Properties of Coloring agents, Pigments, flavoring agents, diluting agents and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam
Colors And Pigments: There are two basic types of coloring agents for pharmaceutical products: dyes and lakes. Dyes are soluble forms of a particular color. They go into solution and can result in very deep, vibrant colors. Lakes are dyes that undergo a processing step that adheres them onto insoluble substrates, such as aluminum or calcium salts. Dyes are usually used in liquid products, whereas lakes are used in chewable products and coating solutions for tablets.
Flavors: These materials were originally natural products; however, many companies have been created to develop synthetic versions of different flavors. Most manufacturers of finished products provide these Flavor Houses with samples of in-process material for flavoring. By using a Flavor House, unique flavor notes can be imparted to the product that will facilitate brand recognition.
Diluents/Fillers: When considering solid dosage forms, such as tablets and capsules, these ingredients function as a bulking agent for low dose actives, facilitating compression or encapsulation. Diluents are also used in lyophilized products, serving the same purpose of providing bulk to the product, but might be different materials.
Examples – Calcium carbonate, Calcium sulfate, Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), Powdered cellulose, Dextrates, Dextrin, Dextrose, Kaolin, Lactose, Maltodextrin, Mannitol, Starch, Sucrose.
1.Calcium carbonate:
INN: Carbonic acid, calcium salt; Calcium carbonate
Synonyms: Cal-Carb; precipitated calcium carbonate
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Carbonic acid calcium salt (471-34-1)
Molecular Formula: CaCO3
Description: Odorless and tasteless white powder, crystals, or granules.
Properties: Moisture content less than 1%, insoluble in all pharmaceutical solvents; particle size can vary depending upon grade. Reacts with acids to release carbon dioxide.
Incompatibilities: All acids and ammonium salts.
Uses: As a diluent in tablet formulations and as an opacifier in tablet coatings. It does have therapeutic uses as a nutritional supplement and as an antacid.
2.Calcium sulfate:
INN: Calcium sulphate dihydrate; Calcium sulfate
Synonyms: Sulfuric acid, calcium salt (1:1); Gypsum; Terra Alba
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Calcium sulfate [7778-18-9]; CaSO 4 dihydrate [10101-414]
Molecular Formula: CaSO4 and CaSO42H2O
Description: Fine, white to slightly yellow-white, odorless powder or granule.
Properties: Dissolves in diluted HCl; slightly soluble in water; free flowing powder/granule with a density of 2.3 g/cc.
Incompatibilities: Forms complexes with amines and amino acids, when excessive moisture is present, certain antibiotic preparations (i.e., tetracycline, erythromycin, which complex with calcium containing products).
Uses: As a diluent in the manufacture of compressed tablets.
3.Microcrystalline cellulose:
INN: Microcrystalline cellulose; Cellulosum
microcrystallinum
Synonyms: Cellulose gel; crystalline cellulose; Avicel PH
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Cellulose [9004-34-6]
Molecular Formula: (C6H10O5)n, where n = 220
Structure:
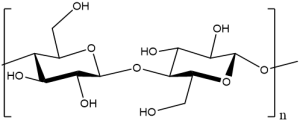
Description: Fine, white, odorless, crystalline powder; consists of free-flowing, non-fibrous particles.
Properties: Insoluble in water, dilute acids, or most organic solvents; slightly soluble in NaOH solution (1 in 20); density approximately 1.5120-1.668 g/cc; moisture content (grade specific) ranges from 1.5–5.0%; particle size varies by grade from <20–200μ.
Incompatibilities: Strong oxidizing agents.
Uses: As a tablet diluent, disintegrant, and dry binder.
4.Powdered cellulose:
INN: Powdered cellulose
Synonyms: Elcema, Solka-Floc
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Cellulose [9004-34-6]
Molecular Formula: (C6H10O5)n
Structure:
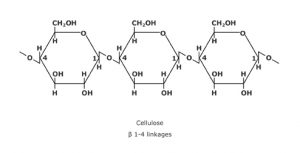
Description: White, odorless substance, consisting of fibrous particles, exhibiting degrees of fineness, ranging from a free-flowing dense powder to a coarse, fluffy, non-flowing material.
Properties: Insoluble in water, dilute acids, and nearly all organic solvents; slightly soluble in NaOH solution (1 in 20); poorly flowing, due to its fibrous nature, but compressible; particle size is dependent upon the grade.
Incompatibilities: No known incompatibilities.
Uses: As a tablet diluent, binder, or adsorbent.
5.Dextrates:
INN: Dextrate
Synonyms: Emdex, Corn Syrup Solids
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Dextrates (39404-33-6)
Molecular Formula: Purified mixture of saccharides (hydrated or anhydrous), with a dextrose equivalent of NLT 93% and NMT 99%
Description: A white, free-flowing, odorless powder that is sweet tasting. Dextrates are comprised of dextrose and 3–5% maltose and lesser amounts of higher dextrose oligomers (maltotriose, maltotetrose, etc.)
Properties: 1 in 1 parts in water, insoluble in ethanol; mean particle size of approximately 200μ; flow 9.3 g/sec.
Incompatibilities: Incompatible with oxidizing agents and under the proper conditions primary and secondary amines.
Uses: As a tablet diluent and sweetening agent for chewable tablets.
6.Dextrin:
INN: Dextrin
Synonyms: British Gum; Starch Gum
Chemical Name & CAs Number: Dextrin (9004-53-9)
Molecular formula: (C6H10O5)n
Structure:
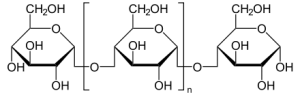
Description: White or yellow, amorphous powder (white: practically odorless; yellow: characteristic odor); dextrorotatory; does not reduce Fehling’s solution; gives a reddish color with iodine.
Properties: Soluble in boiling water (forming a gummy solution); less soluble in cold water; moisture content of 5%; density approximately 1.5 g/cc.
Incompatibilities: Strong oxidizing agents.
Uses: As a tablet diluent and binder; as a suspending agent.
7.Dextrose:
INN: Glucose; Glucose monohydrate; Dextrose; Glucosum monohydricum
Synonyms: Blood Sugar; Anhydrous Dextrose; Dextrose Monohydrate; D-(+)Glucopyranose monohydrate; Medicinal Glucose; Purified Glucose; Grape Sugar; Bread Sugar; Cerelose; Starch Sugar; Corn Sugar
Chemical Name & CAS Number: D-Glucose monohydrate(5996-10-1); anhydrous (50-99-7)
Molecular Formula: Monohydrate: C6H12O6 • H2O
Structure:
Description: White, odorless, sweet tasting crystalline or granular powder.
Properties: Solubility 1 g in 1 mL of water or 100 mL of alcohol; more soluble in boiling water or boiling alcohol; density of 1.5 g/cc; melting point 83°C.
Incompatibilities: Aldehyde form interacts with amines, amides, amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Novobiocin sodium, warfarin sodium, and kanamycin sulfate.
Uses: As a filler/binder in solid dosage forms; sweetening agent for liquids and chewable tablets; and a tonicity agent and vehicle in parenteral formulations.
8.Kaolin:
INN: Heavy Kaolin, Kaolin
Synonyms: Bolus alba; china clay; kaolinite; porcelain clay; weisserton; white bole
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Hydrated aluminum silicate(1332-58-7)
Molecular Formula: Al2H4O9Si2
Structure: Al2O3·2SiO2·2H2O
Description: White to off-white powder that develops an odor of clay when moistened.
Properties: pH 4.0–7.5 for 20% slurry; particle size 0.6-0.8μ.
Incompatibilities: Kaolin has been known to influence to absorption of certain drugs: amoxicillin, cimetidine, digoxin, and phenytoin to name a few.
Uses: As a diluent in tablets and capsules; as a suspension vehicle in liquids.
9.Lactose:
INN: Lactose; Lactose monohydrate; Lactosum
Synonyms: Milk sugar
Chemical Name & CAS Number: O-β-D-Galactopyranosyl-(1-4)-α-D-glucopyranose anhydrous(63-42-3), O-β-D-Galactopyranosyl-(1-4)-α-D-glucopyranose monohydrate (64044515)
Molecular Formula: C12H22O11. H2O
Structure:
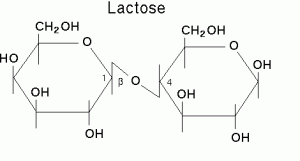
Description: White or creamy white, hard, crystalline masses or powder; odorless; faintly sweet taste.
Properties: 1 g in 5 mL water or 2.6 mL boiling water; very slightly soluble in alcohol; pH 4 6.5 of a 10% aqueous solution; density 1.552g/cc; moisture of 1% for anhydrous and NMT 5% for monohydrate.
Incompatibilities: Maillard reaction with amine containing compounds; amino acids, aminophylline and amphetamines.
Uses: As a diluent in tablet and capsule formulations. The amorphous and mono-hydrate forms are used in wet granulation processing of materials, whereas the spray-dried anhydrous type is used in direct compression formulations. It is an ingredient of the medium used in penicillin production. It is used extensively as an addition to milk for infant feeding.
10.Maltodextrin:
INN: Maltodextrin
Synonyms: Numerous trade names
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Maltodextrin (9050-36-6)
Molecular Formula: (C6H10O5)n.H2O
Structure:
Description: Non-sweet, odorless, white powder or granules.
Properties: Density range 0.13-0.58 g/cc, depending on manufacturer; freely soluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol; viscosity varies, depending on manufacturer.
Incompatibilities: Certain conditions might result in a discoloration with amino acids and amines,
Uses: As a coating agent for tablets; tablet and capsule diluent; tablet binder and viscosity modifier.
11.Mannitol:
INN: Mannitol; d-Mannite; Mannitolum
Synonyms: Cordycepic acid; d-mannitol; manna sugar; mannite
Chemical Name & CAS Number: D-Mannitol (69-65-8)
Molecular Formula: C6H14O6
Structure:
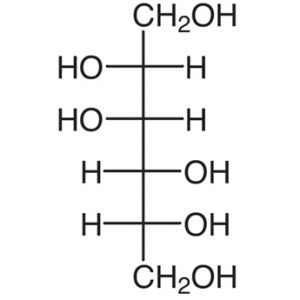
Description: White, odorless crystalline powder or free flowing granules with a sweet taste and a cooling effect.
Properties: Density 1.514 g/cc; heat of solution -120.9J/g; particle size varies, depending on manufacturer; solubility in water is 1 in 5.5, in ethanol 1 in 83, and glycerin is 1 in 18.
Incompatibilities: None reported in dry applications; at concentrations above 20% in solution, salting effects might be seen with potassium or sodium.
Uses: As a sweetening agent for chewable tablets and oral liquids; tablet/capsule diluent; tonicity agent; vehicle for lyophilized products.
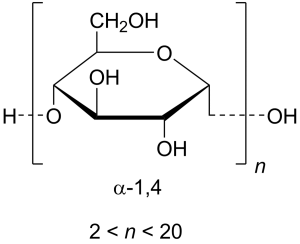
12.Starch:
INN: Maize-, Potato-, Rice-, Tapioca-, Wheat- starch; Maydis-, Oryzae-, Solani-, Tritici- amylum
Synonyms: Corn Starch; Wheat Starch; Potato Starch
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Starch (9005-25-8)
Molecular Formula: (C6H10O5)n
Structure:
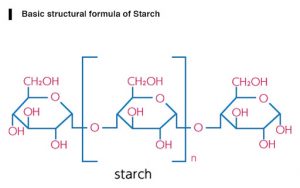
Description: Irregular, angular, white masses or fine powder; odorless; slight, characteristic taste.
Properties: Insoluble in cold water or alcohol; when it is boiled with about 20 times its weight of hot water for a few minutes and then cooled, a translucent, whitish jelly results; aqueous suspension neutral to litmus.
Incompatibilities: No known incompatibilities.
Uses: As a filler, binder, and disintegrant for tablets and capsules.
13.Sucrose:
INN: Sucrose; Saccharum
Synonyms: α-D-glucopyranosyl-β-Dfructofuranoside; Sugar; Cane Sugar;Beet Sugar
Chemical Name & CAS Number: β-D-fructofuranosyl– α-Dglucopyranoside (57-50-1)
Molecular Formula: C12H22O11
Structure:
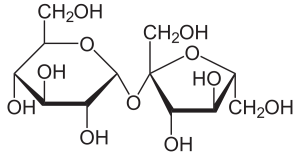
Description: Occurs as a colorless mass or block, or as a white odorless and sweet tasting crystalline powder.
Properties: Solubility 1 g in 0.5 mL water, 170 mL alcohol; density 1.6g/cc; hygroscopic capable of absorbing 1% moisture.
Incompatibilities: Sucrose has no known incompatibilities; however, the naturally occurring trace materials in sucrose could result in issues. These trace materials include heavy metals, which could interfere with some APIs (e.g., ascorbic acid), and sulfite, which could result in discoloration of tablet coatings.
Uses: As a sweetener in oral liquids and solids; coating material for tablets; diluent for parenteral products.
Multiple choice questions:
1.Which of the following are basic types of coloring agents for pharmaceutical products?
a)dyes
b)lakes
c)both of these
d)none of these
2.In which of the following preparations dyes are used?
a)liquid products
b)chewable products
c)coating solutions for tablets
d)all of these
3.In which of the following preparations lakes are used?
a)liquid products
b)chewable products
c)coating solutions for tablets
d) b and c
4.When considering solid dosage forms, such as tablets and capsules, these ingredients function as a bulking agent for low dose actives, facilitating compression or encapsulation. Identify them
a)Diluents
b)Fillers
c)Lubricants
d)a and b
5.Which of the following are examples of diluents?
a)Dextrates
b)Dextrin
c)Dextrose
d)All of these
6.Calcium carbonate is incompatible with
a)All acids and ammonium salts
b)Amino acids
c)Certain antibiotic preparations
d)Strong oxidizing agents
7.Synonym of Calcium sulfate is/are
a)Sulfuric acid
b)Calcium salt
c)Gypsum
d)All of these
8.What are the synonyms of Microcrystalline cellulose?
a)Cellulose gel
b)Crystalline cellulose
c)Avicel PH
d)All of these
9.Powdered cellulose shows incompatibilities with
a)Amino acids
b)Certain antibiotic preparations
c)Strong oxidizing agents
d)No known incompatibilities
10.Dextrates is used as
a)tablet diluent
b)sweetening agent for chewable tablets
c)both of these
d)none of these
11.Dextrin is also known as
a)British Gum
b)Starch Gum
c)Milk sugar
d)a and b
12.C6H12O6 • H2O is molecular formula of
a)Dextrates
b)Dextrin
c)Dextrose
d)Lactose
13.Lactose is also known as
a)British Gum
b)Starch Gum
c)Milk sugar
d)Manna sugar
14.Mannitol is used as
a)agent for chewable tablets and oral liquids
b)tonicity agent
c)vehicle for lyophilized products
d)all of these
15.C12H22O11 is molecular formula for
a)Maltodextrin
b)Starch
c)Sucrose
d)Kaolin
Solutions:
- c)both of these
- a)liquid products
- d) b and c
- d)a and b
- d)All of these
- a)All acids and ammonium salts
- d)All of these
- d)All of these
- d)No known incompatibilities
- c)both of these
- d)a and b
- c)Dextrose
- c)Milk sugar
- d)all of these
- c)Sucrose
References:
- Remington Essential of Pharmaceutics, 1st edition 2013, page no. 688,689,690,691,692,694,695,696,701,702.
- Raymond C Rowe Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th edition, page no. 86-89, 105-107, 129-133, 136-138, 218-225, 352-354, 418-420, 424-428, 685-691, 703-707.
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE