PHENACEMIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
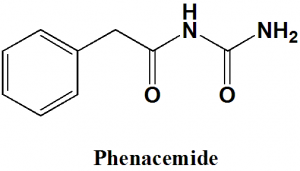
Phenacemide
IUPAC nomenclature
N-Carbamoyl-2-phenyl-acetamide
Classification
Phenacemide is an acetylurea derivative anticonvulsant.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 178.19 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to creamy white crystalline solid. |
| 3 | Melting point | 215°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very slightly soluble in water; slightly soluble I benzene, chloroform, alcohol, ether. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.87 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
i. Phenacemide binds and blocks neuronal sodium channels / voltage sensitive calcium channels.
ii. This results in blockage or suppression of neuronal depolarization and hypersynchronization.
iii. Seizures cause due to hypersynchronization is controlled.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of phenylacylureas can be summarized as follows:
- Branched chain aliphatic acid derivatives of urea are most active.
- Optimum activity can be found at seven carbon atoms.
- Increase in molecular weight results in decrease in anticonvulsant properties.
- Increase in molecular weight further results in hypnotic activities.
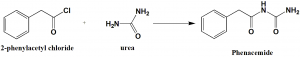
Method of synthesis
Phenacemide can be synthesized by reacting 2-phenylacetyl chloride with urea.
Therapeutic Uses
Phenacemide is used for:
- Treatment of epilepsy
Side Effects
Side effects of Phenacemide are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Mood changes
- Signs of infections
- Rashes
- Rapid breathing
- Fainting
- Liver problems
- Muscle pain’
- Low blood counts
- Weight loss
MCQs
Q.1 Choose the correct statements related with the physicochemical properties of drug phenacemide.
I. Molecular weight = 178.19 gm/mol
II. It is a creamy white crystalline solid
III. Melting point is 215oC
IV. It is freely soluble in water
a) I, III, IV
b) II, IV
c) I, IV
d) I, II, IV
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Phenacemide | A. 4-[bis(2-Chloroethyl)amino]-L-phenylalanine |
| ii. Melphalan | B. 1,1′,1′′-Phosphorothioyltriaziridine |
| iii. Chlorambucil | C. 4-[bis(2-chlorethyl)amino]benzenebutanoic acid |
| iv. Thiotepa | D. N-Carbamoyl-2-phenyl-acetamide |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
d) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
Q.3 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug Phenacemide are?
I. Suppression of neuronal depolarizatioon
II. Stimulation of neuronal depolarization
III. Blocking of neuronal sodium channel
IV. Agonistic effect on neuronal sodium channels
a) I – III
b)II – III
c) III – I
d) IV- II
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Phenacemide: Anticonvulsant drug
- Pilocarpine: Muscarnic agonist
- Scopolamine: Acetylcholine antagonist
- Pancuronium: Nicotinic antagonist
a) TFFT
b) TTTT
c) TFFT
d) FFTF
Q.5 Increase in weight of phenylacylureas leads to?
a) Increase in anticonvulsant properties
b) Decreases in anticonvulsant properties
c) No changes in anticonvulsant activity
d) Unpredictable changes
Q.6 The two chemicals which on reaction with each other produces Phenacemide?
I. 2-phenylacetyl chloride
II. 3-hydroxy-butanoyl chloride
III. Urea
IV. Aniline
a) II, IV
b) II, IV
c) I, III
d) I, II
Q.7 Side effect of drug phenacemide include?
a) Abdominal pain
b) Liver problems
c) Low blood counts
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-d
2-b
3-c
4-b
5-b
6-c
7-d