
A. 30 cm
B. 25 cm
C. 20 cm
D. 35 cm
Ans. B
8. Which part are used to measure unabsorbed radio frequency in NMR ?
A. RF receiver
B. Magnet
C. Sample Holder
D. Recorder
Ans. A
9. Sweep generator used is
A. To vary the strength of the applied magnetic field.
B. Emitted EMR
C. A & B both
D. None of this
Ans A.
10. How many mm diameter of the sample holder in NMR SPECTROSCOPY?
A. 6 mm
B. 7 mm
C. 3 mm
D. 4 mm
Ans .D
Reference:text book of analysis third edition of the Dr. S. Ravi sankar