PROMETHAZINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
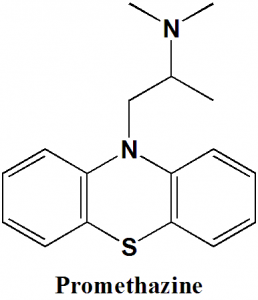
Promethazine
IUPAC nomenclature
N,N-dimethyl-1-phenothiazin-10-ylpropan-2-amine
Classification
- H1-receptor antihistamine
- Phenothiazine derivative antihistamine drug
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 284.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to faint yellow crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 60oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in dilute hydrogen chloride |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 4.4 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Phenothiazine |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Promethazine is an antagonist for histamine H1 receptors, which made it useful for treatment of allergies.
- It has antagonistic effects on muscarinic and NMDA receptors which contribute to its use as a sleep aid and for controlling anxiety and tension.
- These also make promethazine useful for the treatment of nausea and vomiting by producing action at vomiting center.
Structure Activity Relationship
Structure activity of phenothiazine derivatives antihistamines can be summarized as:
- There are 2-3branched alkyl chain between the ring system and the nitrogen atom.
- On unbranching, antipsychotic series of drugs can be obtained.
General structure activity of first generation H1-receptors antagonist can be summarized as:
- Ethylene chain gives maximum activity.
- Increasing or decreasing the chain length decreases the activity of drug, but promethazine is an exception.
- Chain may be present in saturated or unsaturated form, or sometimes a part of a ring system.
- Diaryl substitution is essential for significant H1 receptor affinity.
- Terminal nitrogen atom should be tertiary in nature.
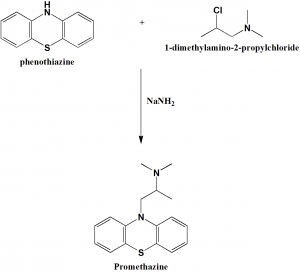
Method of synthesis
Alkylation of phenothiazine with 1-dimethylamino-2-propylchloride gives promethazine. [1]
Medicinal Uses
Promethazine is used for treatment of:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Motion sickness
- Rash
- Itching
- Runny nose
- Tension
- Pain relief
Side Effects
Side effects of Promethazine are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Blurred vision
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
MCQs
Q.1 “N,N-dimethyl-1-phenothiazin-10-ylpropan-2-amine” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Loxapine
b) Clozapine
c) Promethazine
d) Clemastine
Q.2 Melting point of Promethazine is?
a) 284oC
b) 93oC
c) 60 oC
d) 652oC
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Promethazine | A. H1-receptor antihistamine |
| ii. Cimetidine | B. Calcium channel blocker |
| iii. Glipizide | C. Antidiabetic agent |
| iv. Verapamil | D. H2-antihistamine |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Q.4 Mechanism of action of Promethazine includes?
I. Antagonistic effects on H1-receptor.
II. Antagonistic effects on H2-receptor.
III. Effects on Muscarinic receptors
IV. Reduction in acidity of stomach
a) I, II
b) II, IV
c) I, II, III
d)I, III
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of Phenothiazine derivatives antihistamines drugs can be?
- There are 2-3branched alkyl chain between the ring system and the nitrogen atom.
- On unbranching, antipsychotic series of drugs can be obtained.
- Ethylene chain gives maximum activity.
- Increasing or decreasing the chain length decreases the activity of drug, but promethazine is an exception.
a) TTFT
b) TFTF
c) TTTT
d) FFTT
Q.6 Reaction of phenothiazine with 1-dimethylamino-2-propylchloride produces which drug?
a) Promazine
b) Clonidine
c) Mechlorethamine
d) None of the above
Q.7 The drug Promethazine is mainly used for treatment of?
a) Nausea
b) Motion sickness
c) Tension
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-c
2-c
3-a
4-d
5-c
6-d
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.