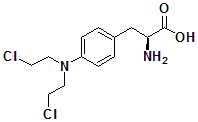
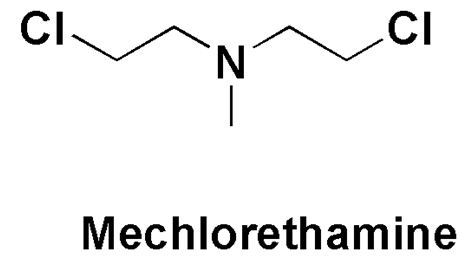
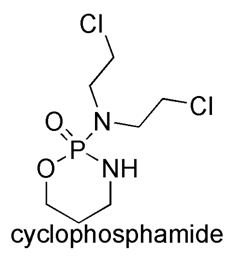
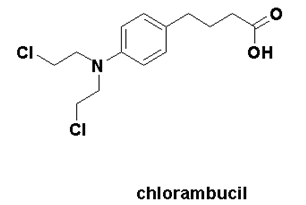
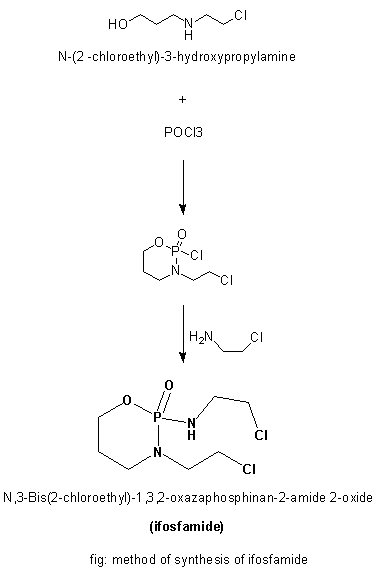
MELPHALAN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ and Chemical Structure
Melphalan It is a Anticancer Drug. IUPAC nomenclature 4-[bis(2-Chloroethyl)amino]-L-phenylalanine Classification Melphalan falls under the category of Nitrogen mustard alkalyting agents. Physiochemical Properties S. NO. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES 1 Molecular weight 305.2 g/mol 2 Appearance White to buff colored powder 3 […]