PENTAERYTHRITOL TETRANITRATE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
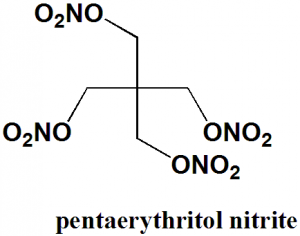
Pentaerythritol tetranitrate
IUPAC nomenclature
2,2-Bis[(nitrooxy)methyl]propane-1,3-diyl dinitrate
Classification
- Organic nitrate antianginal drug
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 316.14 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystals |
| 3 | Melting point | 140.5oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in acetone |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | log Kow = 2.38 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Not present |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
i. The drug releases NO after denitration reaction.
ii. .Activation of enzyme gunanylate cyclase
iii. Increase in concentration of cGMP within vascular smooth muscles
iv. Vasodilation occurs due to cGMP-dependent protein kinase.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of organic nitrate antianginal drugs be summarized as:
- The number of nitrate groups determines the potency of organic nitrate for guanylate cyclase activation.
- Increase in nitric group increases the potency.
- Increase in lipophillicity doesn’t have major effect over activation of drug.
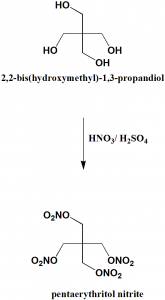
Method of synthesis
2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propandiol is reacted with nitric acid to give pentaerythritol tetranitrate.[1]
Medicinal Uses
Pentaerythritol tetranitrate is used for treatment and prevention of:
- Angina pectoris
Side Effects
Side effects of pentaerythritol tetranitrate are:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Flushing
- Syncope
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Methemoglobinemia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weakness
- Restlessness
- Uncontrolled urination
MCQs
Q.1 “2,2-Bis[(nitrooxy)methyl]propane-1,3-diyl dinitrate” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Pentaerythritol tetranitrate
b) Furosemide
c) Amyl Nitrate
d) Bleomycin
Q.2 Melting point of drug pentaerythritol tetranitrate is?
a) 140.5 oC
b) 256 oC
c) 100 oC
d) 342 oC
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Pentaerythritol tetranitrate | A. Inhalational anesthetics |
| ii. Prazosin | B. α-adrenergic blocker |
| iii. Propranolol | C. ß-adrenergic blocker |
| iv. Isoflurane | D. Organic nitrate antianginal drug |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-C, iv-A
d) i-C, ii-D, iii-B, iv-A
Q.4 Mechanism of action of the drug pentaerythritol tetranitrate includes?
I. The drug releases NO after denitration reaction.
II. ctivation of enzyme gunanylate cyclase
III. Increase in concentration of cGMP within vascular smooth muscles.
a) I, II, III
b) II, III
c) I, III
d) I, II
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of organic nitrate antianginal drugs can be?
- The number of nitrate groups determines the potency of organic nitrate for guanylate cyclase activation.
- Increase in nitric group increases the potency.
- Increase in lipophillicity doesn’t have major effect over activation of drug.
a) TFF
b) FFT
c) TTT
d) FFF
Q.6 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of pentaerythritol tetranitrate
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.7 The drug pentaerythritol tetranitrate is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of angina
b) Treatment of Asthma
c) Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
d) Treatment of Parkinson disease
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-c
4-a
5-c
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.