Electron Transport Chain and MCQs for NEET, NIPER JEE, GATE, GPAT, CSIR NET and DBT BET Exam
The electron transport chain (ETC) also known as respiratory chain is the final pathway in aerobic cells by which the electrons are transferred to the oxygen. These electrons are derived from various substrates. ETC contains a series of oxidation, reduction enzymes, co-enzymes and electron carrier cytochromes. The ETC chain is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The enzymes of ETC cycle are present in the inner mitochondrial membrane in association with the enzymes of oxidative phosphorylation. The energy liberated during the oxidation of bio-molecules is present in the mitochondria as reducing equivalents. The liberated free energy is trapped as high energy phosphate-ATP in the mitochondria.
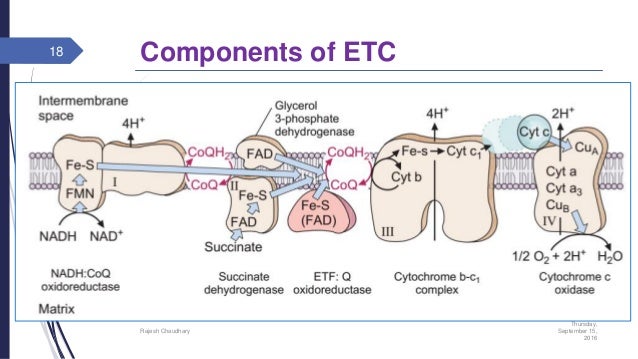
Components of ETC
The major components of ETC or respiratory chain are:
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) of different dehydrogenases
- Flavin mono-nucleotide (FMN) of NADH dehydrogenase and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
- Ubiquinone or co-enzyme Q
- Two different iron containing proteins: iron-sulfur protein and cytochrome b.
- Cytochromes: b, c, c1 and aa3. Cytochrome aa3 is also known as cytochrome oxidases.
Structural organization of respiratory chain
The components of respiratory chain are arranged in increasing order of the redox potential (from more negative redox potential to more positive redox potential. The electron carriers of ETC are associated in 4 enzyme complexes.
- Complex-1:- NADH-Q oxidoreductase (transfers electrons from NADH to Q). this complex is also known as NADH dehydrogenate complex. It is a large enzyme which consist of FMN and at least six iron-sulfur centers.
- Complex-2:- succinate-Q reductase (transfers electrons from FADH2 to Q). It contains succinate dehydrogenase and its iron-sulfur centers. In this complex, NADH2 is formed during conversion of succinate to fumarate (during TCA) and electrons are then transferred via several Fe-S centers to co-enzyme Q
- Complex-3:- Q-cytochrome C oxidoreductase (transfers from Q to cytochrome C). it is also known as cytochrome bc1 complex. It contains cytochrome c1, cytochrome b and Rieske iron-sulfur centers.
- Complex-4:- cytochrome c oxidase-O2( passing electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen and which is further reduced to water. Also known as cytochrome c oxidase and is the terminal component of ETC. It contains 4 redox centers: cytochrome a, cytochrome a3, (Cu)a center (contains copper ions linked to protein through cysteine-SH group) and (Cu)b center which is linked to heme a3.

Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. ETC is the common pathway for which type of cells?
A. Aerobic cell
B. Anerobic cell
C. Both
D. None
2. Why does electron transport chain takes place?
A. to transfer the electrons derived from substrate
B. to transfer the electrons derived from product
C. to transfer the reducing equivalents derived from substrate
D. both A and C
3. Which of the following are involved in electron transport chain? A. Enzymes
B. Co-enzymes
C. Electron carrier cytochrome
D. All of the above
4. What is the full form of NAD+?
A. Nucleotide adenine diamide
B. Nicotinamide adrenaline dinucleotide
C. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
D. None of the above
5. Cytochrome b is a —-containing proteins?
A. Iron
B. Sulfur
C. Chromium
D. Magnesium
6. How are the components of respiratory chain arranged?
A. increasing order of molecular weight
B. increasing order of redox potential
C. decreasing order of molecular weight
D. decreasing order of redox potential
7. Which of the following is the complex-1?
A. Succinate-Q reductase
B. NADH-Q oxidoreductase
C. Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
D. Cytochrome c oxidase-O2
8. Match the following complex with its function-
a. compex-1 1. Transfer electron from Q to cytochrome c
b. complex-2 2. Transfer electron from NADH to Q
c. complex-3 3. Transfer electron from cytochrome c to oxygen
d. complex-4 4. Transfer electrons from FADH2 to Q
9. Which enzyme is present in complex-2?
A. Succinate synthetase
B. Succinase
C. Succinate dehydrogenase
D. Succinyl hydrogenase
10. How many iron-sulfur centers are present in the complex-1?
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 2
11. Which of the following complex is also known as cytochrome bc1 complex?
A. Complex-1
B. Complex-2
C. Complex-3
D. Complex-4
12. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. ETC is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane
B. in complex-3, electrons pass from Q to cytochrome c
C. cytochrome c1 is also called cytochrome oxidases
D. iron-sulfur proteins are associated with FMN
13. Which of the following complex contains succinate dehydrogenase?
A. complex-1
B. complex-4
C. complex-3
D. none of the above
14. What is the full form of FMN?
A. Flavin mini-nucleotide
B. Fluoro mono-nucleotide
C. Fluoro mini-nucleotide
D. Flavin mono-nucleotide
15. Which of the following complex is also known as cytochrome c oxidase?
A. Complex-1
B. Complex-2
C. Complex-3
D. Complex-4
ANSWERS:-
1. Aerobic cell
2. Both A and C
3. All of the above
4. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
5. Iron
6. Increasing order of redox potential
7. NADH-Q oxidoreductase
8. a – 2 b – 4 c – 1 d – 3
9. Succinate dehydrogenase
10. 6
11. Complex-3
12. Cytochrome c1 is also called cytochrome oxidases
13. None of the above
14. Flavin mono-nucleotide
15. Complex-4
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 144-148