Cell Death: Definition, Causes, Processes of Cell Death, Difference between Apoptosis and Necrosis,Changes after Cell Death and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
“Cell death is a biological event of biological cell which cease them from carrying out their regular function.”
Cell death is basically a state of irreversible cell injury.
CAUSES: –
Following are the causes of cell injury:
- Local or Focal Changes in the body like necrosis, autolysis and apoptosis.
- Changes followed by local or focal changes i.e; gangrene and pathological calcification.
- Certain chemical agents and drugs
- Infectious agents
- Immunological reactions
- Genetic derangement
- Nutritional imbalances
PATHOLOGICAL PROCESSES OF CELL DEATH: –
Following are the processes involved in cell Death:
1.] Autolysis: Autolysis or self-digestion is disintegration of cell by its own hydrolytic enzymes secreted by lysosomes. Autolysis can occur in living body due to inflammatory reactions (vital reaction).
2.] Necrosis: Necrosis is defined as localised area of death of tissue followed by degradation of tissue by the hydrolytic enzymes released from the dead cell, which is later accompanied by inflammatory reaction. Necrosis occurs due to lot of factors like Hypoxia, chemical and physical agent, microbial agents etc.
There are 5 types of necrosis listed:
- Coagulative necrosis
- Liquefaction necrosis also called colliquative necrosis
- Caseous necrosis
- Fat necrosis
- Fibrinoid necrosis
3.] Apoptosis: Apoptosis is a coordinated and internally programmed cell death. When the cell is not required pathway of cell death is activated (cell suicide). It is not accompanied by any cell inflammation reaction or collateral tissue damage.
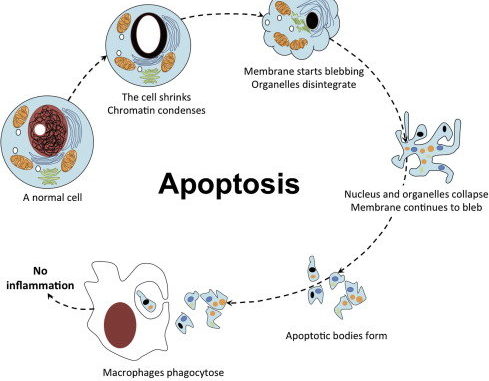
This image is taken for educational purpose from onlinebiologynotes.com
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN NECROSIS AND APOPTOSIS: –
Following are the differences between Apoptosis and Necrosis:

This image is taken for educational purpose from en.wikipedia.org
CHANGES AFTER CELL DEATH: –
Following are the changes occur after cell death:
A.] Gangrene: Gangrene refers to the death of the part of the body due to no blood supply to the tissue because of cell injury or it may be the result of any disease. Gangrenous or necrotising inflammation is characterized primarily by inflammation of virulent bacteria resulting in massive tissue necrosis.
There are two main types of gangrene:
- Dry Gangrene: This type of gangrene begins in the distal parts of limb due to ischemia.
- Wet Gangrene: Wet gangrene occur in naturally moist tissue and organ such as bowel, lung, mouth, cervix, vulva etc.
Following are the different stages of Gangrene: –
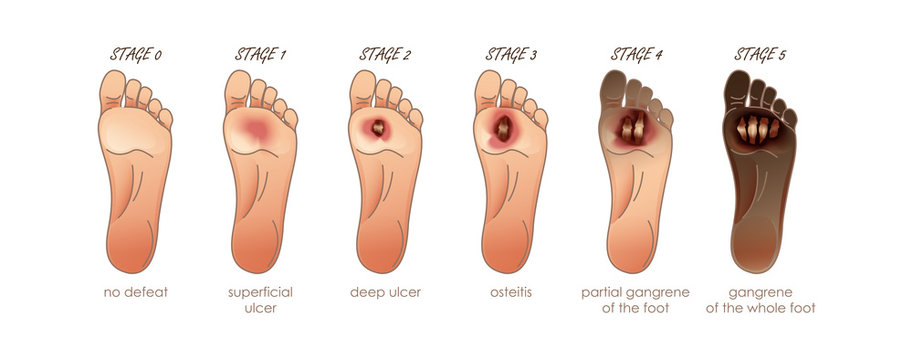
This image is taken for educational purpose from stock.adobe.com
B.] Pathological Calcification: Deposition of calcium salt in tissue other then osteoid or enamel is called pathological calcification or heterotopic calcification.
There are two types pathological calcification listed below:
- Dystrophic Calcification: It is characterised by the deposition of calcium salt in in dead or degenerated tissue with normal calcium metabolism and normal serum calcium level.
- Metastatic Calcification: It is characterised by deposition of calcium salt in normal tissues with reduced calcium metabolism and hypercalcaemia.

This image is taken for educational purpose from slideshare.net

This image is taken for educational purpose from slideshare.net
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION: –
1.] Which of the following is the hallmark of programmed cell death?
a. Apoptosis
b. Coagulation Necrosis
c. Fibrinoid necrosis
d. Liquefaction necrosis
2.] This is an active cell death process?
a. Necrosis
b. Lysis
c. Apoptosis
d. Senescence
3.] In cell death myelin figures are derived from?
a. Nucleus
b. Cell membrane
c. Cytoplasm
d. Mitochondria
4.] Cell death is a type of?
a. Reversible cell injury
b. Irreversible cell injury
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above is correct
5.] Necrosis, Apoptosis is the example of?
a. Local changes
b. Focal changes
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
6.] Which of the following are the causes of cell death?
a. Local or focal changes
b. Chemical and Physical agents
c. Infectious agents
d. All of the above
7.] Self – digestion is also known as?
a. Autolysis
b. Necrosis
c. Apoptosis
d. Calcification
8.] How many types of necrosis are there?
a. 6
b. 7
c. 5
d. 9
9.] Necrosis occurs due to?
a. Hypoxia
b. Microbial agents
c. Chemical and Physical agents
d. All of the above
10.] Apoptosis is accompanied by Collateral tissue damage and inflammation reaction.
a. True
b. False
SOLUTIONS: –
1.] (a) Apoptosis
2.] (c) Apoptosis
3.] (b) Cell membrane
4.] (b) Irreversible cell injury
5.] (c)
6.] (d)
7.] (a) Autolysis
8.] (c) 5
9.] (d)
10.] (b)
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCES: –
1.] Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no.26 – 37.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no.2 – 3.