Enzyme Inhibitors: Reversible Inhibitors and MCQs for GPAT, Pharmacist, Drug Inspector Exam
There are a large no of synthetic and naturally occurring compounds which have the ability to bind to a specific enzyme and alter their activity. These are known as enzyme inhibitors. Examples include: drugs, antibiotics, toxins, anti-metabolites and some natural products to enzyme reactions. Such inhibitors are divided in two classes according to their binding ability:
- Reversible inhibitors
- Irreversible inhibitors.
In this article we will study about reversible inhibitors.
Reversible inhibitors
Reversible inhibitors bind to the enzymes through the non-covalent bonds. Reversible inhibition means that the enzyme activity can be restored fully once the inhibitor is physically removed from the system. Different types of reversible inhibitors are:
- Competitive inhibitor
- Non-competitive inhibitor
- Un-competitive inhibitor
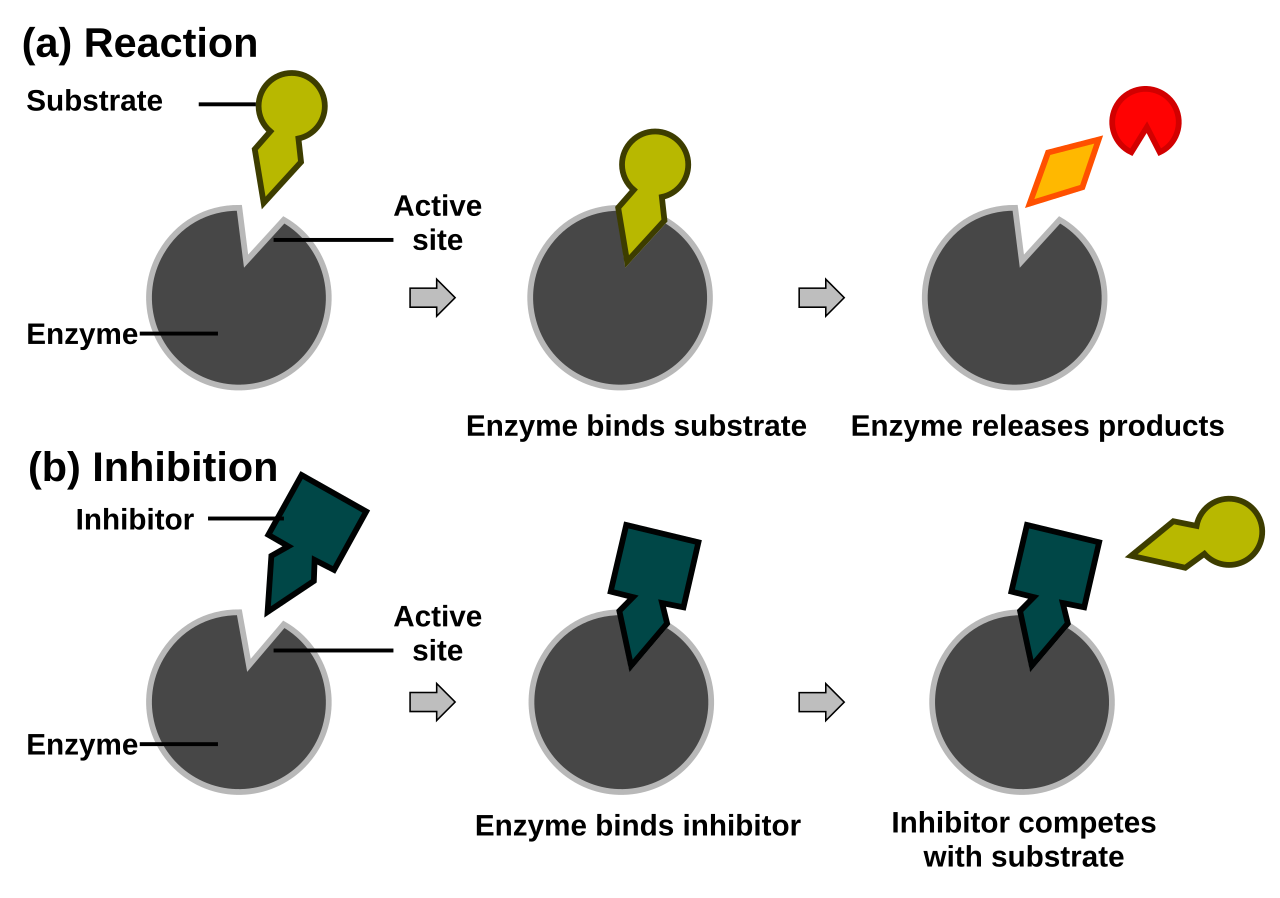
Competitive inhibitor Competitive inhibitor resembles the substrate and thus binds to the active site (substrate binding site) and forms EI complex rather than ES complex. Hence, prevents the substrate from binding at the active site of enzyme. A competitive inhibition decreases the rate of rate by reducing the production of ES complex. But on increasing the substrate concentration, competitive inhibition can be reversed. Under this condition, the substrate successfully competes with the inhibitor and binds to the enzyme. According to the Lineweaver-Burk plot of enzyme kinetics for competitive inhibition shows that in presence of a competitive inhibitor, the enzyme will have same value for Vmax, but the inhibitor increases the value of Km. Examples include:
- Fumerate and malate acts as competitive inhibitor for enzyme succinate dehydrogenase and replaces the substrate succinate.
- Methotrexate (drug for cancer) acts as competitive inhibitor for enzyme dihydrofolate reductase and replaces the substrate dihydrofolate.
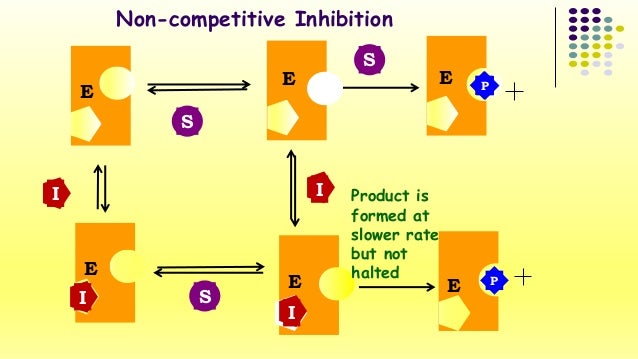
Non-competitive inhibitor In non-competitive inhibition, the inhibitor and substrate, both can bind simultaneously to an enzyme at different binding sites. A non-competitive inhibitor can bind to either a free enzyme or to an ES complex. In non-competitive inhibition, concentration of functional enzyme decreases but it does not lower the no. of ES complex. It decreases the turnover no and the value of Vmax. In non-competitive inhibition, feedback inhibition takes place, that is during enough concentration of product, the product itself acts as an inhibitor for the enzyme. Even after the formation of EI complex, the substrate can bind to the enzyme and forms ESI complex; but it can no longer form product. According to the Lineweaver-Burk plot of enzyme kinetics for non-competitive inhibition shows that in presence of a non-competitive inhibitor, the enzyme will have same value for Km, but the inhibitor decreases the value of Vmax. Example:
- Deoxycycline, an antibiotic acts as non-competitive inhibitor of collagenase enzyme.
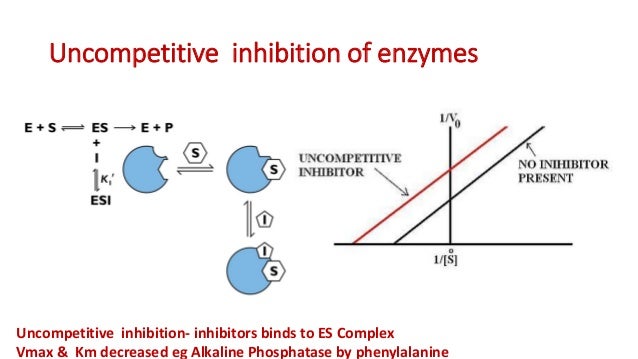
Un-competitive inhibitor Un-competitive inhibitor can bind only to the ES complex. The binding site of un-competitive inhibitor on the enzyme is created only after the formation of ES complex. The ESI complex does not form the products. Un-competitive inhibition cannot be restored at the high concentration of substrate Un-competitive inhibition lowers the Km, because inhibitor forms ESI complex and depletes ES complex. According to the Lineweaver-Burk plot of enzyme kinetics for un-competitive inhibition shows that in presence of a un-competitive inhibitor, the enzyme will have decreased value for both Vmax and Km. Example: A herbicide, glyphosate acts as un-competitive inhibitor of an enzyme in the synthesis of aromatic amino acids.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What type of compounds are enzyme inhibitors?
A. naturally occurring
B. synthetic occurring
C. both
D. none
2. Inhibitors are classified in how many types?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
3. How many types of reversible enzyme inhibitors are present?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
4. Match the following-
a. Reversible inhibition 1. Vmax unaffected
b. Irreversible inhibition 2. Vmax decreases
c. Competitive inhibition 3. Complete loss of enzymatic reaction
d. Non-competitive inhibition 4. Reaction can come back to normal
5. In which type of inhibition, the inhibitor resembles the substrate?
A. Competitive
B. Non-competitive
C. Un-competitive
D. None of these
6. For which enzyme, fumerate and malate acts as inhibitor and replaces succinate?
A. Succinase
B. Succinate dehydrogenase
C. Hexokinase
D. Succinate synthase
7. In non-competitive inhibition, what happens to the value of Vmax?
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains constant
D. No effect
8. In un-competitive inhibition, what happens to the value of Km?
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains constant
D. No effect
9. In which type of inhibition, feedback inhibition takes place?
A. Competitive
B. Non-competitive
C. Un-competitive
D. None of these
10. In competitive inhibition, what happens to the value of Km?
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains constant
D. No effect
11. In which type of inhibition, inhibitor only binds to the ES complex?
A. Competitive
B. Non-competitive
C. Un-competitive
D. All of the above
12. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. In competitive inhibition, rate of reaction decreases
B. In competitive inhibition, positive feedback takes place
C. The ES complex form binding site for un-competitive inhibitor
D. Glyphosate is also known as roundup.
13. Which of the following drug act as competitive inhibitor?
A. Mevinolin
B. Allopurinol
C. Lovastatin
D. All of the above
14. Methotrexate is the drug for which disease?
A. Cancer
B. Gout
C. Hypertension
D. Renal failure
15. In which type of inhibition, both Vmax and Km are decreased?
A. Competitive
B. Non-competitive
C. Both
D. None of the above
ANSWERS:-
1. Both
2. 2
3. 3
4. a – 4 b – 3 c – 1 d – 2
5. Competitive
6. Succinate dehydrogenase
7. Decreases
8. Decrease
9. Non-competitive
10. Increase
11. Un-competitive
12. In competitive inhibition, positive feedback takes place
13. All of the above
14. Cancer
15. None of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 91-94