TENOXICAM Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
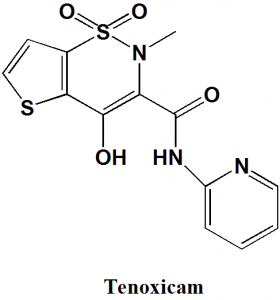
Tenoxicam
IUPAC nomenclature
4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-ylthieno[2,3-e]thiazine-3-carboxamide
Classification
- NSAID
- Oxicames
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 337.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 211oC |
| 4 | Solubility | 14.1 mg/ml |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.9 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyridine, thiophene, thiazine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Tenoxicam inhibits Cyclooxygenase which in turn reduces the prostaglandin synthesis.
- Antipyretic effect of drug is due to its action on the hypothalamus which results in peripheral dilation, increased blood flow and heat loss.
Structure Activity Relationship
General SAR for Oxicams can be summarized as follows:
- Substitution on the nitrogen atom of the thiazine ring gives optimum activity.
- Substitution on the caboxamide with aryl group gives compounds with greater activity than when substituents are alkyl groups.
- N-heterocyclic compounds are more acidic than N-aryl carboxamides.
- Primary carboxamides are more potent than secondary carboxamides.
- m-substituted derivatives are more potent than p-substituted derivatives.
- Maximum activity is found with m-Cl substituent in the aryl series.
- Substitution on the carboxamide Nitrogen with heteroaryl group gives compound with seven fold greater anti-inflammatory activity than the aryl group substitution. [1]
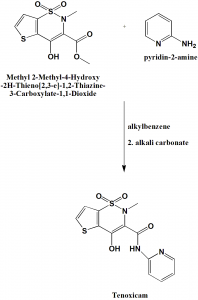
Method of synthesis
i. Methyl 2-Methyl-4-Hydroxy-2H-Thieno[2,3-e]-1,2-Thiazine-3-Carboxylate-1,1-Dioxide is mixed with 2-aminopyridine in alkylbenzene.
ii. Alkali carbonate is added afterwards, dried and activated at 150o
iii. Crude drug is obtained from the crystals which are generated on cooling and filtering it.[2]
Therapeutic Uses
Tenoxicam is used for:
- Treatment of pain and swelling due to rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, bursitis and perarthritis.
Side Effects
Side effects of Tenoxicam are:
- Abdominal pain
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Ringing in ears
- Palpitations
- Skin rash
- Itching
- Swellings of limbs
- Allergic reactions
- Shortness of breath
- Easy bleeding
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Tenoxicam?
a) 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)-1,1-dioxo-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide
b) 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)-1,1-dioxo-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-Carboxylic acid
c) 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-ylthieno[2,3-e]thiazine-3-carboxamide
d) 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-ylthieno[2,3-e]thiazine-3-Carboxylic acid
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of oxicams?
I. Substitution on the caboxamide with aryl group gives compounds with lesser activity than when substituents are alkyl groups.
II. N-heterocyclic compounds are less acidic than N-aryl carboxamides.
III. Primary carboxamides are more potent than secondary carboxamides.
IV. m-substituted derivatives are more potent than p-substituted derivatives.
a) I
b) II
c) I, II
d) IV
Q.3 Medicinal uses of tenoxicam is/are?
a) Treatment of pain due to rheumatoid arthritis
b) Treatment of Bradycardia
c) Reducing Blood pressure
d) All of the above
Q.4 Side effects of drug Tenoxicam is/are?
a) Ringing in ears
b) Abdominal pain
c) Easy bleeding
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with the correct number of the chiral carbons they have in their structure:
| i. Tenoxicam | A. 5 |
| ii. Bitolterol | B. 0 |
| iii. Atropine | C. 4 |
| iv. Metaraminol | D. 1 |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Q.6 An example of drug from class NSAIDs?
a) Tenoxicam
b) Propantheline
c) Ethopropazine
d) Salbutamol
Q.7 The type of ring system found in Tenoxicam?
I. Isoxazole
II. Pyridine
III. Thiazine
IV. Thiophene
a) I, III
b)II, III, IV
c) I, III, IV
d) II, IV
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-c
3-a
4-d
5-d
6-a
7-b