Cushing’s Syndrome : Definition, Pathogenesis, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
” Cushing’s syndrome is caused due to chronic excessive production of cortisol. The condition is then called or termed as hypercortisolism.”
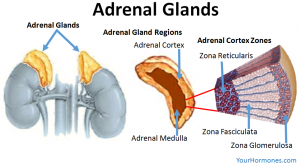
The above image is taken for education purpose only from completechiromd.com
PATHOGENESIS :-
Basically, there are four possible sources of excess cortisol. The most obvious and most common is prolonged administration of the glucocorticoids for therapeutic reasons, such as immunosupperession following transplantation. The other three spontaneous sources of the hypercortisolism can be categorized as Cushing’s syndrome :
- Pituitary secretion of ACTH.
- Ectopic production of ACTH or CRH by a non – endocrine neoplasm.
- Hypersecretion of cortisol by an adrenal adenoma, carcinoma, or nodular hyperplasia – ACTH independent.
CAUSES :-
Your body may produce high level of cortisol for a variety of reasons, including :
- High stress level, including stress related to an acute illness, surgery, injury, or pregnancy especially in the final trimester.
- Athletic training.
- Malnutrition.
- Alcoholism
- Depression, panic disorder, or high level of emotional stress.
SYMPTOMS :-
The most common symptom of this condition are :
- Weight gain
- Fatty deposit, especially in the midsection, the face, and between the shoulders and the upper back
- Purple stretch marks on the breasts, arms, abdomen, and thighs
- Thinning skin that bruises easily
- Acne
- Fatigue
- muscle weakness
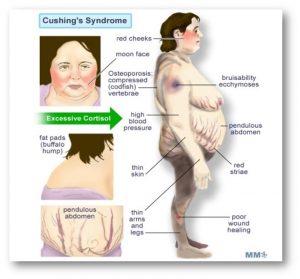 The above image is taken for education purpose only from sterotx.com
The above image is taken for education purpose only from sterotx.com
TREATMENT :-
The overall purpose of Cushing’s syndrome treatment is to lower the level of cortisol in your body. Medications which block the effect of cortisol on your tissues are as follows :
- ketoconazole (Nizoral)
- mitotane (Lysodren)
- metyrapone (Metopirone)
- pasireotide (Signifor)
- mifepristone (Korlym, Mifeprex)
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :-
1.] In Cushing’s syndrome the tumor is associated with ?
a. Increased level of epinephrine
b. Decreased level of epinephrine
c. Elevated level of cortisol
d. Increased level of non epinephrine
2.] Most common cause of Cushing’s syndrome is ?
a. Exogenous corticosteroids
b. Pituitary tumor
c. Adrenal adenoma
d. Adrenal carcinoma
3.] Most common cause of Cushing’s syndrome is ?
a. Pituitary adenoma
b. Adrenal adenoma
c. Exogenous steroids
d. Ectopic ACTH
4.] Pseudo – cushing syndrome is seen in ?
a. Chronic alcoholism
b. Adrenal carcinoma
c. Incidentaloma
d. Nelson syndrome
5.] True about Cushing’s syndrome is ?
a. Associated with MEN 1 syndrome
b. Bronchial carcinoid causes Cushing’s syndrome
d. Hypokalemia
d. Associated with coronary accidents
6.] Cushing’s syndrome is commonly caused by ?
a. Adrenal adenoma
b. Adrenal hyperplasia
c. Ectopic adrenal hormone production
d. Adrenal carcinoma
7.] Not seen in Cushing’s syndrome ?
a. Hypoglucemia
b. Hypertension
c. Frank psychosis
d. Hypokalemia
8.] In Cushing’s syndrome which of the following feature is most common ?
a. Hypertension
b. Purple skin striae
c. Thin skin
d. Truncal obesity
9.] Primary cause of death in Cushing’s syndrome ?
a. Cardiovascular disease
b. Infection
c. Suicide
d. Renal failure
10.] Drugs useful in the treatment of Cushing’s disease include ?
a. Aminoglutehimide
b. Cyproheptadine
c. Etomidate
d. All of the above
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (c) Elevated level of cortisol
2.] (a) Exogenous corticosteroids
3.] (c) Exogenous steroids
4.] (a) Chronic alcoholism
5.] (a) Associated with MEN 1 syndrome
6.] (c) Ectopic adrenal hormone production
7.] (a) Hypogucemia
8.] (c) Thin skin
9.] (a) Cardiovascular disease
10.] (d)
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 788 – 789.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no. 1150 – 1153.