Anatomy of Male Reproductive System, Notes, Lecture, and Question answer for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse Exam
Function of Male Reproductive System
the figure
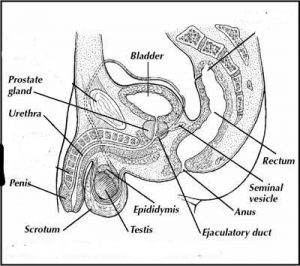
The organs of male reproductive system are described as follows:-
SCROTUM
it is a bunch of skin, connective fibrous and smooth muscle tissue.it is divided in two compartments, each having one testis and one epididymis. it lies below the pubic symphysis behind the penis.
TESTES
These are the male reproductive glands just like ovaries in female of about 4.5cm long, 3.5cm wide and 3cm thick and are suspended in the scrotum. Testes are surrounded by 3 layers of tissue-the outer covering known as tunica vaginalis, the middle fibrous covering known as tunica albuginea and the inner layer consisting of capillaries called as tunica vasculosa.
In each testis, there are 200-300 lobules and within each lobule are 1-4 convoluted loops of epithelial cells known as seminiferous tubules.
EPIDIDYMIS, VAS DEFERENS ANATOMY LECTURE
SPERMATIC CORDS
The spermatic cords suspend the testes in the scrotum. Each cord contains testicular artery, testicular veins lymphatic vessels and testicular nerves. the cord is covered with the sheet of smooth muscle, connective and fibrous tissue and extend through the inguinal canal and is attached to the testes on the posterior wall.
SEMINAL VESICLES
these are two small pouches of fibrous tissue and smooth muscle and are about 5cm long and lies on the posterior side of the bladder. At its lower end, each vesicle opens into a short duct, which joins with the deferent duct to form an ejaculatory duct.
EJACULATORY DUCTS
the ejaculatory ducts are the two tubes of about 2cm and each formed from the seminal vesicles and deferent duct (ductus deferens). they pass through the prostate gland and carries the seminal fluid and spermatozoa to the urethra. their walls are composed of smooth muscle and fibrous tissue.
PROSTATE GLAND
It lies in the pelvic cavity in front of the rectum and is completely surrounding the urethra when it comes from the bladder , outer layer is fibrous covering and inner glandular part is covered with smooth muscle. It weighs about 8g in youth and at the age of 50, the weight increases to 50g.
URETHRA
The male urethra provides common pathway for both urine and semen.It is about 20cm long and consist of three parts-the prostatic urethra which passes through the prostate gland, the membranous urethra which is the shortest and narrowest and extends from the prostate gland to the penis and lastly the spongiose/penile urethra which lies within the penis.
PENIS
The penis has a root and a shaft. the root lies in the perineum and the shaft or body is externally visible and is the movable portion of the penis. It is formed by the erectile tissue and smooth muscle present in the form of cylindrical mases. The erectile tissue is supported by fibrous tissue and has a great blood supply.
Multiple Choice Questions(MCQs)
1. Which of the following organ is known as male reproductive gland?
A. Scrotum B. testes
C. seminal vesicles D. penis
2. Where the scrotum lies?
A. below the pubic symphysis B. above the pubic symphysis
C. behind the pubic symphysis D. in front of pubic symphysis
3. Which of the following comes under the functions of male reproductive system?
A. production of spermatozoa B. delivery of spermatozoa in semen
C. maturation D. all of the above
4. Which layer of testis divides the glandular structure of testis into lobules?
A. tunica vaginalis B. tunica albuginea
C. tunica vasculosa D. both A and B
5. Which organ suspends the testes in the scrotum?
A. seminal vesicles B. spermatic cords
C. scrotum itself D. ejaculatory ducts
6. Match the following-
a) testis 1.lies in front of rectum
b) scrotum 2. Has 2 parts, root and shaft
c) penis 3. Lies behind the penis
d) prostate gland 4. Consist of 200-300 lobules
7. What are the characteristics of the shaft part of the penis?
A. externally visible b.movable part of the organ
C. both A and B D. none of the above
8. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. within each lobule of testis are the seminiferous tubules
B. the seminal vesicles contract and expel their stored contents
C. the deferent duct passes downward from the testis through the inguinal canal
D. tunica vasculosa consist of no. of capillaries.
9. Which structure is formed from the union of the seminal vesicles and deferent duct?
A. ejaculatory duct b. prostate gland
C. urethra D. spermatic cords
10. Which organ works as a passageway for both urine as well as semen?
A. penis B. testis
C. spermatic cords D. none of the above
ANSWERS:-
1. testis
2. below the pubic symphysis
3. all of the above
4. tunica albuginea
5. spermatic cords
6. a) – 4 b) – 3 c) – 2 d) – 1
7. both A and B
8. the deferent duct passes downward from the testis through the inguinal canal
9. ejaculatory ducts
10. none of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFRENCE: 1. Ross and Wilson-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.-: 459-462.