METHADONE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
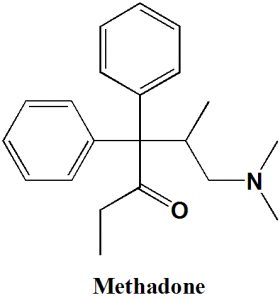
Methadone
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenylheptan-3-one
Classification
- Methadone falls under category of opioid analgesics.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 309.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 235°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in ethanol. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.93 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Methadone shows full agonist activity at the mu-opioid receptor which is the primary mechanism for the treatment of pain.
- It also acts as an agonist for kappa- and sigma-opioid receptors within the peripheral and central nervous system.
- Methadone is also an antagonist for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.
- It also strongly inhibits serotonin and norepinephrine uptake which is responsible for its antinociceptive activity.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR for Opiates can be summarized as follows:
- Replacement of phenolic hydroxyl into –OCH3/-OC2H5 will make the drug less analgesic and cough suppression will also takes place.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCH3 makes the compound 5 times more active.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with -OC2H5 makes the compound 2.4 times more active than morphine.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCOCH3 will also activates the compound by 4.2 times.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with ketone group inactivates the compound and makes it lesser active.
- By hydrogenation of alicyclic unsaturated linkage, activity increases by 1.2 times.
- On replacement of the methyl group from tertiary nitrogen by hydrogen atom, activity decreases.
- On replacement of N-CH3 by NCH2CH2Ph, activity increases by 14 times.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N-allyl/methallyl/propyl, the compound so formed acts like the Morphine antagonist.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N(CH3)2 Cl– , compound have curare action and it do not possesses any analgesic activity.
Method of synthesis
i. Alkylation of 1-dimethylamino-2-propylchloride in presence of sodium amide to give 4-dimethylamino-2,2-dephenylvaleronitrile.
ii. The last compound is reacted with ethylmagnesiumbromide followed by hydrolysis.
iii. (-)-methadone is separated from racemic mixture by using (+)-tartaric acid. [1]
Therapeutic Uses
Methadone is used for:
- Treatment of addiction to opioids such as heroin
- Preventing withdrawal symptoms caused due to stopping of consumption of other opioids.
Side Effects
Side effects Methadone are:
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness
- Sleep apnea
- Mood changes
- Confusion
- Hallucinations
- Abdominal pain
- Difficulty urinating
- Loss of appetite
- Tiredness
- Weight loss
- Allergic reactions
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the Methadone.
| i. Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with ketone group | A. Activity increases |
| ii. On replacement of the methyl group from tertiary nitrogen by hydrogen atom | B. Activity decreases |
| C. Activity increases | |
| D. Activity decreases |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Methadone: Ethyl 1-methyl-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate
- Lorazepam: 7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one.
- Atropine: (N-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate
- Ephedrine: (1R,2S)-2-(methylamino)-1-phenylpropan-1-ol
a) TFFF
b) FTFT
c) TTTT
d) FTTF
Q.3 Correct statement related with the solubility of the drug Methadone from the following is?
a) Practically insoluble in ethanol
b) Slightly soluble in ethanol
c) Soluble in ethanol
d) Very soluble in ethanol
Q.4 Primary mechanism of action of methadone is due to?
a) Agonist activity at mu-opioid receptor
b) Agonist activity at sigma-opioid receptor
c) Antagonist activity at mu-opioid receptor
d) Antagonist activity at sigma-opioid receptor
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug Methadone?
a) As an antidiarrheal agent
b) Relief from moderate to severe pain
c) Treatment of addiction to opioids such as heroin
d) Treatment of seizures
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Methadone: opioid analgesics
II. Haloperidol: buterophenone antipsychotic drug
III. Oxazepam: benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
IV. Bitolterol: ß2-adrenergic agonist
a) I
b) II, IV
c) II, III
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 (-)-Methadone can be separated from the racemate by using?
a) (+)-tartaric acid
b) (-)-tartaric acid
c) Hydroxylamine
d) Sulfuric acid
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-d
2-b
3-d
4-a
5-c
6-d
7-a