PARACETAMOL (ACETAMINOPHEN) Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
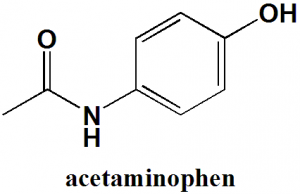
Acetaminophen
or
Paracetamol
IUPAC nomenclature
[2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acidClassification
- Analgesic- antipyretic with poor anti-inflammatory action
- Paraaminophenol derivative
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 151.16 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline solid; forms monoclinic crystals from water |
| 3 | Melting point | 170°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very slightly soluble in cold water; freely soluble in alcohol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.46 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Acetaminophen inhibits cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2) which in turn decreases the production of prostaglandins.
- Prostaglandins are responsible for the transmission of pain and inflammation and thus, reducing the amount of prostaglandins helps in reducing the pain and inflammation in the body.
- There is no peripheral anti-inflammatory effect by the drug as it does not inhibit COX in peripheral tissues.
- Acetaminophen also selectively inhibits COX-3 enzymes.
- The antipyretic action of the drug is due to direct action of the drug on the heat-regulating centers in the brain. This results in sweating, vasodilation and loss of body heat.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of Acetaminophen can be summarized as follows:
- Aminophenols are less toxic than corresponding aniline.
- Etherification of the phenolic function with methyl or propyl groups results in the derivatives having greater side effects than with ethyl groups.
- Substitution on the nitrogen with such groups that decreases the basicity also reduces the activity of the drug.
- Amides derived from aromatic acids are less active or inactive. [1]
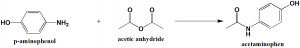
Method of synthesis
Acetaminophen can be synthesised by reactio of p-amiophenol with acetic anhydride. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Acetaminophen is used for:
- Treatment of mild to moderate pains
- Reducing fever
Side Effects
Side effects of Acetaminophen are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Allergic reactions
- Insomnia
MCQs
Q.1 “[2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Paracetamol
b) Acetaminophen
c) Methotrexate
d) Both a) and b)
Q.2 Types of crystals formed by paracetamol on treatment with water?
a) Monoclinic
b) Triclinic
c) Orthorhombic
d) Cubic
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Acetaminophen | A. Carbamate cholinesterase inhibitor |
| ii. Physostigmine | B. α-adrenergic blocker |
| iii. Phentolamine | C. Benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic |
| iv. Alprazolam | D. Analgesic-antipyretic |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
Q.4 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug acetaminophen can be?
I. Decreases in prostaglandin synthesis
II. Increase in prostaglandin synthesis
III. Stimulation of COX-2
IV. Inhibition of COX-2
a) I – IV
b) III – II
c) IV – I
d) I – III
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug acetaminophen can be?
- Aminophenols are more toxic than corresponding aniline.
- Etherification of the phenolic function with methyl or propyl groups results in the derivatives having greater side effects than with ethyl groups.
- Substitution on the nitrogen with such groups that decreases the basicity increases the activity of the drug.
- Amides derived from aromatic acids are less active or inactive.
a) TTFF
b) FFTF
c) FTFT
d) FTTF
Q.6 Acetaminophen can be synthesized by reacting acetic anhydride with?
a) p-aminophenol
b) p-aminobenzoic acid
c) 3-chlorophenol
d) tert-butyl alcohol
Q.7 The drug acetaminophen is mainly used for?
a) Reducing pain and fever
b) Systematic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
c) Treatment of severe cholinergic toxicity
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-d
2-a
3-b
4-c
5-c
6-a
7-a