Amino Acids: Structure Classification Functions and Properties and Question for GPAT, UPSC, GATE, SSC Exams
Amino acids are the monomeric units or the building blocks of proteins. These are joined together by a special type of linkages known as peptide bond. The properties of proteins depend on the sequence of amino acids.
Structure of amino acid
All the 20 amino acids which are found in proteins have a carboxyl group (-COOH) and amino group (-NH2) bound to a same carbon known as alpha-carbon.
The 20 amino acids of proteins are known as the primary or standard amino acids. These standard amino acids have been given a three letter abbreviation and one letter symbol. The abbreviations of the amino acids are the first 3 letters of the names like Serine (Ser). But 3 amino acids are exceptions which are aspargine (Asn), glutamine (Gln) and tryptophan (Trp). One of the 20 amino acids, proline is an imino acid because it contains (-NH) group and not (-NH2) group.
Classification of amino acids
Amino acids are classified on 5 basis which are as follows-
- Chemical nature of amino acid
- Structure of the side chain of amino acid
- Nature or polarity of the side chain of amino acid
- Nutritional requirement of amino acids
- Metabolic products of amino acids
Classification on the basis of chemical nature:- According to this type, amino acids are classified as-
- Neutral amino acids- Amino acids which are neutral in nature, that is that these are mono-amino and mon-carboxylic amino acids. Examples include: glycine, alanine, serine, threonine, tyrosine, proline, leucine, isoleucine glutamine etc.
- Acidic amino acid- These are mono-amino and di-carboxylic amino acids. These include: aspartic acid and glutamic acid
- Basic amino acid- These are di-amino and mono-carboxylic amino acids. These include: lysine, arginine and histidine.
Classification based on the structure of the side chain of amino acids
- Aliphatic amino acids:- Amino acids having aliphatic side chains. Examples: glycine, alanine, valine, leucine and isoleucine
- Hydroxy amino acids: Amino acids having hydroxy group in the side chain. It includes: threonine, serine and tyrosine.
- Sulfur amino acids:– Amino acids containing sulfur side chains. Examples: cysteine, methionine.
- Dicarboxylic acids and their amides:– Amino acids having carboxylic acids in the side chain. It includes: glutamic acid, aspartic acid and glutamine.
- Di-amino Acids:- Amino acids having amino group in the side chain. Examples are: lysine, arginine and histidine.
- Aromatic amino acids:- Amino acids containing aromatic side chains, examples: phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan.
- Imino acids:– Amino acids containing secondary amino acids like proline.
Classification based on nature or polarity of amino acids
The below provided flowchart describes this classification.
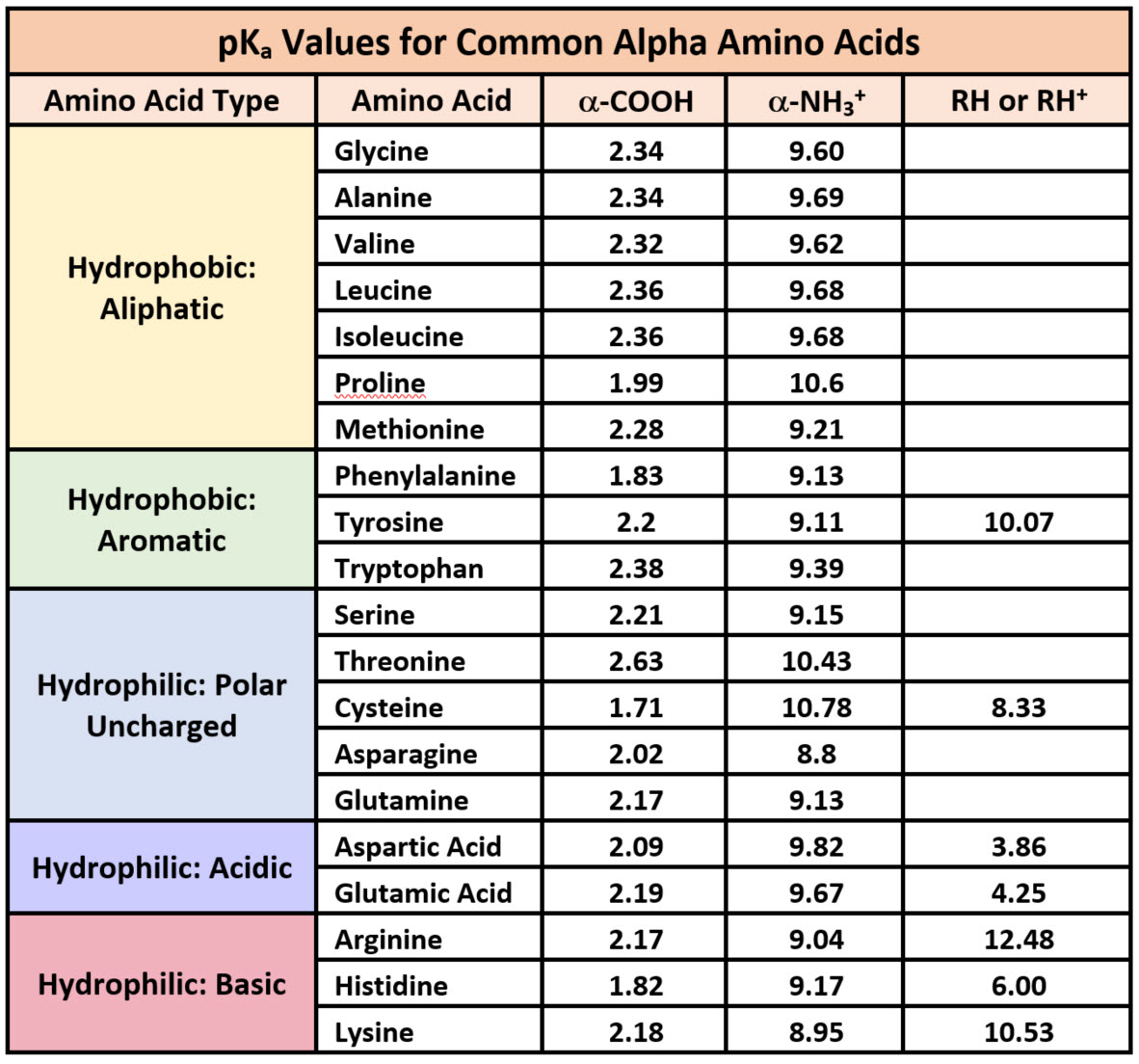
The above image is taken from wou.edu for education purpose only.
Nutritional Classification of amino acids
- Essential amino acids:- These amino acids are not synthesized in the body and hence are required to be taken n the diet. Examples are: valine, arginine, lysine, leucine, tryptophan, histidine etc.
- Non-essential amino acids:- These amino acids are synthesized in the body itself. Eg: glycine, cysteine, glutamine, glutamic acids, proline etc.
Metabolic classification of amino acids
- Glucogenic amino acids:– Those which can be converted into glucose. Fourteen out of twenty amino acids fall in this category
- Ketogenic amino acids:- Those which are converted into ketone bodies. Eg: leucine and lysine
- Both ketogenic as well as glucogenic :- Those which are converted to both glucose as well as ketone bodies. Example: isoleucine, phenylalanine, tryptophan and tyrosine.
Functions of amino acids
- Formation of proteins:- Amino acids are joined to each other to form proteins an peptides
- Formation of glucose:- Glucogenic amino acids are converted into glucose.
- Enzyme activity:- The thiol group of cysteine plays an important role in enzyme activity
- It is the transport and storage form of ammonia
- It acts as buffer solutions
- Amino acids like glycine and cysteine are involved in detoxification reactions
Properties of amino acids
- Physical properties: Amino acids are
- Colorless
- Crystalline
- Soluble in water
- Optical properties:- All the naturally occurring amino acids are optically active except glycine. All amino acids have same configuration and hence they are L-alpha amino acids.
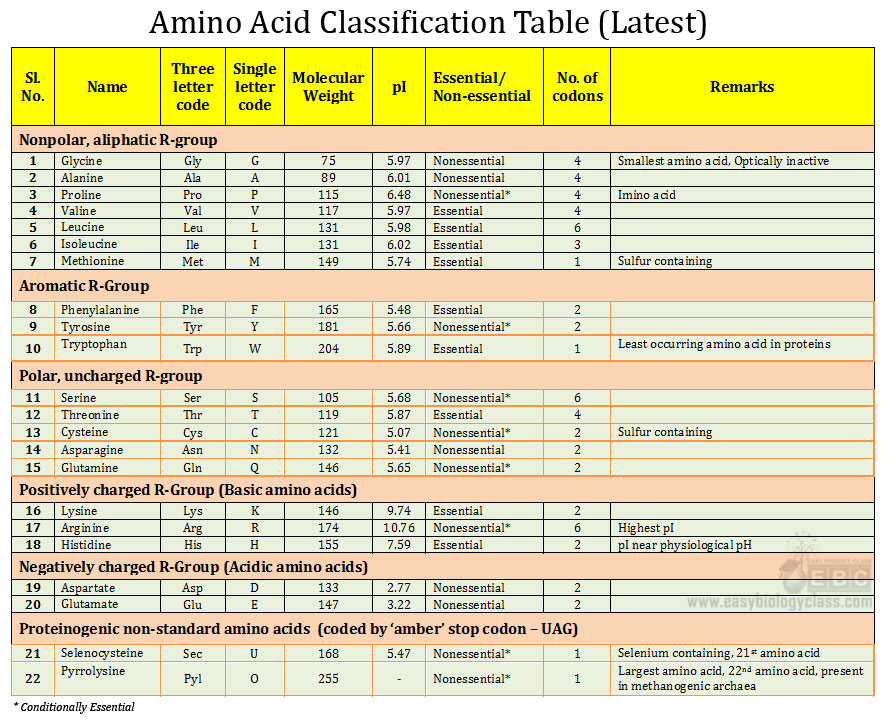
Above image is taken from easybiologyclass.com for education purpose only
Multiple choice questions (MCQs)
1. Amino acids are building blocks of which biomolecule?
A. Lipids
B. Proteins
C. Carbohydrates
D. Vitamins
2. Which group is present in the structure of amino acids?
A. Hydroxyl group
B. Carboxyl group
C. Amino group
D. Both B and C
3. Which amino acid contains imino group instead of amino group?
A. Glycine
B. Glutamine
C. Proline
D. Aspartic acid
4. Which of the following is the example of neutral amino acid?
A. Aspartic acid
B. Histidine
C. Lysine
D. Valine
5. Which of the following is the example of acidic amino acid?
A. Aspartic acid
B. Histidine
C. Lysine
D. Valine
6. On the basis of polarity of side chain of amino acid, amino acids are classified in how many types?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 5
D. 4
7. Match the following category and its respective example-
A. Hydroxyl amino acid 1. valine
B. Sulfur amino acid 2. phenylalanine
C. Aromatic amino acid 3. cysteine
d. Aliphatic amino acid 4. serine
8. Which of the following amino acid is an exception for the abbreviation rule?
A. Glutamine
B. Proline
C. Glycine
D. Cysteine
9. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. Hydrophilic amino acid are serine and tyrosine
B. Hydrophobic amino acid include tryptophan
C. Histidine is both basic as well as aliphatic amino acid
D. Tyrosine is both hydroxylic as well as aromatic amino acid
10. Which of the following is counted as an importance of amino acid?
A. Formation of proteins
B. Forms glucose
C. Act as buffer
D. All of the above
11. Which of the following is NOT the physical property of amino acid?
A. Crystalline
B. Soluble in water
C. Colorless
D. None of the above
12. Which amino acid has ketogenic as well as glucogenic products?
A. Tryptophan
B. Leucine
C. Glycine
D. All of the above
13. Which amino acid is counted as hydroxyl group amino acid?
A. Serine
B. Alanine
C. Both
D. None
14. Which amino acid is counted as aromatic group amino acid?
A. Glutamine
B. Tyrosine
C. Both
D. None
15. Which amino acid is counted as aliphatic group amino acid?
A. Serine
B. Alanine
C. Both
D. None
ANSWERS:-
- Proteins
- Both B and C
- Proline
- Valine
- Aspartic acids
- 2
- a – 4 b – 3 c – 2 d – 1
- Glutamine
- Histidine is both basic as well as aliphatic amino acid
- All of the above
- None of the above
- Leucine
- Serine
- Tyrosine
- Alanine
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 56-63