Pentose Phosphate Pathway (HMP shunt) and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, GATE, CSIR NET exam
Pentose phosphate pathway is an alternative route for the oxidation of glucose. It is the pathway for the formation of pentose sugar. It is also known as hexose monophosphate shunt (HMP shunt).
The enzymes for HMP shunt are present in the cytosol of the cell. This pathway takes place in all the cells
Characteristics of HMP shunt
1. It is a multi-cyclic process in which 3 molecules of glucose-6-phosphate give rise to the three molecules of CO2 and 3 molecules of ribulose-5-phosphate(5 carbon sugar).
2. the three molecules of ribulose-5-phosphate are arranged to form 2 molecules of fructose-6-phosphate and 1 molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
3. It does not generate ATP.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
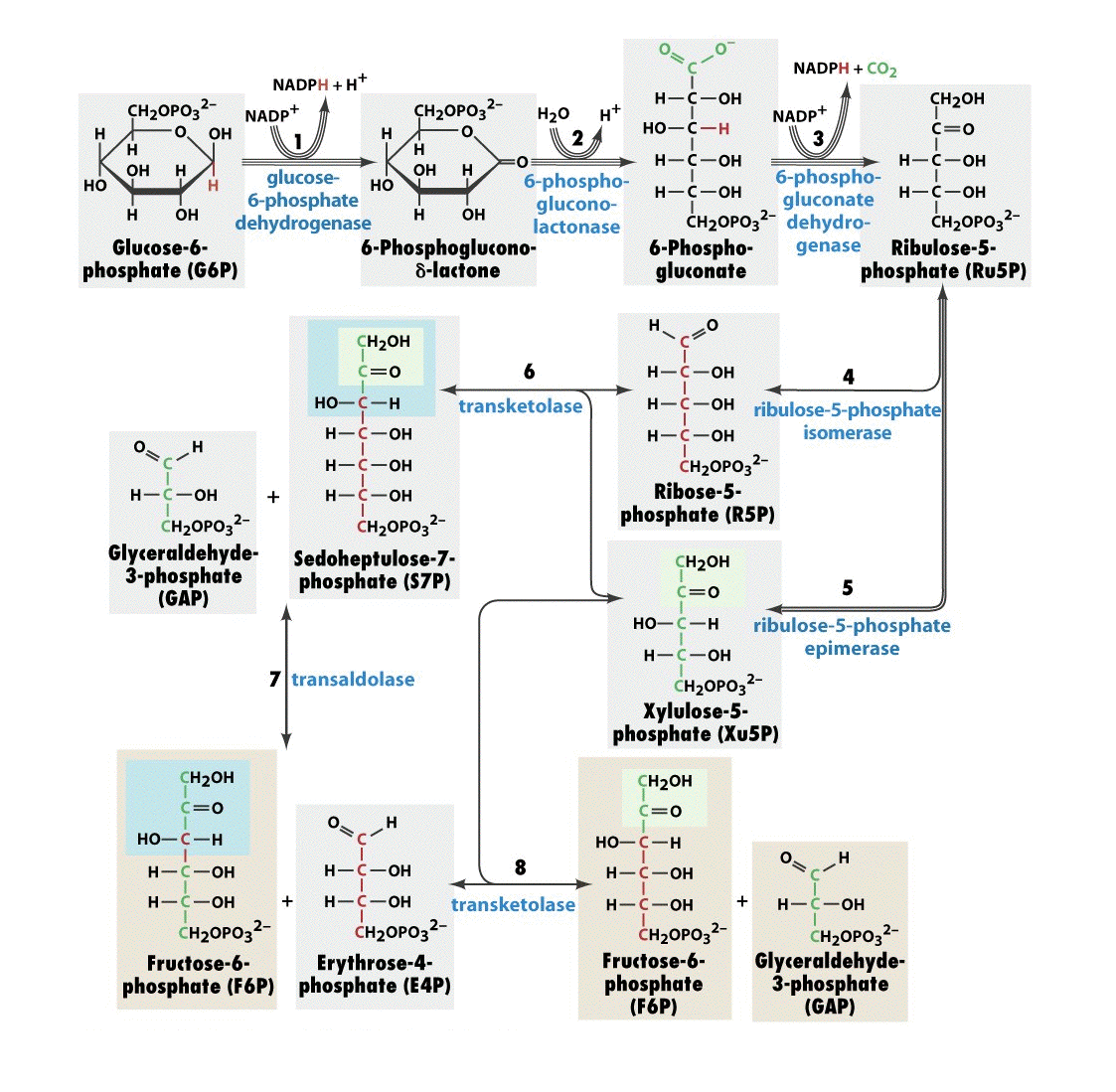
Reactions involved:- The reactions of the pathway are divided in two phases
- 1st phase- oxidative irreversible phase
- 2nd phase- non-oxidative reversible phase
1st phase
1. dehydrogenation of glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone is catalyzed by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase using NADP.
2. 6-phosphogluconolactone is hydrolyzed to 6-phosphogluconate.
3. oxidative decarboxylation of 6-phosphogluconate is catalyzed by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; this produces ribulose-5-phosphate, CO2 molecules and second molecule of NADPH.
2nd phase
4. Ribulose-5-phosphate serves as a substrate for two enzymes:
- ribulose-5-phosphate epimerase which catalyzes the epimerization of ribulose-5-phosphate to xylulose-5-phosphate.
- ribulose-5-phosphate isomerase catalyzes the isomerization of ribulose-5-phosphate to ribose-5-phosphate.
5. Transketolase enzyme catalyzes the transfer of 2 carbon units from xylulose-5-phosphate to ribose-5-phosphate; hence forming sedoheptulose-7-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate. This reaction requires a co-enzyme thiamine pyrophosphate(TPP) and Mg ions.
6. Transaldolase catalyzes the transfer of 3 carbon units from sedoheptulose-7-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate; hence forming fructose-6-phosphate and erythrose-4-phosphate.
7. Again, the transketolase catalyzes the transfer of 2 carbon units from xylulose-5-phosphate to erythroe-4-phosphate; hence produces glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate.
8. Further, fructose-6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate are catabolized through the glycolysis and TCA cycle.
Regulation of Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) catalyzes the 1st step of the pathway and is the rate limiting step. This enzyme is regulated by concentration of NADPH. high concentration of NADPH inhibits the enzyme, which in turn inhibits the pathway.
- under well-fed condition, the concentration of NADPH decreases, hence the HMP shunt is stimulated.
- under starvation and diabetes, the concentration of NADPH is high, hence the pathway is inhibited.
Insulin also regulates the pathway. High concentration of insulin stimulates the pathway by stimulating G-6-PD and 6-phosphogluconolactone dehydrogenase.
Significance of HMP shunt
1. Ribose-5-phosphate required for the biosynthesis of DNA and RNA are provided by this pathway
2. It provides the route for the interconversion of pentoses to hexoses.
3. It generates NADPH which is required for the biosynthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol, steroid hormones and neurotransmitters.
4. NADPH also keeps the iron of hemoglobin in ferrous state and prevents the formation of methemoglobin.
5. NADPH is important for phagocytosis carried out by WBCs
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. HMP shunt is required for which kind of metabolism?
A. carbohydrate metabolism B. fat metabolism
C. lipid metabolism D. amino acid metabolism
2. What is the product generated after the completion of 1st phase?
A. ribulose-5-phosphate B. CO2
C. NADPH D. all of the above
3. What is the location of pentose phosphate pathway to take place?
A. cell membrane B. cytosol
C. ribosomes D. mitochondria
4. Match the following-
a. insulin 1. Oxidative irreversible
b. high concentration of NADPH 2. Stimulates HMP shunt
c. 1st phase 3. Non-oxidative reversible
d. 2nd phase 4. Inhibits HMP shunt
5. What type of reactions occurs in 2nd phase?
A. oxidative reversible B. non-oxidative reversible
C. non-oxidative irreversible D. oxidative irreversible
6. What is the role of NADPH in RBCs?
A. transports O2 B. forms Hb
C. keeps iron of Hb in ferrous form D. none of the above
7. transaldolase enzyme catalyzes the transfer of how many carbon units from sedoheptulose-7-phosphate?
A. 2 units C. 3 units
C. 4 units D. 5 units
8. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. HMP shunt stands for hexose monophosphate shunt
B. HMP shunt does not generate CO2
C. HMP does not generate ATP
D. pentose phosphate pathway takes place in cytosol
9. What stimulates the pentose phosphate pathway?
A. high concentration of insulin B. low level of NADPH
C. high level of NADPH d. both A and B
10. Which enzyme requires thiamine pyrophosphate as the co-enzyme?
A. transketolase B. ribulose-5- phosphate isomerase
C. transaldolase D. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
11. what is the product generated after the transketolase catalyzes the transfer of 2 carbon units from xylulose-5-phosphate to erythrose-4-phosphate?
A. fructose-4-phosphate B. glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate
C. fructose-6-phosphate D. both B and C
12. Which enzyme belongs to the 2nd phase of HMP shunt?
A. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase B. 6-phosphogluconate
C. 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase D. none of the above
13. What type of reactions occurs in the 1st phase of pentose phosphate pathway?
A. oxidative reversible B. non-oxidative reversible
C. non-oxidative irreversible D. oxidative irreversible
14. What is the function of ribulose-5-phosphate epimerase?
A. epimerization of glucose-6-phosphate
B. epimerization of ribulose-5-phosphate
C. epimerization of xylulose-5-phosphate
D. epimerization of fructose -4-phosphate
15. Which form of energy is used by the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme?
A. ATP B. AMP
C. GTP D. NADPH
ANSWERS:-
- carbohydrate metabolism
- all of the above
- cytosol
- a – 2 b – 4 c – 1 d – 3
- non oxidative reversible
- keeps the iron of Hb in ferrous form
- 3 units
- HMP shunt does not generate CO2
- Both A and B
- transketolase
- both B and C
- none of the above
- oxidative irreversible
- ribulose-5-phosphate
- NADPH
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 187-190.