PHENACETIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
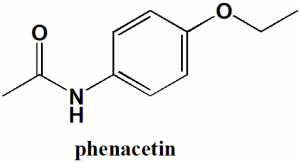
Phenacetin
IUPAC nomenclature
N-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)acetamide
Classification
- NSAID
- Acetamide
- Non-narcotic analgesic
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 179.22 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Fine white crystalline (monoclinic) solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 137.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in pyrimidine; soluble in ethanol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.58 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Phenacetin produces actions on sensory tracts of the spinal cord and produces analgesic effects.
- Drug also produces depressant actions on the heart by acting as a negative inotropic agent.
- It also produces effects on the heat-controlling centers in the brain to act as an antipyretic rug.
- In the body, it converts into acetaminophen which also a relevant analgesic and antipyretic agent.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of phenacetin and acetaminophen can be summarized as follows:
- Aminophenols are less toxic than corresponding aniline.
- Etherification of the phenolic function with methyl or propyl groups results in the derivatives having greater side effects than with ethyl groups.
- Substitution on the nitrogen with such groups that decreases the basicity also reduces the activity of the drug.
- Amides derived from aromatic acids are less active or inactive. [1]
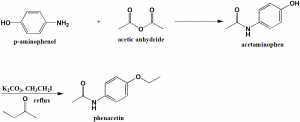
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of p-amiophenol with acetic anhydride to produce acetaminophen.
ii. Acetaminophen is treated with anhydrous potassium carbonate, ethyl iodide and 2-butanone at reflux to produce phenacetin.
Therapeutic Uses
Phenacetin is used for:
- Anti-inflammatory drug
- Antipyretic
- Analgesic
- Treatment of subacute rheumatoid arthritis
- Treatment of intercostals neuralgia
- Treatment of ataxias
Side Effects
Side effects of phenacetin are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Allergic reactions
- Interstitial nephritis
- Tumorigenicity
- Bladder cancer
- Colon cancer
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of phenacetin?
a) N-(3-Ethoxyphenyl)acetamide
b) N-(3-Ethoxyphenyl)acetic acid
c) N-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)acetamide
d) N-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)acetic acid
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of phenacetin?
I. Aminophenols are more toxic than corresponding aniline.
II. Etherification of the phenolic function with methyl or propyl groups results in the derivatives having greater side effects than with ethyl groups.
III. Substitutions on the nitrogen with such groups that decreases the basicity also reduces the activity of the drug.
a) I, II
b) I, III
c) I
d) II, III
Q.3 The correct order for the synthesis of drug phenacetin from p-aminophenol can be?
I. Treatment with potassium carbonate, ethyl iodide and 2-butanone
II. Reaction with acetic anhydride
III. Reaction with acetaminophen
IV. Reduction
a) III – II – IV
b) II – I
c) I – II – IV
d) IV – I – III – II
Q.4 Side effects of drug phenacetin is/are?
a) Inflammation
b) Ataxias
c) Bladder cancer
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with the correct number of the chiral carbons they have in their structure:
| i. Phenacetin | A. 4 |
| ii. Nalorphine | B. 0 |
| iii. Atazanavir | C. 2 |
| iv. Thiopental | D. 5 |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Q.6 An example of drug from class NSAIDs?
a) Tolazoline
b) Phenacetin
c) Amphetamine
d) All of the above
Q.7 The type of ring system found in phenacetin?
a) Phenanthrene
b) Furan
c) Pyran
d) None of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-c
3-b
4-c
5-d
6-b
7-d