Pharmaceutical Aerosols: Components and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam
Components of aerosols:
- Propellant
- Container
- Valve and actuator
- Product concentrate
1.Propellant – Responsible for developing proper pressure within the container. Provide driving force to expel the product from the container.
For detailed description on propellants refer to the article ‘Pharmaceutical Aerosols: Propellants and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam’.
2.Container – They must be able to withstand pressures as high as 140 to 180 psig (pounds per sq. inch gauge) at 130 ° F.
AEROSOL CONTAINERS –
A . Metals
1.Tinplated steel 2.Aluminum 3.Stainless steel
B. Glass
1. Uncoated glass 2. Plastic coated glass
Metal containers
1.Tinplated steel – It consist of a sheet of steel plate, this sheet is coated with tin by electrolytic process . The coated sheet is cut into three pieces ( top , bottom and body) . The top, bottom are attached to body by soldering. When required it is coated with organic material usually oleo resin, phenolic , vinyl or epoxy coating. Welding eliminates soldering process, saves considerable manufacturing time and decreases the product/container interaction. Recent developments in welding include Soudronic system and Conoweld system.
2.Aluminum – Used for inhalation and topical aerosols . Manufactured by impact extrusion process. Light in weight, less fragile, less incompatibility due to its seamless nature. Greater resistance to corrosion. Pure water and pure ethanol cause corrosion to Al containers. Added resistance can be obtained by coating inside of the container with organic coating like phenolic , vinyl or epoxy and polyamide resins.
3.Stainless steel – Used for inhalation aerosols.
Advantages:
- Extremely Strong.
- Resistant to many materials.
- No need for internal coating.
Disadvantage:
- Costly.
Glass containers
These containers are preferred because of its Aesthetic value and absence of incompatibilities. These containers are limited to the products having a lower pressure (33 psig) and lower percentage of the propellant. Used for topical and MDI aerosols. Two types of glass aerosol container
i) Uncoated glass container: Less cost and high clarity and contents can be viewed at all times.
ii) Plastic coated glass containers: These are protected by plastic coating that prevents the glass from shattering in the event of breakage.
3.Valve and actuator –
VALVES: Easy to open and close . Capable of delivering the content in the desired form such as spray, foam, solid stream etc. It can deliver a given amount of medicament.
TYPES OF VALVES : 1.Continuous spray valve 2.Metering valves
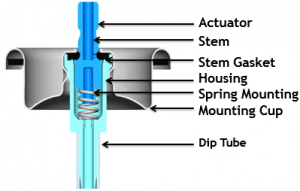
Figure 1 – Valve components
Continuous spray valve – Used for topical aerosols. Valves assembly consists of
- Ferrule or mounting cup
- Valve body or housing
- Stem
- Dip tube
- Gasket
- Spring
FERRULE OR MOUNTING CUP : Used to attach valve to container. Made from Tin plated steel, Al , Brass. Under side of the valve cup is coated with single or double epoxy or vinyl resins.
VALVE BODY OR HOUSING : Made up of Nylon or Derlin and contains a opening at the point of attachment of dip tube. (0.013 to 0.080 inch).
STEM : Made from Nylon or Derlin , brass and stainless steel can also be used. (orifice – 0.013 to 0.030 inch).
DIP TUBE : The dip tube which extends from the housing down into the product concentrate serves to bring the formulation from the container to the valve. The dip tubes are made from polyethylene or polypropylene. Inner diameter is 0.120 – 0.125 inch. However for Capillary dip tube inner diameter is 0.050 inch and for highly viscous products it is 0.195 inch. Dip tube is used for the following purposes:
- It conveys the liquid from the bottom of the container to the valve at the top.
- It prevents the propellant to come out without dispensing the contents of the package.
GASKET : Made from Buna-N and neoprene rubber.
SPRING : Made from Stainless steel . Used to hold gasket in place.
Metering valves – Used for dispensing of potent medication. Operates on the principle of a chamber whose size determines the amount of medication dispensed. Approximately 50 to 150 mg ±10 % of liquid materials can be dispensed at one time with the use of such valve.
ACTUATORS : These are specially designed buttons which helps in delivering the drug in desired form i.e., spray, wet stream, foam or solid stream.
TYPES OF ACTUATORS :
- Spray actuators
- Foam actuators
- Solid steam actuators
- Special actuators
SPRAY ACTUATORS – It can be used for topical preparation, such as antiseptics, local anesthetics and spray on bandages etc. It allows the stream of product concentrate and propellant to pass through various openings and dispense as spray.
FOAM ACTUATORS – It consist of large orifice which ranges from 0.070—0.125 inch.
SOLID STREAM ACTUATORS – These actuators are required for dispensing semi solid products such as ointments.
SPECIAL ACTUATORS – These are used for a specific purpose. It delivers the medicament to the appropriate site of action such as throat, nose, dental and eyes etc.
METERED DOSE INHALERS(MDI) – Used to minimize the number of administration errors. To improve the drug delivery of aerosolized particles into the nasal passageways and respiratory tract.
Advantages of MDI:
- It delivers specified amount of dose.
- Portable and compact.
- Quick to use , no contamination of product.
- Dose-dose reproducibility is high.
Disadvantages of MDI :
- Low lung deposition ; high pharyngeal deposition.
- Coordination of MDI actuation and patient inhalation is needed.
4.Product concentrate – Active ingredient or mixture of active ingredients and other necessary agents such as solvents, anti oxidants and surfactants.
Multiple choice questions:
1.Which of the following are components of aerosols?
a)Propellant
b)Container
c)Valve
d)All of these
2.Which of the following is responsible for developing proper pressure within the container?
a)Propellant
b)Container
c)Valve
d)Product concentrate
3.Propellant provide ____ force to expel the product from the container.
a)driving
b)withdrawing
c)both of these
d)none of these
4.Aerosol container must be able to withstand pressures as high as ____ at 130 ° F.
a)100 to 180 psig
b)120 to 170 psig
c)140 to 180 psig
d)140 to 200 psig
5.Aerosol containers are made up of
a)metals
b)glass
c)plastic
d)a and b
6.Metals used for aerosol containers are
a)Tinplated steel
b)Aluminum
c)Stainless steel
d)All of these
7.Glass used for aerosol containers is/are
a)Uncoated glass
b)Plastic coated glass
c)Both of these
d)None of these
8.Which of the following consist of a sheet of steel plate, this sheet is coated with tin by electrolytic process?
a)Tinplated steel
b)Aluminum
c)Stainless steel
d)All of these
9. When required Tinplated steel is coated with
a)oleo resin
b)phenolic coating
c)vinyl or epoxy coating
d)all of these
10.Which of the following material is used for inhalation and topical aerosols containers?
a)Tinplated steel
b)Aluminum
c)Stainless steel
d)All of these
11.Which of the following is not an advantage of stainless steel metal container for aerosols?
a)Costly
b)Extremely Strong
c)Resistant to many materials
d)No need for internal coating
12.Glass containers are preferred because of its Aesthetic value and absence of incompatibilities.
a)true
b)false
13.Valves may be
a)Continuous spray valve
b)Metering valves
c)Both of these
d)None of these
14.The dip tubes are made from
a)Nylon
b)Derlin
c)Buna-N
d)Polyethylene
15.Disadvantage of MDI is
a)Low lung deposition ; high pharyngeal deposition
b)It delivers specified amount of dose
c)Portable and compact
d)Quick to use , no contamination of product
Solutions:
- d)All of these
- a)Propellant
- a)driving
- c)140 to 180 psig
- d)a and b
- d)All of these
- c)Both of these
- a)Tinplated steel
- d)all of these
- b)Aluminum
- a)Costly
- a)true
- c)Both of these
- d)Polyethylene
- a)Low lung deposition ; high pharyngeal deposition
References:
- Remington Essential of Pharmaceutics, 1st edition 2013, page no. 639-643.
- The Theory & Practice Of Industrial Pharmacy by Leon Lachman , H.A.Lieberman, 4th edition.
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE