ZALEPLON Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Zaleplon
IUPAC nomenclature
N-(3-(3-cyanopyrazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidin-7-yl)phenyl)-N-ethylacetamide
Classification
Zaleplon is a nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 305.33 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 157-159°C |
| 4 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.9 |
| 5 | Solubility | Very low solubility in water as well as in alcohol |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyrrozolol pyrimidine, benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Zaleplon modulate the subunit GABABZ receptor chloride channel macromolecular complex.
- It also selectively binds to brain Omega1 receptor which is present on the α-subunit of the GABAA chloride ion channel receptor complex and potentiates t-butyl-bicyclophosphorothionate binding.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Zaleplon exhibit 10-fold greater selectivity for the α1 than α3 and α5 containing GABAA receptors with comparison to indiplon which shows only 1.6- and4-fold selectivity.
- The affinity of indiplon for α1, α3 and α5 containing receptors is 3-, 12- and 17- folds higher than the zaleplon.
- Indiplon is more than 100-fold more potent than zaleplon.
- Electronic factors are responsible for the selectivity. [1]
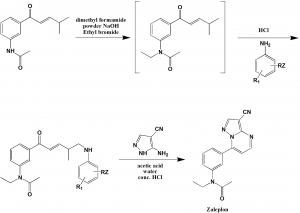
Method of synthesis
i. N-[3- [3-(dimethylamino)-1-oxo-2-propenyl]phenyl]acetamide is mixed with dimethyl formamide wand stired. Powdered sodium hydroxide is then addedfollowed by addition of tetrabutylammonium bromide. Ethyl bromide is added thereafter.
ii. P-chloroanilie is then added to the reaction vessel followed by addition of hydrochloric acid.
iii. Zaleplon can be obtained in crystalline form which is then filtered and washed with water.
Therapeutic Uses
Zaleplon is used for:
- Treatment of insomnia
Side Effects
Side effects of Zaleplon are:
- Dizziness
- Difficulty in coordination
- Drowsiness
- Short-term memory loss
- Allergic reactions
MCQ
Q.1 Zaleplon binds with acetylcholine nicotinic receptors results in?
a) Agonizing effect on muscarinic receptors
b) Antagonizing effect on muscarinic receptors
c) Do not produce any significant effect
d) Do not bind with nicotinic receptor
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug Zaleplon is/are?
a) Treatment of Acute alcohol withdrawal
b) Treatment of Insomnia
c) Treatment of anxiety
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of drug Zaleplon?
I. Zaleplon exhibit 10-fold greater selectivity for the α1 than α3 and α5 containing GABAA receptors with comparison to indiplon which shows only 1.6- and4-fold selectivity.
II. he affinity of indiplon for α1, α3 and α5 containing receptors is 3-, 12- and 17- folds higher than the zaleplon.
III. Indiplon is more than 100-fold more potent tha zaleplon.
IV. Electronic factors are resposnsible for the selectivity.
a) I, IV
b) I, II, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) II, III, IV
Q.4 Type of ring structures present in the structure of Zaleplon?
a) Triazole
b) Pyrrozolol pyrimidine
c) Diazepine
d) All of the above
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug solifenacin?
I. Molecular weight is 208.8 gm/mol
II. Produces violet crystals from ethylacetate
III. Melting point is between 228-229°C
IV. Diazepine ring is present
a) TFTF
b) TTTT
c) FFFF
d)FFFT
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the are?
I. Solifenacin: (3R)-1-Azabicyclo[2 2 2]oct-3-yl (1S)-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate
II. Zaleplon: N-(3-(3-cyanopyrazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidin-7-yl)phenyl)-N-ethylacetamide
III. Alprazolam: 7-Chloro-1,3-dihydro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-3H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
IV. Diazepam: 8-Chloro-1-methyl-6-phenyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine
a) II, IV
b) I, II
c) I, III, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Solifenacin | A. Barbiturate sedative-hypnotic |
| ii. Thiobarbital | B. Benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic |
| iii. Alprazolam | C. Acetylcholine antagonist |
| iv. Zaleplon | D. Nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
c) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT, Pharmacist,Drug Inspector
ANSWERS
1-d
2-b
3-c
4-b
5-c
6-b
7-a